alpha-MangostinCAS# 6147-11-1 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 6147-11-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5281650 | Appearance | Yellow powder |
| Formula | C24H26O6 | M.Wt | 410.5 |
| Type of Compound | Xanthones | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | α-Mangostin | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 37 mg/mL (90.14 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
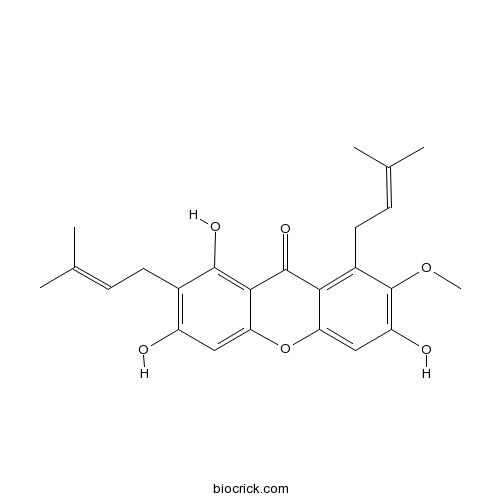
| Chemical Name | 1,3,6-trihydroxy-7-methoxy-2,8-bis(3-methylbut-2-enyl)xanthen-9-one | ||
| SMILES | CC(=CCC1=C(C=C2C(=C1O)C(=O)C3=C(C(=C(C=C3O2)O)OC)CC=C(C)C)O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GNRIZKKCNOBBMO-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Alpha-Mangostin has neuroprotective, anti-cancer, antifungal, neuroprotective, renoprotective, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. Alpha-Mangostin exhibits peripheral and central antinociception through modulation of opioid and vanilloid receptors, the glutamatergic system, and the larginine/NO/cGMP/PKC/K(+)-ATP pathways; it suppresses phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate-induced MMP-2/MMP-9 expressions via alphavbeta3 integrin/FAK/ERK and NF-kappaB signaling pathway in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells. Alpha-Mangostin is also a novel competitive histamine H1 receptor antagonist in smooth muscle cells. |
| Targets | Estrogen receptor | NO | PKC | Calcium Channel | ATPase | Potassium Channel | STAT | Caspase | ROS | MMP(e.g.TIMP) | FAK | ERK | NF-kB | PPAR | GLUT | Bcl-2/Bax | JNK | Histamine Receptor | Progestogen receptor |
| In vitro | Inhibition of CHOP accentuates the apoptotic effect of α-mangostin from the mangosteen fruit (Garcinia mangostana) in 22Rv1 prostate cancer cells.[Pubmed: 25261723]Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Oct 10;453(1):75-80.The mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana) fruit has been a popular food in Southeast Asia for centuries and is increasing in popularity in Western countries.
α-Mangostin Improves Glucose Uptake and Inhibits Adipocytes Differentiation in 3T3-L1 Cells via PPARγ, GLUT4, and Leptin Expressions.[Pubmed: 25873982]Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:740238.Obesity has been often associated with the occurrence of cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, and cancer. The development of obesity is also accompanied by significant differentiation of preadipocytes into adipocytes. Alpha-mangostin induces Ca2+-ATPase-dependent apoptosis via mitochondrial pathway in PC12 cells.[Pubmed: 15153648]J Pharmacol Sci. 2004 May;95(1):33-40.We investigated the cell death effects of eight xanthones on PC12 rat pheochromocytoma cells. |
| Kinase Assay | Pharmacological properties of alpha-mangostin, a novel histamine H1 receptor antagonist.[Pubmed: 8957258]Alpha-mangostin suppresses phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate-induced MMP-2/MMP-9 expressions via alphavbeta3 integrin/FAK/ERK and NF-kappaB signaling pathway in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells.[Pubmed: 20652762]Preferential target is mitochondria in alpha-mangostin-induced apoptosis in human leukemia HL60 cells.[Pubmed: 15498656]Bioorg Med Chem. 2004 Nov 15;12(22):5799-806.Our previous study has shown that alpha-Mangostin, a xanthone from the pericarps of mangosteen, induces caspase-3-dependent apoptosis in HL60 cells. In the current study, we investigated the mechanism of apoptosis induced by alpha-Mangostin in HL60 cells. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2010 Sep;58(1):31-44.The purpose of this study is to investigate the anti-metastatic effect of alpha-Mangostin on phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA)-induced matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) expressions in A549 human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1996 Oct 31;314(3):351-6.
|
| Cell Research | ROS scavenging capacity and neuroprotective effect of alpha-mangostin against 3-nitropropionic acid in cerebellar granule neurons.[Pubmed: 19108999 ]Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2009 Sep;61(5):491-501.alpha-Mangostin is a xanthone with antioxidant properties isolated from mangosteen fruit. The reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging capacity and the potential protective effect of alpha-Mangostin against the mitochondrial toxin 3-nitropropionic acid (3-NP) in primary cultures of cerebellar granule neurons (CGNs) were studied in the present work. It was found that alpha-Mangostin was able to scavenge in a concentration-dependent way singlet oxygen, superoxide anion and peroxynitrite anion. In contrast, alpha-Mangostin was unable to scavenge hydroxyl radicals and hydrogen peroxide. Furthermore, alpha-Mangostin was able to ameliorate in a concentration-dependent way the neuronal death induced by 3-NP. This protective effect was associated with an amelioration of 3-NP-induced reactive oxygen species formation. |
| Animal Research | Mechanisms of α-mangostin-induced antinociception in a rodent model.[Pubmed: 25504952 ]Biol Res Nurs. 2015 Jan;17(1):68-77.Elucidate the antinociceptive mechanisms of alpha-Mangostin isolated from Garcinia malaccensis Linn. |

alpha-Mangostin Dilution Calculator

alpha-Mangostin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4361 mL | 12.1803 mL | 24.3605 mL | 48.7211 mL | 60.9013 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4872 mL | 2.4361 mL | 4.8721 mL | 9.7442 mL | 12.1803 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2436 mL | 1.218 mL | 2.4361 mL | 4.8721 mL | 6.0901 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0487 mL | 0.2436 mL | 0.4872 mL | 0.9744 mL | 1.218 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0244 mL | 0.1218 mL | 0.2436 mL | 0.4872 mL | 0.609 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Alpha-mangostin is a dietary xanthone with broad biological activities, such as antioxidant, anti-allergic, antiviral, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and anticancer effects. It is an inhibitor of mutant IDH1 (IDH1-R132H) with a Ki of 2.85 μM.
In Vitro:Alpha-mangostin exhibits a selective inhibitory effect on IDH1-R132H, but not on IDH1. Alpha-mangostin competitively inhibits the binding of alpha-mangostin (α-KG) to IDH1-R132H. The structure–relationship study reveals that alpha-mangostin exhibits the strongest core inhibitor structure. Alpha-mangostin selectively promotes demethylation of 5-methylcytosine (5mC) and histone H3 trimethylated lysine residues in IDH1 (+/R132H) MCF10A cells[1]. Cell proliferation significantly decreases in a dose-dependent manner in the cells treated with alpha-mangostin. Alpha-mangostin also increases the levels of Bax (pro-apoptotic), cleaved caspase-3, cleaved caspase-9 and cleaved-poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP)[2]. Alpha-mangostin significantly inhibits light-induced degeneration of photoreceptors and 200 μM H2O2-induced apoptosis of RPE cells. 200 μM H2O2-induced generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and light-induced generation of malondialdehyde (MDA) are suppressed by alpha-mangostin[3].
In Vivo:Alpha-mangostin reduces risk of liver fibrosis through the decrease in p53 expression as compared to the TAA_DMSO treatment. The serum levels of the liver enzymes AST and ALT after treatment with α-mangostin decrease as compared to DMSO alone[4].
References:
[1]. Kim HJ, et al. Discovery of α-mangostin as a novel competitive inhibitor against mutant isocitrate dehydrogenase-1. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015 Dec 1;25(23):5625-31.
[2]. Lee HN, et al. Antitumor and apoptosis-inducing effects of α-mangostin extracted from the pericarp of the mangosteen fruit (Garcinia mangostana L.) in YD-15 tongue mucoepidermoid carcinoma cells. Int J Mol Med. 2016 Apr;37(4):939-48.
- Lup-20(29)-ene-2alpha,3beta-diol
Catalog No.:BCN4612
CAS No.:61448-03-1
- CIS-Resveratrol
Catalog No.:BCC8150
CAS No.:61434-67-1
- Bisabola-3,10-dien-2-one
Catalog No.:BCN7510
CAS No.:61432-71-1
- Z-D-Ala-ol
Catalog No.:BCC2589
CAS No.:61425-27-2
- 2-Amino-3-Formylchromone
Catalog No.:BCC8526
CAS No.:61424-76-8
- Carmofur
Catalog No.:BCC1214
CAS No.:61422-45-5
- Rolipram
Catalog No.:BCC2282
CAS No.:61413-54-5
- 2,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4139
CAS No.:614-82-4
- 2-Hydroxycinnamic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5039
CAS No.:614-60-8
- Procainamide HCl
Catalog No.:BCC5492
CAS No.:614-39-1
- 3-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8609
CAS No.:614-19-7
- Naginata ketone
Catalog No.:BCN7801
CAS No.:6138-88-1
- Quercetin Dihydrate
Catalog No.:BCN2967
CAS No.:6151-25-3
- (+)-Nortrachelogenin
Catalog No.:BCN7020
CAS No.:61521-74-2
- Oxytetracycline Dihydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4820
CAS No.:6153-64-6
- Verbasoside
Catalog No.:BCN8197
CAS No.:61548-34-3
- L-Rhamnose
Catalog No.:BCN6302
CAS No.:6155-35-7
- Acetylatractylodinol
Catalog No.:BCN8111
CAS No.:61582-39-6
- DHBP dibromide
Catalog No.:BCC6811
CAS No.:6159-05-3
- Vasicine
Catalog No.:BCN4140
CAS No.:6159-55-3
- 15,16-Epoxy-12R-hydroxylabda-8(17),13(16),14-triene
Catalog No.:BCN1400
CAS No.:61597-55-5
- 13-Hydroxy-8,11,13-podocarpatrien-18-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1399
CAS No.:61597-83-9
- H-DL-Nle-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3301
CAS No.:616-06-8
- Acetylcysteine
Catalog No.:BCC3716
CAS No.:616-91-1
Alpha-mangostin induces Ca2+-ATPase-dependent apoptosis via mitochondrial pathway in PC12 cells.[Pubmed:15153648]
J Pharmacol Sci. 2004 May;95(1):33-40.
We investigated the cell death effects of eight xanthones on PC12 rat pheochromocytoma cells. Among these compounds, alpha-Mangostin, from the fruit hull of Garcinia mangostana L., had the most potent effect with the EC(50) value of 4 microM. alpha-Mangostin-treated PC12 cells demonstrated typical apoptotic DNA fragmentation and caspase-3 cleavage (equivalent to activation). The flow cytometric analysis indicated that this compound induced apoptosis in time-and concentration-dependent manners. alpha-Mangostin showed the features of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway such as mitochondrial membrane depolarization and cytochrome c release. Furthermore, alpha-Mangostin inhibited the sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPase markedly. There was a correlation between the Ca(2+)-ATPase inhibitory effects and the apoptotic effects of the xanthone derivatives. On the other hand, c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase (JNK/SAPK), one of the signaling molecules of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, was activated with alpha-Mangostin treatment. These results suggest that alpha-Mangostin inhibits Ca(2+)-ATPase to cause apoptosis through the mitochondrial pathway.
Alpha-mangostin suppresses phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate-induced MMP-2/MMP-9 expressions via alphavbeta3 integrin/FAK/ERK and NF-kappaB signaling pathway in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells.[Pubmed:20652762]
Cell Biochem Biophys. 2010 Sep;58(1):31-44.
The purpose of this study is to investigate the anti-metastatic effect of alpha-Mangostin on phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA)-induced matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) expressions in A549 human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Firstly, alpha-Mangostin could inhibit PMA-induced abilities of the adhesion, invasion, and migration. Data also showed alpha-Mangostin could inhibit the activation of alphavbeta3 integrin, focal adhesion kinase (FAK), and extracellular signal-regulated kinase1/2 (ERK1/2) involved in the downregulation the enzyme activities, protein and messenger RNA levels of MMP-2 and MMP-9 induced by PMA. Next, alpha-Mangostin also strongly inhibited PMA-induced degradation of inhibitor of kappaBalpha (IkappaBalpha) and the nuclear levels of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB). Also, a dose-dependent inhibition on the binding abilities of NF-kappaB by alpha-Mangostin treatment was further observed. Furthermore, reduction of FAK or ERK1/2 phosphorylation by FAK small interfering RNA (FAK siRNA) potentiated the effect of alpha-Mangostin. Finally, the transient transfection of ERK siRNA significantly down-regulated the expressions of MMP-2 and MMP-9 concomitantly with a marked inhibition on cell invasion and migration. Presented results indicated alpha-Mangostin is a novel, effect, anti-metastatic agent that functions by downregulating MMP-2 and MMP-9 gene expressions.
alpha-Mangostin Improves Glucose Uptake and Inhibits Adipocytes Differentiation in 3T3-L1 Cells via PPARgamma, GLUT4, and Leptin Expressions.[Pubmed:25873982]
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:740238.
Obesity has been often associated with the occurrence of cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, and cancer. The development of obesity is also accompanied by significant differentiation of preadipocytes into adipocytes. In this study, we investigated the activity of alpha-Mangostin, a major xanthone component isolated from the stem bark of G. malaccensis, on glucose uptake and adipocyte differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells focusing on PPARgamma, GLUT4, and leptin expressions. alpha-Mangostin was found to inhibit cytoplasmic lipid accumulation and adipogenic differentiation. Cells treated with 50 muM of alpha-Mangostin reduced intracellular fat accumulation dose-dependently up to 44.4% relative to MDI-treated cells. Analyses of 2-deoxy-D-[(3)H] glucose uptake activity showed that alpha-Mangostin significantly improved the glucose uptake (P < 0.05) with highest activity found at 25 muM. In addition, alpha-Mangostin increased the amount of free fatty acids (FFA) released. The highest glycerol release level was observed at 50 muM of alpha-Mangostin. qRT-PCR analysis showed reduced lipid accumulation via inhibition of PPARgamma gene expression. Induction of glucose uptake and free fatty acid release by alpha-Mangostin were accompanied by increasing mRNA expression of GLUT4 and leptin. These evidences propose that alpha-Mangostin might be possible candidate for the effective management of obesity in future.
ROS scavenging capacity and neuroprotective effect of alpha-mangostin against 3-nitropropionic acid in cerebellar granule neurons.[Pubmed:19108999]
Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2009 Sep;61(5):491-501.
alpha-Mangostin is a xanthone with antioxidant properties isolated from mangosteen fruit. The reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging capacity and the potential protective effect of alpha-Mangostin against the mitochondrial toxin 3-nitropropionic acid (3-NP) in primary cultures of cerebellar granule neurons (CGNs) were studied in the present work. It was found that alpha-Mangostin was able to scavenge in a concentration-dependent way singlet oxygen, superoxide anion and peroxynitrite anion. In contrast, alpha-Mangostin was unable to scavenge hydroxyl radicals and hydrogen peroxide. Furthermore, alpha-Mangostin was able to ameliorate in a concentration-dependent way the neuronal death induced by 3-NP. This protective effect was associated with an amelioration of 3-NP-induced reactive oxygen species formation. It is concluded that alpha-Mangostin is able to scavenge directly several ROS and has a neuroprotective effect against 3-NP in primary cultures of CGNs, which is associated with its ability to ameliorate 3-NP-induced ROS production.
Inhibition of CHOP accentuates the apoptotic effect of alpha-mangostin from the mangosteen fruit (Garcinia mangostana) in 22Rv1 prostate cancer cells.[Pubmed:25261723]
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Oct 10;453(1):75-80.
The mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana) fruit has been a popular food in Southeast Asia for centuries and is increasing in popularity in Western countries. We identified alpha-Mangostin as a primary phytochemical modulating ER stress proteins in prostate cancer cells and propose that alpha-Mangostin is responsible for exerting a biological effect in prostate cancer cells. Two human prostate cancer cell lines, 22Rv1 and LNCaP, and prostate epithelial cells procured from two patients undergoing radical prostatectomy were treated with alpha-Mangostin and evaluated by RT-PCR, Western blot, fluorescent microscopy and siRNA transfection to evaluate ER stress. Next, we evaluated alpha-Mangostin for microsomal stability, pharmacokinetic parameters, and anti-cancer activity in nude mice. alpha-Mangostin significantly upregulated ER stress markers in prostate cancer cells. Interestingly, alpha-Mangostin did not promote ER stress in prostate epithelial cells (PrECs) from prostate cancer patients. CHOP knockdown enhanced alpha-Mangostin-induced apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. alpha-Mangostin significantly suppressed tumor growth in a xenograft tumor model without obvious toxicity. Our study suggests that alpha-Mangostin is not the only active constituent from the mangosteen fruit requiring further work to understand the complex chemical composition of the mangosteen.
Mechanisms of alpha-mangostin-induced antinociception in a rodent model.[Pubmed:25504952]
Biol Res Nurs. 2015 Jan;17(1):68-77.
OBJECTIVE: Elucidate the antinociceptive mechanisms of alpha-Mangostin isolated from Garcinia malaccensis Linn. METHODS: Male mice/rats (n = 6/group) were used in this between-group study. To determine alpha-Mangostin's antinociceptive profile, animals were given alpha-Mangostin orally (3, 30, or 100 mg/kg) 60 min before the start of the abdominal constriction or formalin tests. In the hot plate test, the noxious stimulus was applied before and 60, 90, 120, 150, 180, and 210 min after treatment with test solutions. Positive controls received 100 mg/kg acetylsalicylic acid (ASA; oral) or 5 mg/kg morphine (intraperitoneal injection) for the abdominal constriction and hot plate tests, respectively, and either ASA or morphine for the formalin test. Negative controls received vehicle only. To explore alpha-Mangostin's mechanisms of action, we performed (i) the hot plate test with naloxone (5 mg/kg) pretreatment to verify involvement of opioid receptors; (ii) the abdominal constriction test with 20 mg/kg l-arginine, N(G)-nitro-l-arginine methyl esters (l-NAME), methylene blue (MB), l-arginine plus l-NAME, or l-arginine plus MB or 10 mg/kg glibenclamide pretreatment to verify involvement of the l-arginine/nitric oxide (NO)/cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) and K+-ATP pathways; and (iii) the paw-licking test using capsaicin (1.6 mug capsaicin/paw), glutamate (10 mumol glutamate/paw), or phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA; 0.05 microg/paw) to verify involvement of vanilloid receptors, the glutamatergic system, and protein kinase C (PKC). RESULTS: alpha-Mangostin significantly inhibited nociception (p < .05) in all models. Only naloxone, l-arginine, methylene blue, PMA, and glibenclamide affected alpha-Mangostin antinociception significantly (p < .05). CONCLUSION: alpha-Mangostin exhibits peripheral and central antinociception through modulation of opioid and vanilloid receptors, the glutamatergic system, and the l-arginine/NO/cGMP/PKC/K(+)-ATP pathways.
Preferential target is mitochondria in alpha-mangostin-induced apoptosis in human leukemia HL60 cells.[Pubmed:15498656]
Bioorg Med Chem. 2004 Nov 15;12(22):5799-806.
Our previous study has shown that alpha-Mangostin, a xanthone from the pericarps of mangosteen, induces caspase-3-dependent apoptosis in HL60 cells. In the current study, we investigated the mechanism of apoptosis induced by alpha-Mangostin in HL60 cells. alpha-Mangostin-treated HL60 cells demonstrated caspase-9 and -3 activation but not -8, which leads us to assume that alpha-Mangostin may mediate the mitochondrial pathway in the apoptosis. Parameters of mitochondrial dysfunction including swelling, loss of membrane potential (deltapsim), decrease in intracellular ATP, ROS accumulation, and cytochrome c/AIF release, were observed within 1 or 2 h after the treatment. On the other hand, alpha-Mangostin-treatment did not affect expression of bcl-2 family proteins and activation of MAP kinases. These findings indicate that alpha-Mangostin preferentially targets mitochondria in the early phase, resulting in indication of apoptosis in HL60 cells. Furthermore, we examined the structure-activity relationship between xanthone derivatives including alpha-Mangostin and the potency of deltapsim-loss in HL60 cells. Interestingly, replacement of hydroxyl group by methoxy group remarkably decreased its potency. It was also shown that the cytotoxicity substantially correlated with deltapsim decrease. These results indicate that alpha-Mangostin and its analogs would be candidates for preventive and therapeutic application for cancer treatment.
Pharmacological properties of alpha-mangostin, a novel histamine H1 receptor antagonist.[Pubmed:8957258]
Eur J Pharmacol. 1996 Oct 31;314(3):351-6.
In the isolated rabbit thoracic aorta and guinea-pig trachea, alpha-Mangostin inhibited histamine-induced contractions in a concentration-dependent manner in the presence or absence of cimetidine, a histamine H2 receptor antagonist. But KCl-, phenylephrine- or carbachol-induced contractions were not affected by alpha-Mangostin. The concentration-contractile response curve for histamine was shifted to the right in a parallel manner by alpha-Mangostin. In the presence of chlorpheniramine, a histamine H1 receptor antagonist, alpha-Mangostin did not affect the relaxation of the rabbit aorta induced by histamine. In the guinea-pig trachea, alpha-Mangostin had no effect on the relaxation induced by dimaprit, a histamine H2 receptor agonist. alpha-Mangostin caused a concentration-dependent inhibition of the binding of [3H]mepyramine, a specific histamine H1 receptor antagonist to rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Kinetic analysis of [3H]mepyramine binding indicated the competitive inhibition by alpha-Mangostin. These results suggest that alpha-Mangostin is a novel competitive histamine H1 receptor antagonist in smooth muscle cells.


