Alternanthera philoxeroides
Alternanthera philoxeroides
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Alternanthera philoxeroides
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
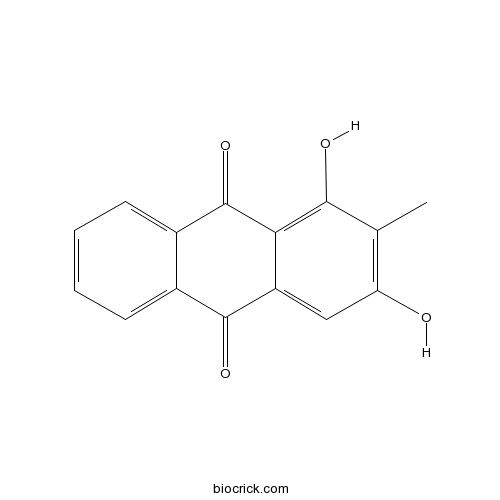
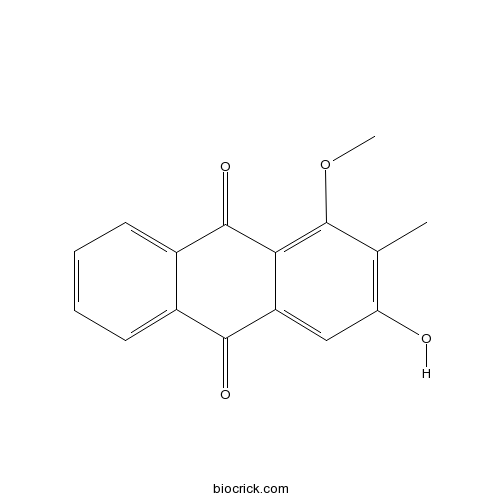
BCN6047
Rubiadin117-02-2
Instructions
-
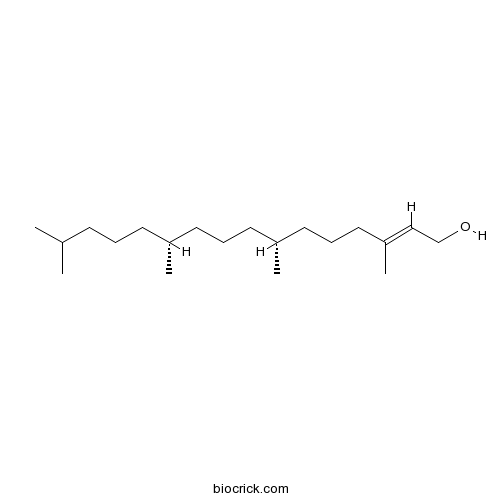
BCN1673
Phytol150-86-7
Instructions
-
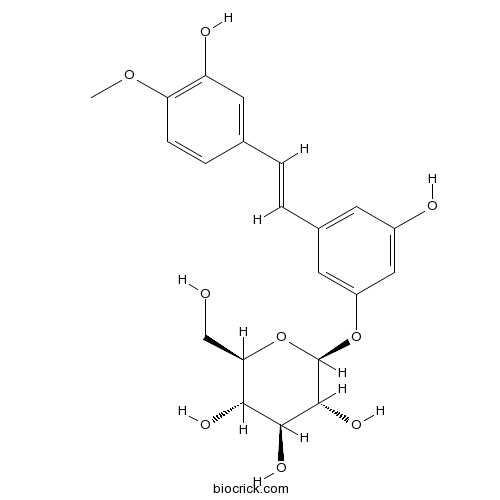
BCN5392
Rhaponiticin155-58-8
Instructions
-
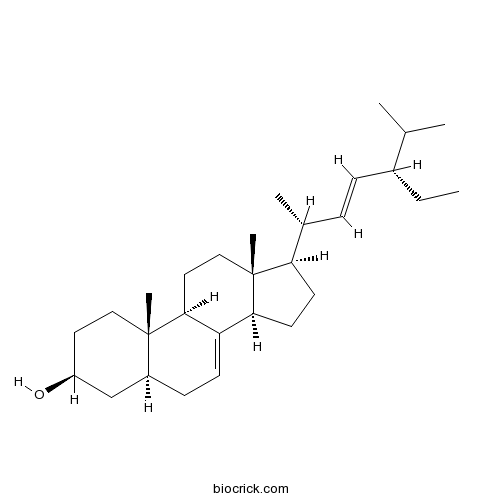
BCN5564
alpha-Spinasterol481-18-5
Instructions
-
BCN4298
Rubiadin 1-methyl ether7460-43-7
Instructions
Latitudinal variation in soil biota: testing the biotic interaction hypothesis with an invasive plant and a native congener.[Pubmed: 30013163]
Soil biota community structure can change with latitude, but the effects of changes on native plants, invasive plants, and their herbivores remain unclear. Here, we examined latitudinal variation in the soil biota community associated with the invasive plant Alternanthera philoxeroides and its native congener A. sessilis, and the effects of soil biota community variation on these plants and the beetle Agasicles hygrophila. We characterized the soil bacterial and fungal communities and root-knot nematodes of plant rhizospheres collected from 22 °N to 36.6 °N in China. Soil biota community structure changed with latitude as a function of climate and soil properties. Root-knot nematode abundance and potential soil fungal pathogen diversity (classified with FUNGuild) decreased with latitude, apparently due to higher soil pH and lower temperatures. A greenhouse experiment and lab bioassay showed native plant mass, seed production, and mass of beetles fed native foliage increased with soil collection latitude. However, there were no latitudinal patterns for the invasive plant. These results suggest that invasive and native plants and, consequently, their herbivores have different responses to latitudinal changes in soil-borne enemies, potentially creating spatial variation in enemy release or biotic resistance. This highlights the importance of linking above- and below-ground multitrophic interactions to explore the role of soil biota in non-native plant invasions with a biogeographic approach.
Heat sensitivity of eggs attributes to the reduction in Agasicles hygrophila population.[Pubmed: 29851277]
Agasicles hygrophila has been introduced worldwide as a control agent for the invasive weed Alternanthera philoxeroides. However, global warming has potential impact on its controlling efficacy. The aim of this research was to explore the primary factors responsible for the greatly reduced A. hygrophila population in hot summers. To imitate the temperature conditions in summers, different developmental stages of A. hygrophila were treated with high temperatures from 32.5 °C to 45 °C for 1-5 h. Based on the survival rate, the heat tolerance of each developmental stage was ranked from lowest to highest as follows: egg, 1st, 2nd, 3rd instar larva, adult and pupa. Eggs showed the lowest heat tolerance with 37.5 °C as the critical temperature affecting larval hatching. Heat treatment of the A. hygrophila eggs at 37.5 °C for 1 h decreased the hatch rate to 24%. Our results indicated that when compared with the control at 25 °C, 1 h treatment at 37.5 °C prolonged the duration of the egg stage, shortened the duration of oviposition and total longevity, and changed the reproductive pattern of A. hygrophila. The net reproductive rate, intrinsic rate and finite rate were all significantly reduced. The results suggest that low heat tolerance of the eggs was the major factor responsible for the reduction of A. hygrophila populations, and the key temperature was 37.5 °C. Therefore, appropriate measures should be taken to protect eggs in order to maintain the efficacy of A. hygrophila in the biological control of A. philoxeroides in hot summers.
Physiological and quantitative proteomic analyses unraveling potassium deficiency stress response in alligator weed (Alternanthera philoxeroides L.) root.[Pubmed: 29777486]
Physiological and iTRAQ based proteomic analysis provided new insights into potassium deficiency stress response in alligator weed root. Alligator weed (Alternanthera philoxeroides) has a strong ability to adapt to potassium deficiency (LK) stress. Proteomic changes in response to this stress are largely unknown in alligator weed. In this study, we investigated physiological and molecular mechanisms under LK using isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantitation to characterize proteome-level changes in this plant. First, root physiology, 2, 3, 5-Triphenyl-trazolium chloride (TTC) assay and peroxidase activity were significantly altered after 10 and 15 days of LK treatment. The comparative proteomic analysis suggested a total of 375 proteins were differential abundance proteins. The proteomic results were verified by western blot assays and quantitative real-time PCR. Correlation analysis of transcription and proteomics suggested protein processing in the endoplasmic reticulum, endocytosis, and spliceosome pathways were significantly enriched. The protein responsible for energy metabolism, signal sensing and transduction and protein degradation played crucial roles in this stress. Twelve ubiquitin pathway related proteins were identified in our study, among them 11 proteins were up-regulated. All protein ubiquitination of lysine using pan antibodies were also increased after LK treatment. Our study provide a valuable insights of molecular mechanism underlying LK stress response in alligator weed roots and afford a vital basis to further study potassium nutrition molecular breeding of other plant species.
Response to Short-Term Cold Storage for Eggs of Agasicles hygrophila (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae), a Biological Control Agent of Alligator Weed Alternanthera philoxeroides (Caryophyllales: Amaranthaceae).[Pubmed: 29741710]
The alligator weed flea beetle, Agasicles hygrophila Selman & Vogt (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) has been used very successfully for the biological control of the widely-distributed invasive weed Alternanthera philoxeroides (Mart.) Griseb (Caryophyllales: Amaranthaceae). In order to extend the 'shelf life' of natural enemies released in biological control programs, cold storage has proven to be a valuable commercial procedure. To determine a suitable low temperature for storage of A. hygrophila, we conducted short-term cold storage treatments of eggs (4°C for 0.5, 1, 2, 5 d, and 7.5, 10, 15°C for 5 d and a control of 25°C; all eggs were returned to 25°C after the treatments). We evaluated the effects of these treatments on the subsequent fitness of the populations based on a demographic analysis using group-reared age-stage two-sex life tables. For 5 d storage, temperatures below 10°C had lethal effects, which were also observed at 4°C for 2 d storage. Storage at 4°C for 0.5 d did not affect the fitness of A. hygrophila, but it did not prolong the developmental time. Storage at 10°C for 5 d significantly decreased rates of population increase compared with 25°C. A. hygrophila stored at 15°C for 5 d had similar age-(stage) specific survival rates, rates of population increase, increased longevity and reproductive capability to the controls at 25°C. It is concluded that there were no significant fitness costs after 5 d storage at 15°C, which is therefore potentially a suitable storage temperature for A. hygrophila eggs.
Responses in shoot elongation, carbohydrate utilization and growth recovery of an invasive species to submergence at different water temperatures.[Pubmed: 29321607]
Widely distributed amphibious exotic plant species may respond plastically to water temperatures when submerged. Alternanthera philoxeroides, a highly flood-tolerant species, originates from tropical regions and has successfully invaded temperate regions. The wide distribution of this species suggests it can respond to flooding at different water temperatures. In this study, the plastic responses of A. philoxeroides plants to submergence at water temperatures of 10 °C, 20 °C and 30 °C were investigated. The A. philoxeroides plants had large pools of non-structural carbohydrates, which were readily mobilized upon submergence. Submergence hindered biomass accumulation and decreased the carbohydrate content level and respiration rate (P < 0.05). Water temperature had remarkable effects on shoot elongation, carbohydrate utilization and recovery growth. With decreasing water temperature, the respiration rate was lower and carbohydrate content decreased more slowly, but the post-submergence biomass accumulation was faster (P < 0.05), indicating a beneficial effect of low water temperature for recovery. However, high water temperatures accelerated shoot elongation (P < 0.05), which benefitted the submerged plants more if contact with air was restored. These results suggest that the species can respond to different water temperatures plastically, which may provide hints for its invasion success in regions with diverse climates.
The mutual restraint effect between the expansion of Alternanthera philoxeroides (Mart.) Griseb and cadmium mobility in aquatic environment.[Pubmed: 29065373]
Alternanthera philoxeroides (Mart.) Griseb is one of the most malignant weeds in its invision habitats. While in the cadmium-contaminated aquatic environment, does A. philoxeroides possess good tolerance and adaptability? To demonstrate the effects of cadmium on A. philoxeroides in the polluted water bodies, a hydroponic stress experiment was conducted over a gradient of Cd concentrations (0, 2.5 and 5mg/l) in triplicate. The seedlings were cultured in a greenhouse and harvested on days 0, 10, 20, 30 and 40, respectively. The results showed the effects of mutual restraint between Cd and A. philoxeroides. The A. philoxeroides seedlings were enriched with large amounts of Cd, and the toxicity of Cd inhibited the rapid growth of A. philoxeroides and induced the rapid degradation of chlorophylls in its tissues. Furthermore, the use of iron plaque effectively immobilized Cd of 1123-2883mg/kg·DW on the root surface, thus it decreased the transferability of Cd in the aquatic environment. Due to its extensive adaptability, good Cd tolerance and the immobilization of Cd predominantly in the roots (the highest Cd concentration enriched was 7588.65±628.90mg/kg·DW in roots). A. philoxeroides effectively restrained the translocation of Cd and partitioned Cd in the roots within water bodies.


