Xylazineα2-adrenoceptor agonist CAS# 7361-61-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 7361-61-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5707 | Appearance | Powder |
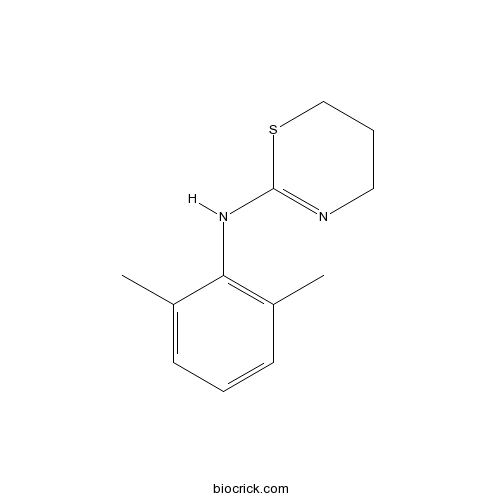
| Formula | C12H16N2S | M.Wt | 220.33 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | >9.8mg/mL in DMSO | ||
| Chemical Name | N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-5,6-dihydro-4H-1,3-thiazin-2-amine | ||
| SMILES | CC1=C(C(=CC=C1)C)NC2=NCCCS2 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | BPICBUSOMSTKRF-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C12H16N2S/c1-9-5-3-6-10(2)11(9)14-12-13-7-4-8-15-12/h3,5-6H,4,7-8H2,1-2H3,(H,13,14) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Xylazine Dilution Calculator

Xylazine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.5386 mL | 22.6932 mL | 45.3865 mL | 90.7729 mL | 113.4662 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.9077 mL | 4.5386 mL | 9.0773 mL | 18.1546 mL | 22.6932 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4539 mL | 2.2693 mL | 4.5386 mL | 9.0773 mL | 11.3466 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0908 mL | 0.4539 mL | 0.9077 mL | 1.8155 mL | 2.2693 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0454 mL | 0.2269 mL | 0.4539 mL | 0.9077 mL | 1.1347 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Xylazine is a strong agonist of α2-adrenoceptor [1].
Xylazine has been reported to stimulate the proliferation of rat thymocytes in vivo (at doses of 2.5 mg/kg and 5 mg/kg) and in vitro (at concentration of 5 mM) [2]. In the analgesic testing, Xylazine has shown a significant prolongation of the analgesic effects in the presence of naloxine in 40 and 50 mins. In addition, Xylazine has also shown the inhibitory effect in the mouse vas deferens bioassay with the IC50 value of 18nM. Furthermore, Xylazine has displayed a potent specific [3H]-dihydromorphine binding inhibition with the IC50 value of 8μM in opiate receptor binding test [1].
References:
[1] S. BROWNING, D.LAWRENCE1, A.LIVINGSTON & B.MORRIS. Interaction of drugs active at opiate receptors and drugs active at α2-adrenoceptors on various test systems
[2] Colić M1, Cupić V, Pavicić L, Vucević D, Varagić VM. Xylazine, an alpha 2-adrenergic agonist, modulates proliferation of rat thymocytes in vivo and in vitro. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 2000 Sep;22(7):557-62.
- 3-Hydroxybenzylamine
Catalog No.:BCN1804
CAS No.:73604-31-6
- (-)-Bicuculline methobromide
Catalog No.:BCC6555
CAS No.:73604-30-5
- Omeprazole
Catalog No.:BCC1254
CAS No.:73590-58-6
- 27-p-Coumaroyloxyursolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4288
CAS No.:73584-67-5
- Mevastatin
Catalog No.:BCN2568
CAS No.:73573-88-3
- cis-ACBD
Catalog No.:BCC6587
CAS No.:73550-55-7
- 7-Acetyllycopsamine
Catalog No.:BCN2000
CAS No.:73544-48-6
- Tetrachyrin
Catalog No.:BCN4776
CAS No.:73483-88-2
- 1-Deoxymannojirimycin hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6995
CAS No.:73465-43-7
- Dehydrobruceine A
Catalog No.:BCN7620
CAS No.:73435-47-9
- Norandrostenedione
Catalog No.:BCC9103
CAS No.:734-32-7
- AR 231453
Catalog No.:BCC5143
CAS No.:733750-99-7
- 1-(4-Methoxycinnamoyl)pyrrole
Catalog No.:BCN4027
CAS No.:736140-70-8
- 5-Amino-1-(2-hydroxyethyl)pyrazole
Catalog No.:BCC8727
CAS No.:73616-27-0
- p-Coumaric acid ethyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN4289
CAS No.:7362-39-2
- H-Asp-OBzl
Catalog No.:BCC2882
CAS No.:7362-93-8
- HEPES
Catalog No.:BCC7590
CAS No.:7365-45-9
- Naringenin 5-rhamnoside
Catalog No.:BCN2747
CAS No.:
- Onysilin
Catalog No.:BCN3379
CAS No.:73695-94-0
- Oxypeucedanin
Catalog No.:BCN2494
CAS No.:737-52-0
- Acetylursolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4290
CAS No.:7372-30-7
- Fmoc-Ser-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3541
CAS No.:73724-45-5
- Fmoc-Thr-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3549
CAS No.:73731-37-0
- Broussonin B
Catalog No.:BCN4593
CAS No.:73731-86-9
Comparison between the effects of postanesthetic xylazine and dexmedetomidine on characteristics of recovery from sevoflurane anesthesia in horses.[Pubmed:28258815]
Vet Anaesth Analg. 2017 Mar;44(2):273-280.
OBJECTIVE: To compare postanesthetic Xylazine and dexmedetomidine on recovery characteristics from sevoflurane anesthesia in horses. STUDY DESIGN: Randomized, crossover study. ANIMALS: Six geldings, mean+/-standard deviation (SD) (range), 17+/-4 (11-24) years and 527+/-80 (420-660) kg. METHODS: Horses were anesthetized with sevoflurane for 60 minutes under standardized conditions for a regional limb perfusion study. In recovery, horses were administered either Xylazine (200 mug kg(-1)) or dexmedetomidine (0.875 mug kg(-1)) intravenously. Recoveries were unassisted and were video-recorded for later evaluation of recovery events and quality by two individuals unaware of treatment allocation. Recovery quality was assessed using a 100 mm visual analog scale (VAS) (0=poor recovery, 100=excellent recovery), the Edinburgh Scoring System (ESS) (0-100; 100=excellent recovery) and the mean attempt interval (MAI) (longer=better). Data are mean+/-SD. RESULTS: All recovery quality assessments (Xylazine and dexmedetomidine, respectively: VAS: 71+/-21 mm, 84+/-13 mm; ESS: 65+/-22, 67+/-30; MAI: 52+/-24 minutes, 60+/-32 minutes) and events (first limb movement: 37+/-8 minutes, 42+/-10 minutes; first attempt to lift head: 44+/-12 minutes, 48+/-9 minutes; first attempt to sternal posture: 57+/-28 minutes, 50+/-7 minutes; number of head bangs: 2.0+/-3.0, 0.5+/-0.5; time to first attempt to stand: 72+/-6 minutes, 78+/-13 minutes; time to standing: 79+/-14 minutes, 84+/-13 minutes) did not differ significantly between treatments (p>0.05). CONCLUSIONS AND CLINICAL RELEVANCE: Recovery characteristics did not differ significantly between postanesthetic Xylazine and dexmedetomidine following 1 hour of sevoflurane anesthesia in horses in this study. Further evaluations in more horses and in younger horses are required to confirm these results.
Cytotoxicity of ketamine, xylazine and Hellabrunn mixture in liver-, heart- and kidney-derived cells from fallow deer.[Pubmed:28263534]
Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2016 Dec 18;37(Suppl1):78-83.
OBJECTIVES: Chemical restraint of wild animals is practiced to accomplish intended procedures such as capture, clinical examination, collection of diagnostic samples, treatment and/or transport. Extra-label use of animal medicinal drugs is often necessary in wildlife because most approved therapeutics do not list wild species on the labelling. Here, we used cellular in vitro models, a cutting-edge tool of biomedical research, to examine cytotoxicity of anaesthetic agents in fallow deer and extrapolate these data for anaesthetic risks in wildlife. METHODS: We examined the cytotoxic effects of ketamine, Xylazine, and ketamine-Xylazine, i.e. the Hellabrunn mixture, on liver-, heart- and kidney-derived cell cultures prepared from a fallow deer (Dama dama) specimen. In line with preliminary studies we exposed cells to 10 microM, 50 microM, 100 microM, 1 mM, and 10 mM ketamine or Xylazine. The combination of ketamine-Xylazine was dosed at 0.025+0.02 mg/ml, 0.05+0.04 mg/ml, 0.75+0.06 mg/ml, 0.1+0.08 mg/ml, and 0.125+0.1 mg/ml per one well containing 10 000 cells. The quantification of cytotoxicity was based on lactate dehydrogenase activity released from damaged cells. RESULTS: Liver-derived cells show higher sensitivity to the cytotoxic effects of both ketamine and Xylazine administered as single drugs when compared with cells cultured from the heart and kidney. The Hellabrunn mixture induced significantly higher cytotoxicity for kidney-derived cells ranging from 16.78% to 35.6%. Single and combined exposures to ketamine and Xylazine resulted only in high-dose cytotoxicity in the heart-derived cells. CONCLUSIONS: Our results indicate that immobilization drugs significantly differ in their cytotoxic effects on cells derived from various organs of the fallow deer.
Comparison of Atipamezole with Yohimbine for Antagonism of Xylazine in Mice Anesthetized with Ketamine and Xylazine.[Pubmed:28315642]
J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2017 Mar 1;56(2):142-147.
The alpha2 adrenergic agonist Xylazine produces a sedative effect and is typically combined with ketamine and used for anesthesia or chemical restraint of laboratory mice. Xylazine's sedative effect-and its undesirable side effects of bradycardia, hypotension, and poor tissue perfusion-can be reversed by administration of alpha2 antagonists, such as atipamezole or yohimbine. Although atipamezole and yohimbine dosing guidelines are available for mice, no controlled comparison has been performed to guide the lab animal community in the selection of one over the other. This study is a single-dose crossover comparison of these 2 antagonist drugs, given intraperitoneally at clinically recommended doses, to determine which results in more rapid recovery of mice from Xylazine-ketamine anesthesia. Time to return of righting reflex was used as the primary outcome measure. Mice were anesthetized with Xylazine (10 mg/kg IP) and ketamine (80 mg/kg IP), followed 15 min later by injection of an alpha2 antagonist or saline (control). Time to return of righting reflex differed significantly among groups, with mice recovering in an average of 10.3 min after administration of atipamezole (1 mg/kg IP) as compared with 21.3 min after yohimbine (1.5 mg/kg IP) and 38.2 min after saline. When rapid recovery of mice after Xylazine-ketamine anesthesia is desirable, administration of an antagonist to reverse the effects of the Xylazine is indicated. When injection of the antagonist by the technically simple intraperitoneal route is desirable, our data indicate that (at the doses evaluated) atipamezole is more effective than yohimbine.
Effects of xylazine and dexmedetomidine on equine articular chondrocytes in vitro.[Pubmed:28259429]
Vet Anaesth Analg. 2017 Mar;44(2):295-308.
OBJECTIVE: To assess the effects of Xylazine and dexmedetomidine on equine chondrocytes, in vitro. STUDY DESIGN: Prospective, experimental study. STUDY MATERIAL: Equine articular chondrocytes from five male horses. METHODS: Chondrocytes were isolated from healthy equine articular cartilage of the metacarpo/metatarsophalangeal joints. Cell viability was assessed using the WST-8 assay by exposing chondrocytes to Xylazine (0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, 16.6, 25, 50 mg mL(-1)) or dexmedetomidine (0.001, 0.005, 0.01, 0.05, 0.175, 0.25 mg mL(-1)) for 15, 30 and 60 minutes. Based on the results of these tests, cells were treated with Xylazine (1, 4, 25 mg mL(-1)) or dexmedetomidine (0.05, 0.175, 0.25 mg mL(-1)) for 15 minutes to further evaluate: cell viability by neutral red uptake; cell membrane integrity by lactate dehydrogenase release and by fluorescence microscopy with Hoechst 33342 and propidium iodide (PI), and apoptosis by flow cytometry using double staining with annexin V-fluorescein isothiocyanate/PI and by cell morphology. RESULTS: Both drugs reduced cell viability in a dose-dependent manner. Specifically, all Xylazine concentrations, except 0.5 mg mL(-1) and 1 mg mL(-1), significantly reduced cell viability, whereas the effects of dexmedetomidine were evident only at 0.175 mg mL(-1) and 0.25 mg mL(-1). The highest concentrations of Xylazine (25 mg mL(-1)) and dexmedetomidine (0.25 mg mL(-1)) caused loss of membrane integrity. Cell morphology and flow cytometry analyses demonstrated signs of late apoptosis in Xylazine-treated cells, and signs of late apoptosis and necrosis in dexmedetomidine-treated cells. CONCLUSIONS AND CLINICAL RELEVANCE: This study offers new insights into the potential chondrotoxicity induced by dexmedetomidine and Xylazine. Therefore, the intra-articular administration of alpha2-agonists should be conducted with care, especially for doses of >/= 4 mg mL(-1) of Xylazine and 0.175 mg mL(-1) and 0.25 mg mL(-1) of dexmedetomidine.


