WortmanninPI3K inhibitor,selective and irreversible CAS# 19545-26-7 |
- CZC24832
Catalog No.:BCC1507
CAS No.:1159824-67-5
- PI3Kγ inhibitor 1
Catalog No.:BCC4180
CAS No.:1172118-03-4
- CUDC-907
Catalog No.:BCC2154
CAS No.:1339928-25-4
- CAL-101 (Idelalisib, GS-1101)
Catalog No.:BCC1270
CAS No.:870281-82-6
- BEZ235 (NVP-BEZ235)
Catalog No.:BCC3655
CAS No.:915019-65-7
- GDC-0941
Catalog No.:BCC3626
CAS No.:957054-30-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 19545-26-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 312145 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C23H24O8 | M.Wt | 428.43 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | SL-2052 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 50 mg/mL (116.71 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
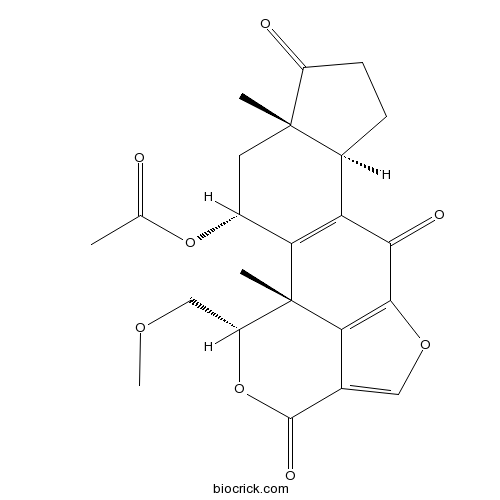
| SMILES | CC(=O)OC1CC2(C(CCC2=O)C3=C1C4(C(OC(=O)C5=COC(=C54)C3=O)COC)C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QDLHCMPXEPAAMD-QAIWCSMKSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C23H24O8/c1-10(24)30-13-7-22(2)12(5-6-14(22)25)16-18(13)23(3)15(9-28-4)31-21(27)11-8-29-20(17(11)23)19(16)26/h8,12-13,15H,5-7,9H2,1-4H3/t12-,13+,15+,22-,23-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent, selective, cell-permeable and irreversible inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI 3-kinase) (IC50 = 2 - 4 nM). Also potently inhibits polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) (IC50 = 5.8 nM). |

Wortmannin Dilution Calculator

Wortmannin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3341 mL | 11.6705 mL | 23.341 mL | 46.6821 mL | 58.3526 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4668 mL | 2.3341 mL | 4.6682 mL | 9.3364 mL | 11.6705 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2334 mL | 1.1671 mL | 2.3341 mL | 4.6682 mL | 5.8353 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0467 mL | 0.2334 mL | 0.4668 mL | 0.9336 mL | 1.1671 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0233 mL | 0.1167 mL | 0.2334 mL | 0.4668 mL | 0.5835 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Wortmannin is a selective and irreversible inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase with IC50 value of 1.9nM [1].
Wortmannin is a microbial product. It is produced by a fungal strain, Talaromyces wortmannin KY12420 and is screened out as a potent inhibitor of myosin light chain kina (MLCK). Wortmannin inhibits MLCK as directly interacting with the catalytic domain but not the calmodulin or the regulatory domains. It is found to be a non-competitive inhibitor. The IC50 value of wortmannin for MLCK is 1.9μM. Wortmannin inhibits the phosphorylation and contraction of myosin light chain in rat aort. As an inhibitor of MLCK, wortmannin is developed as vasodilators and anti-inflammatory agent [2].
Wortmannin is also found to be an inhibitor of PI3K with IC50 of 1.9nM in antiphosphotyrosine immunoprecipitates from Swiss 3T3 cells. The inhibition mode is noncompetitive with respect to ATP. Wortmannin is a highly selective inhibitor of PI3K. It has no inhibition effect on Ptdlns-4-kinase, protein kinase C, c-src protein tyrosine kinase and phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C [1].
References:
[1] Powis G, Bonjouklian R, Berggren M M, et al. Wortmannin, a potent and selective inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase. Cancer Research, 1994, 54(9): 2419-2423.
[2] Nakanishi S, Kakita S, Takahashi I, et al. Wortmannin, a microbial product inhibitor of myosin light chain kinase. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1992, 267(4): 2157-2163.
- Bay 11-7821(BAY 11-7082)
Catalog No.:BCC2244
CAS No.:19542-67-7
- JAK2 Inhibitor V, Z3
Catalog No.:BCC1667
CAS No.:195371-52-9
- Alphitolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1189
CAS No.:19533-92-7
- Galantamine hydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCN2869
CAS No.:1953-04-4
- Tiopronin (Thiola)
Catalog No.:BCC3870
CAS No.:1953-02-2
- GLP-2 (rat)
Catalog No.:BCC5892
CAS No.:195262-56-7
- N-(3-Methoxybenzyl)oleamide
Catalog No.:BCC6942
CAS No.:883715-21-7
- 4-DAMP
Catalog No.:BCC6661
CAS No.:1952-15-4
- Dihydrosenkyunolide C
Catalog No.:BCC8942
CAS No.:195142-72-4
- 4-Hydroxycinnamamide
Catalog No.:BCN1188
CAS No.:194940-15-3
- Daphnetin 7-methyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN2734
CAS No.:19492-03-6
- ACPT-I
Catalog No.:BCC5702
CAS No.:194918-76-8
- Chiirirhamnin
Catalog No.:BCN3179
CAS No.:195450-50-1
- AP1903
Catalog No.:BCC5361
CAS No.:195514-63-7
- Piromidic Acid
Catalog No.:BCC3840
CAS No.:19562-30-2
- Methyl 4-O-feruloylquinate
Catalog No.:BCC9041
CAS No.:195723-10-5
- 2,16,19-Kauranetriol 2-O-beta-D-allopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN1510
CAS No.:195723-38-7
- (+-)-Byakangelicin
Catalog No.:BCN5000
CAS No.:19573-01-4
- Atrasentan hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1380
CAS No.:195733-43-8
- 2,6,16-Kauranetriol 2-O-beta-D-allopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN1509
CAS No.:195735-16-1
- HTMT dimaleate
Catalog No.:BCC6736
CAS No.:195867-54-0
- (R)-Nepicastat HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4315
CAS No.:195881-94-8
- 25S-Inokosterone
Catalog No.:BCN3873
CAS No.:19595-18-7
- 17 alpha-propionate
Catalog No.:BCC1296
CAS No.:19608-29-8
PI3K inhibitor LY294002, as opposed to wortmannin, enhances AKT phosphorylation in gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells.[Pubmed:28000865]
Int J Oncol. 2017 Feb;50(2):606-612.
LY294002 and Wortmannin are chemical compounds that act as potent inhibitors of phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3Ks). Both of them are generally used to inhibit cell proliferation as cancer treatment by inhibiting the PI3K/protein kinase B (AKT) signaling pathway. In this study, LY294002 (but not Wortmannin) showed an abnormal ability to enhance AKT phosphorylation (at Ser472) specifically in gemcitabine (GEM)-resistant pancreatic cancer (PC) cell lines PK59 and KLM1-R. LY294002 was shown to activate AKT and accumulate phospho-AKT at the intracellular membrane in PK59, which was abolished by treatment with AKTi-1/2 or Wortmannin. Inhibiting AKT phosphorylation by treatment with AKTi-1/2 or Wortmannin further enhanced LY294002-induced cell death in PK59 and KLM1-R cells. In addition, treatment with Wortmannin alone failed to inhibit cell proliferation in both PK59 and KLM1-R cells. Thus, our results reveal that LY294002 displays the opposite effect on PI3K-dependent AKT phosphorylation, which maintains cell survival from the cytotoxicity introduced by LY294002 itself in GEM-resistant pancreatic cancer cells. We suggest that targeting the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway with inhibitors may be counterproductive for patients with PC who have acquired GEM-resistance.
Wortmannin-induced vacuole fusion enhances amyloplast dynamics in Arabidopsis zigzag1 hypocotyls.[Pubmed:27816929]
J Exp Bot. 2016 Dec;67(22):6459-6472.
Gravitropism in Arabidopsis shoots depends on the sedimentation of amyloplasts in the endodermis, and a complex interplay between the vacuole and F-actin. Gravity response is inhibited in zigzag-1 (zig-1), a mutant allele of VTI11, which encodes a SNARE protein involved in vacuole fusion. zig-1 seedlings have fragmented vacuoles that fuse after treatment with Wortmannin, an inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, and underscore a role of phosphoinositides in vacuole fusion. Using live-cell imaging with a vertical stage microscope, we determined that young endodermal cells below the apical hook that are smaller than 70 mum in length are the graviperceptive cells in dark-grown hypocotyls. This result was confirmed by local Wortmannin application to the top of zig-1 hypocotyls, which enhanced shoot gravitropism in zig-1 mutants. Live-cell imaging of zig-1 hypocotyl endodermal cells indicated that amyloplasts are trapped between juxtaposed vacuoles and their movement is severely restricted. Wortmannin-induced fusion of vacuoles in zig-1 seedlings increased the formation of transvacuolar strands, enhanced amyloplast sedimentation and partially suppressed the agravitropic phenotype of zig-1 seedlings. Hypergravity conditions at 10 g were not sufficient to displace amyloplasts in zig-1, suggesting the existence of a physical tether between the vacuole and amyloplasts. Our results overall suggest that vacuole membrane remodeling may be involved in regulating the association of vacuoles and amyloplasts during graviperception.
Profiling Kinase Activity during Hepatitis C Virus Replication Using a Wortmannin Probe.[Pubmed:27617927]
ACS Infect Dis. 2015 Sep 11;1(9):443-52.
To complete its life cycle, the hepatitis C virus (HCV) induces changes to numerous aspects of its host cell. As kinases act as regulators of many pathways utilized by HCV, they are likely enzyme targets for virally induced inhibition or activation. Herein, we used activity-based protein profiling (ABPP), which allows for the identification of active enzymes in complex protein samples and the quantification of their activity, to identify kinases that displayed differential activity in HCV-expressing cells. We utilized an ABPP probe, Wortmannin-yne, based on the kinase inhibitor Wortmannin, which contains a pendant alkyne group for bioconjugation using bioorthogonal chemistry. We observed changes in the activity of kinases involved in the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway, apoptosis pathways, and cell cycle control. These results establish changes to the active kinome, as reported by Wortmannin-yne, in the proteome of human hepatoma cells actively replicating HCV. The observed changes include kinase activity that affect viral entry, replication, assembly, and secretion, implying that HCV is regulating the pathways that it uses for its life cycle through modulation of the active kinome.
AKTs/PKBs: molecular characterization, tissue expression and transcriptional responses to insulin and/or wortmannin in yellow catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco.[Pubmed:28000079]
Fish Physiol Biochem. 2017 Jun;43(3):719-730.
In the present study, four AKT isoforms termed AKT1, AKT2, AKT3a and AKT3b were isolated and characterized from yellow catfish. Their molecular characterizations, tissue expressions and transcriptional responses to insulin and/or Wortmannin were determined. The validated complementary DNA (cDNA) of yellow catfish AKT1, AKT2, AKT3a and AKT3b were 1422, 1431, 1389 and 1440 bp in length, encoding the peptide of 472, 475, 462 and 479 amino acid residues, respectively. The amino acid sequences of yellow catfish AKTs possessed all the characteristics of AKTs in other species. AKT1, AKT2 and AKT3b contained a conserved domain structure including a specific PH domain, a central catalytic domain and a C-terminal regulatory domain, while AKT3a lacked the C-terminal regulatory domain. All mRNAs of AKTs were expressed at the highest levels in the ovary. Among other tissues, the messenger RNA (mRNA) of AKT1 was widely distributed in all tested tissues, and AKT2 mRNA was more abundant in the muscle, liver and fat and lowest in other tested tissues, while AKT3a mRNA was predominant in the brain and showed no significant difference among other tested tissues, and AKT3b mRNA was highly expressed in the ovary, followed by the brain, muscle and fat and was relatively low in other tissues. Intraperitoneal insulin injection and incubation increased the mRNA expression of AKT1 and AKT2, but not that of AKT3a and AKT3b in the liver and hepatocytes of yellow catfish. Wortmannin reduced the mRNA level of all AKT isoforms and also alleviated the insulin-induced changes of AKT2 expression. The present study cloned full-length cDNA sequences of four AKTs in fish and determined their tissue expression profiles and studied their transcriptional responses to insulin and/or Wortmannin, which serves to increase our understanding of their physiological function in lipid metabolism in fish.
Wortmannin, a widely used phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor, also potently inhibits mammalian polo-like kinase.[Pubmed:15664519]
Chem Biol. 2005 Jan;12(1):99-107.
Polo-like kinases (PLKs) play critical roles throughout mitosis. Here, we report that Wortmannin, which was previously thought to be a highly selective inhibitor of phosphoinositide (PI) 3-kinases, is a potent inhibitor of mammalian PLK1. Observation of the Wortmannin-PLK1 interaction was enabled by a tetramethylrhodamine-Wortmannin conjugate (AX7503) that permits rapid detection of PLK1 activity and expression in complex proteomes. Importantly, we show that Wortmannin inhibits PLK1 activity in an in vitro kinase assay with an IC(50) of 24 nM and when incubated with intact cells. Taken together, our results indicate that, at the concentrations of Wortmannin commonly used to inhibit PI 3-kinases, PLK1 is also significantly inhibited.
In vitro and in vivo antitumor activity of the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase inhibitor, wortmannin.[Pubmed:7653991]
Anticancer Res. 1995 Jul-Aug;15(4):1135-9.
The microbial product Wortmannin has previously been shown to be a potent inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase. In view of the potential role of this enzyme in transduction of mitogenic signals, we determined the cytotoxic activity of Wortmannin against several human tumor cell lines in vitro. The most sensitive lines included GC3 colon carcinoma, IGROV1 ovarian carcinoma, and CCRF-CEM leukemia (IC-50s ranging from 0.7-2.1 microM). The cytotoxicity of Wortmannin was decreased approximately 10-fold by serum-free conditions. Wortmannin was generally less active in low passage human breast cancer cell lines that overexpress either epidermal growth factor receptor or Her2/neu. Wortmannin was also tested for in vivo antitumor activity against seven murine tumor and ten human tumor xenograft models. Activity (> 60% inhibition of tumor growth) was observed in only the C3H mammary carcinoma and the human BxPC-3 pancreatic carcinoma xenograft. In vivo antitumor activity did not correlate with in vitro sensitivity to Wortmannin cytotoxicity.
Wortmannin, a potent and selective inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase.[Pubmed:8162590]
Cancer Res. 1994 May 1;54(9):2419-23.
Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase is an important enzyme for intracellular signaling. The microbial product Wortmannin and some of its analogues have been shown to be potent inhibitors of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase. The 50% inhibitory concentration for inhibition by Wortmannin is 2 to 4 nM. Kinetic analysis demonstrates that Wortmannin is a noncompetitive, irreversible inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase, with inactivation being both time- and concentration-dependent. Wortmannin has previously been reported to be an inhibitor of myosin light chain kinase but with an inhibitory concentration of 0.2 microM. Wortmannin was found not to be an inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol-4-kinase, protein kinase C, or protein tyrosine kinase. Wortmannin inhibited the formation of phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphates in intact cells. The results of the study suggest that Wortmannin and its analogues may have utility as pharmacological probes for studying the actions of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase.
Wortmannin is a potent phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor: the role of phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate in neutrophil responses.[Pubmed:8257416]
Biochem J. 1993 Dec 1;296 ( Pt 2):297-301.
Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate (PtdInsP3) is rapidly produced upon exposure of neutrophils to the chemoattractant N-formylmethionyl-leucylphenylalanine (fMLP), and has been proposed to act as a second messenger mediating actin polymerization and respiratory-burst activity. Here we present evidence that Wortmannin, a known inhibitor of respiratory-burst activity, acts on PtdIns 3-kinase, the enzyme producing PtdInsP3 from PtdIns(4,5)P2. Pretreatment of 32P-labelled human neutrophils with 100 nM Wortmannin totally abolished fMLP-mediated PtdInsP3 production, raised PtdInsP2 levels, and did not affect cellular PtdInsP and PtdIns contents. The inhibitory effect on PtdInsP3 formation in intact cells was dose-dependent, with an IC50 of approximately 5 nM. Similar results were obtained with PtdIns 3-kinase immunoprecipitated by antibodies against the p85 regulatory subunit: Wortmannin totally inhibited PtdIns3P production in immunoprecipitates at concentrations of 10-100 nM (IC50 approximately 1 nM). These results illustrate the direct and specific inhibition of PtdIns 3-kinase by Wortmannin. Since agonist-mediated respiratory-burst activation is most sensitive to Wortmannin (IC50 = 12 nM), this suggests that agonist-mediated PtdInsP3 formation is indispensable for this cell response. Neutrophils pretreated with Wortmannin develop oscillatory changes in F-actin content, but actin polymerization in response to fMLP is not inhibited. This, and the absence of PtdInsP3 under these conditions, are in agreement with a modulatory role for PtdInsP3 in cytoskeletal rearrangements, but imply that PtdInsP3 production is not a primary event triggering elongation of actin filaments in neutrophils.


