Apium graveolens
Apium graveolens
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Apium graveolens
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN2311
Apiin26544-34-3
Instructions
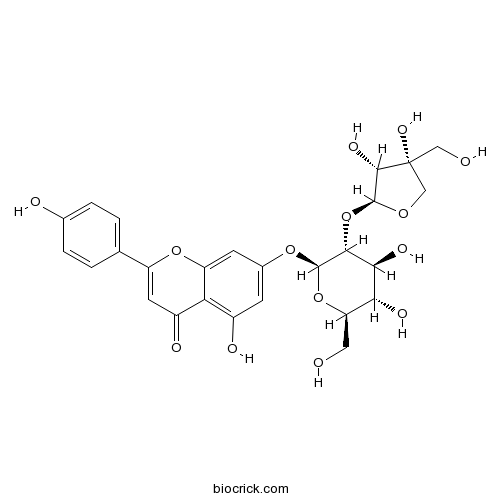
-
BCN5658
Apigenin520-36-5
Instructions
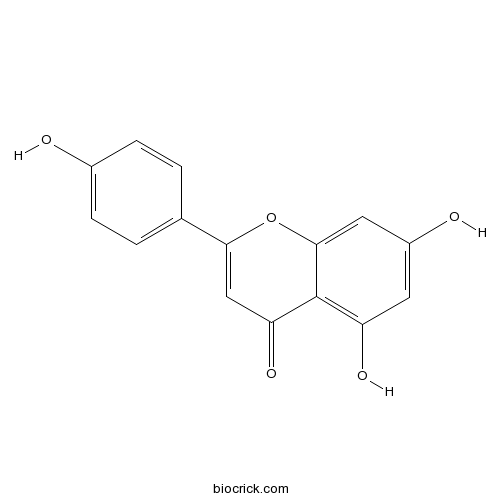
AgMYB2 transcription factor is involved in the regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in purple celery (Apium graveolens L.).[Pubmed: 30099650]
This study showed that an R2R3-MYB transcription factor, AgMYB2, functions in anthocyanin biosynthesis and accumulation in purple celery. Anthocyanins are involved in tissue coloration and stress response in plants. Foods containing high anthocyanin content are also beneficial to human health. Purple celery accumulated amounts of anthocyanins in the petioles. The biosynthesis of anthocyanin in plants is mainly regulated by the R2R3-MYB transcription factor (TF). However, the R2R3-MYB TF that controls anthocyanin accumulation in purple celery remains unclear. In this study, an R2R3-MYB TF gene, AgMYB2, was cloned from purple celery and characterized as anthocyanin biosynthetic regulator. Sequence analysis indicated that AgMYB2 contained highly conserved R2R3 domain and two anthocyanin characteristic motifs, ANDV motif and KPRPR[S/T]F motif. The relative expression level of AgMYB2 in purple celery was significantly higher than that in non-purple celery at three developmental stages. Heterologous expression of AgMYB2 in Arabidopsis generated more anthocyanins and resulted in dark-purple leaves and flowers. The expression levels of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes and the antioxidant activity of transgenic Arabidopsis carrying AgMYB2 were up-regulated. The determination of anthocyanin glycosylation activity of Arabidopsis crude enzyme verified the anthocyanin biosynthesis regulatory function of AgMYB2 at the protein level. The interaction between AgMYB2 and bHLH proteins was shown by yeast two-hybrid assay. The results will help to elucidate the molecular mechanism of anthocyanin biosynthesis in purple celery and provide an approach for cultivating plants with high anthocyanin content.
CeleryDB: a genomic database for celery.[Pubmed: 29992323]
Celery (Apium graveolens L.) is a plant belonging to the Apiaceae family, and a popular vegetable worldwide because of its abundant nutrients and various medical functions. Although extensive genetic and molecular biological studies have been conducted on celery, its genomic data remain unclear. Given the significance of celery and the growing demand for its genomic data, the whole genome of 'Q2-JN11' celery (a highly inbred line obtained by artificial selfing of 'Jinnan Shiqin') was sequenced using HiSeq 2000 sequencing technology. For the convenience of researchers to study celery, an online database of the whole-genome sequences of celery, CeleryDB, was constructed. The sequences of the whole genome, nucleotide sequences of the predicted genes and amino acid sequences of the predicted proteins are available online on CeleryDB. Home, BLAST, Genome Browser, Transcription Factor and Download interfaces composed of the organizational structure of CeleryDB. Users can search the celery genomic data by using two user-friendly query tools: basic local alignment search tool and Genome Browser. In the future, CeleryDB will be constantly updated to satisfy the needs of celery researchers worldwide.Database URL: http://apiaceae.njau.edu.cn/celerydb.
Dl-3-n-Butylphthalide improves lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive-like behavior in rats: involvement of Nrf2 and NF-κB pathways.[Pubmed: 29943092]
Dl-3-n-Butylphthalide (NBP), a small molecule compound extracted from the seeds of Apium graveolens, possesses a large range of biological effects. Here, we attempted to explore the therapeutic effects of NBP on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced major depressive disorder (MDD) and gain further insight into the underlying mechanisms of the antidepressant effects of NBP.
Dl-3-n-Butylphthalide (NBP): A Promising Therapeutic Agent for Ischemic Stroke.[Pubmed: 29895257]
Stroke is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in both developed and developing countries all over the world. The only drug for ischemic stroke approved by FDA is recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rtPA). However, only 2-5% stroke patients receive rtPAs treatment due to its strict therapeutic time window. As ischemic stroke is a complex disease involving multiple mechanisms, medications with multi-targets may be more powerful compared with single-target drugs. Dl-3-n-Butylphthalide (NBP) is a synthetic compound based on l-3-n- Butylphthalide that is isolated from seeds of Apium graveolens. The racemic 3-n-butylphthalide (dl- NBP) was approved by Food and Drug Administration of China for the treatment of ischemic stroke in 2002. A number of clinical studies indicated that NBP not only improved the symptoms of ischemic stroke, but also contributed to the long-term recovery. The potential mechanisms of NBP for ischemic stroke treatment may target different pathophysiological processes, including anti-oxidant, antiinflammation, anti-apoptosis, anti-thrombosis, and protection of mitochondria et al. Conclusion: In this review, we have summarized the research progress of NBP for the treatment of ischemic stroke during the past two decades.
Assessment of Antihyperlipidemic and Antitumor Effect of Isolated Active Phytoconstituents from Apium graveolens L. through Bioassay-Guided Procedures.[Pubmed: 29624455]
None


