Angelica keiskei
Angelica keiskei
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Angelica keiskei
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
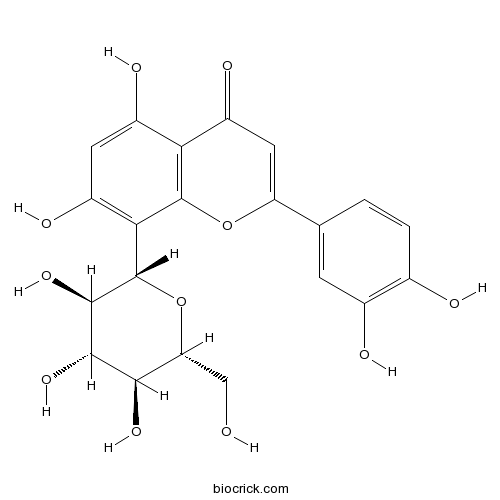
BCN4984
Orientin28608-75-5
Instructions
-
BCN5232
Isobavachin31524-62-6
Instructions
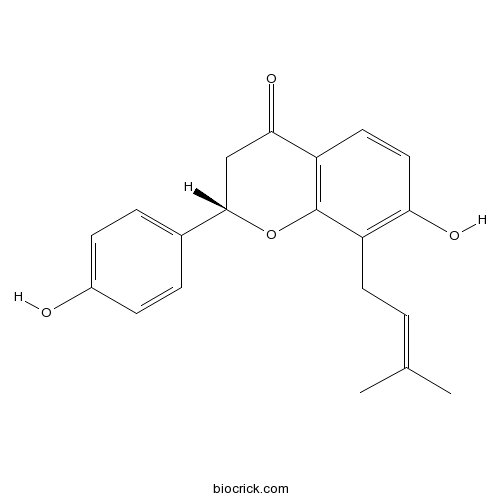
The Ashitaba (Angelica keiskei) chalcones 4-hydroxyderricin and xanthoangelol suppress melanomagenesis by targeting BRAF and PI3-K.[Pubmed: 29980517]
Malignant melanoma is an aggressive tumor of the skin and still lacks effective preventive and therapeutic treatments. In melanoma, both the BRAF/MEK/ERK and PI3-K/AKT signaling pathways are constitutively activated through multiple mechanisms, which result in cell cycle progression and prevention of apoptosis. Therefore, the development of novel strategies for targeting BRAF and PI3-K are of utmost importance. In the current study, we found that Ashitaba (Angelica keiskei) chalcones, 4-hydroxyderricin (4HD) and xanthoangelol (XAG), suppressed melanoma development by directly targeting both BRAFV600E and PI3-K, which blocked the activation of downstream signaling. This led to the induction of G1 phase cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in melanoma cells. Importantly, 4HD or XAG dramatically attenuated tumor incidence and volume in the BRAF-activated Pten-deficient melanoma mouse model. Our findings suggest that 4HD and XAG are promising chemopreventive or potential therapeutic agents against melanomagenesis that act by targeting both BRAF and PI3-K, providing hope for rapid clinical translation.
Ashitaba (Angelica Keiskei) Exudate Prevents Increases in Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 Induced by Obesity in Tsumura Suzuki Obese Diabetic Mice.[Pubmed: 29708806]
Angelica keiskei koidzumi (ashitaba) is consumed as a traditional folk medicine and health food in Japan. Ashitaba extract contains abundant flavonoids containing chalcones. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) is the primary physiological inhibitor of tissue plasminogen activator. Excessive amounts of PAI-1 in plasma disrupt the fibrinolytic balance and promote a prothrombotic state with which thrombosis and cardiovascular diseases are associated. In the present study, we investigated the effects of ashitaba yellow exudate (AE) on enhanced PAI-1 levels in Tsumura Suzuki obese diabetic (TSOD) mice. AE significantly decreased food efficiency and plasma PAI-1 in TSOD mice but did not affect lean control Tsumura Suzuki nonobese (TSNO) mice. AE also decreased some parameters in the plasma, such as glucose, insulin, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and gains in body weight, subcutaneous, mesenteric fat weight in TSOD mice but had little effect on these parameters in TSNO mice. Levels of adipose PAI-1 were significantly higher in TSOD than in TSNO mice. Major sources of plasma PAI-1 are thought to be adipose tissue and liver. AE significantly suppressed PAI-1 protein levels in the livers of both TSOD and TSNO mice. These results suggest that AE decreased plasma PAI-1 levels by suppressing both the adipose tissue retention of PAI-1 protein and liver PAI-1 production in TSOD mice. Supplementing the diet with AE might help to prevent thrombotic diseases or alleviate the risk of thrombotic diseases as well as to suppress metabolic state in obese individuals.
Hierarchical cluster analysis of technical replicates to identify interferents in untargeted mass spectrometry metabolomics.[Pubmed: 29681286]
Mass spectral data sets often contain experimental artefacts, and data filtering prior to statistical analysis is crucial to extract reliable information. This is particularly true in untargeted metabolomics analyses, where the analyte(s) of interest are not known a priori. It is often assumed that chemical interferents (i.e. solvent contaminants such as plasticizers) are consistent across samples, and can be removed by background subtraction from blank injections. On the contrary, it is shown here that chemical contaminants may vary in abundance across each injection, potentially leading to their misidentification as relevant sample components. With this metabolomics study, we demonstrate the effectiveness of hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA) of replicate injections (technical replicates) as a methodology to identify chemical interferents and reduce their contaminating contribution to metabolomics models. Pools of metabolites with varying complexity were prepared from the botanical Angelica keiskei Koidzumi and spiked with known metabolites. Each set of pools was analyzed in triplicate and at multiple concentrations using ultraperformance liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS). Before filtering, HCA failed to cluster replicates in the data sets. To identify contaminant peaks, we developed a filtering process that evaluated the relative peak area variance of each variable within triplicate injections. These interferent peaks were found across all samples, but did not show consistent peak area from injection to injection, even when evaluating the same chemical sample. This filtering process identified 128 ions that appear to originate from the UPLC-MS system. Data sets collected for a high number of pools with comparatively simple chemical composition were highly influenced by these chemical interferents, as were samples that were analyzed at a low concentration. When chemical interferent masses were removed, technical replicates clustered in all data sets. This work highlights the importance of technical replication in mass spectrometry-based studies, and presents a new application of HCA as a tool for evaluating the effectiveness of data filtering prior to statistical analysis.
Integration of Biochemometrics and Molecular Networking to Identify Antimicrobials in Angelica keiskei.[Pubmed: 29571174]
None
FGFR2 regulation by picrasidine Q inhibits the cell growth and induces apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.[Pubmed: 28857247]
Fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) 2 and its downstream signaling cascades, PI3 K/AKT/mTOR is playing an important role in cell survival and proliferations. In this study, we firstly found that picrasidine Q (PQ), an alkaloid component extracted from Angelica keiskei species, has the capacity of anti-cell transformation and anti-cancer. After ligand shape similarity approach of PQ, we found that PQ targeted FGFR 2 and verified by FGFR2 kinase assay as well as computational docking model. FGFR2 highly expressed in esophageal cancer tissues and PQ inhibited fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-induced cell transformation. Furthermore, PQ inhibited cell proliferation and induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in KYSE30, KYSE410, and KYSE450 esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) cells. It was confirmed by detecting of biological markers such as cyclinD1, cyclinD3 and cyclinB1 for cell cycle or cleaved caspase-7, caspase-3, and PARP for apoptosis. PQ targeting of FGFR2 kinase activities suppressed downstream target proteins including phosphorylation of AKT and mTOR but not MEK/ERK signaling pathways. Taken together, our results are the first to identify that PQ might be a chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic agent by direct targeting FGFR2 and inhibiting cell proliferation of ESCC cells.
Minor phenolics from Angelica keiskei and their proliferative effects on Hep3B cells.[Pubmed: 28571822]
A new coumarin, (-)-cis-(3'R,4'R)-4'-O-angeloylkhellactone-3'-O-β-d-glucopyranoside (1) and two new chalcones, 3'-[(2E)-5-carboxy-3-methyl-2-pentenyl]-4,2',4'-trihydroxychalcone (4) and (±)-4,2',4'-trihydroxy-3'-{2-hydroxy-2-[tetrahydro-2-methyl-5-(1-methylethenyl)-2-furanyl]ethyl}chalcone (5) were isolated from the aerial parts of Angelica keiskei (Umbelliferae), together with six known compounds: (R)-O-isobutyroyllomatin (2), 3'-O-methylvaginol (3), (-)-jejuchalcone F (6), isoliquiritigenin (7), davidigenin (8), and (±)-liquiritigenin (9). The structures of the new compounds were determined by interpretation of their spectroscopic data including 1D and 2D NMR data. All known compounds (2, 3, and 6-9) were isolated as constituents of A. keiskei for the first time. To identify novel hepatocyte proliferation inducer for liver regeneration, 1-9 were evaluated for their cell proliferative effects using a Hep3B human hepatoma cell line. All isolates exhibited cell proliferative effects compared to untreated control (DMSO). Cytoprotective effects against oxidative stress induced by glucose oxidase were also examined on Hep3B cells and mouse fibroblast NIH3T3 cells and all compounds showed significant dose-dependent protection against oxidative stress.


