Campsis radicans
Campsis radicans
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Campsis radicans
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
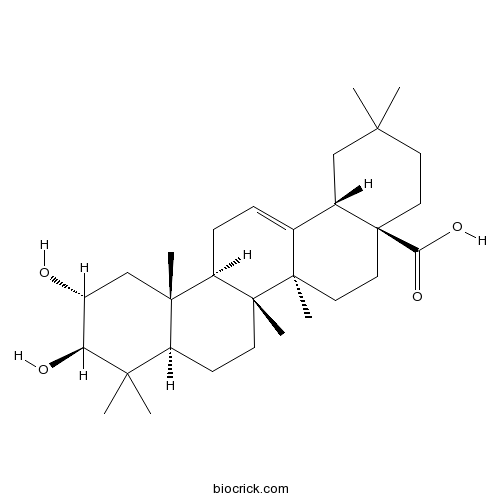
BCN5487
Crategolic acid4373-41-5
Instructions
Nectar protein content and attractiveness to Aedes aegypti and Culex pipiens in plants with nectar/insect associations.[Pubmed: 25792420]
We chose five easily propagated garden plants previously shown to be attractive to mosquitoes, ants or other insects and tested them for attractiveness to Culex pipiens and Aedes aegypti. Long term imbibition was tested by survival on each plant species. Both mosquito species survived best on Impatiens walleriana, the common garden impatiens, followed by Asclepias curassavica, Campsis radicans and Passiflora edulis, which sponsored survival as well as the 10% sucrose control. Immediate preference for imbibition was tested with nectar dyed in situ on each plant. In addition, competition studies were performed with one dyed plant species in the presence of five undyed plant species to simulate a garden setting. In both preference studies I. walleriana proved superior. Nectar from all plants was then screened for nectar protein content by SDS-PAGE, with great variability being found between species, but with I. walleriana producing the highest levels. The data suggest that I. walleriana may have value as a model plant for subsequent studies exploring nectar delivery of transgenic mosquitocidal proteins.
Quantifying the attachment strength of climbing plants: a new approach.[Pubmed: 19818882]
In order to grow vertically, it is essential for climbing plants to firmly attach to their supporting structures. In climbing plants, different strategies for permanent attachment can be distinguished. Besides twining stems and tendrils, many plants use attachment pads or attachment roots for this purpose. Using a novel custom-built tensile testing setup, the mechanical properties of different permanent attachment structures of self-clinging plant species were investigated, namely the attachment pads of Boston ivy (Parthenocissus tricuspidata), the attachment roots of ivy (Hedera helix) and the clustered attachment roots of trumpet creeper (Campsis radicans). Force-displacement measurements of individual attachment pads as well as of complete structures consisting of several pads or roots were conducted for both natural and laboratory growth conditions. The shapes of the curves and the maximum forces determined indicate clear differences in the detachment process for the different plants and structures tested. Based on these findings, it is argued that the attachment structures are displacement-optimized rather than force-optimized.
Consequences of mixed pollinations in Campsis radicans.[Pubmed: 28311280]
I examined the effects of pollen loads containing pollen from one, three and five donors on fruit production and fruit quality in Campsis radicans. Number of pollen donors had no significant effect on % fruit production, seed number, seed weight or seed germination. In singledonor pollinations the identity of the donor did have a strong effect on the above parameters. Furthermore, the best single donor sired fruits with more seeds and heavier seeds than any mixture containing this donor. This pattern indicates interference of pollens or preemption of some ovules by the inferior pollen. In Campsis, therefore, the number of pollen donors contributing to a pollen load is less important than the identity of these donors in determining fruit production and fruit quality. Seeds from fruits resulting from mixed pollination were slightly more variable than seeds from fruits resulting from single-donor pollinations.
Nectar: its production and functions in trumpet creeper.[Pubmed: 17813706]
Studies of the trumpet creeper, Campsis radicans (L.) Seem. (Bignoniaceae), reveal five distinct nectary systems, a phenomenon never before reported among temperate zone plants. Ant activity, centered around the four extrafloral systems, clearly demonstrates the ant-guard symbiosis usually associated only with tropical or subtropical species. Floral nectar, an attractant for hummingbird and bumblebee pollinators, differs chemically from the ant-attracting nectar produced extraflorally.


