ThioperamideH4 inverse agonist and H3 antagonist CAS# 106243-16-7 |
- Lomeguatrib
Catalog No.:BCC1133
CAS No.:192441-08-0
- 5-Azacytidine
Catalog No.:BCC1130
CAS No.:320-67-2
- Zebularine
Catalog No.:BCC1136
CAS No.:3690-10-6
- RG 108
Catalog No.:BCC1134
CAS No.:48208-26-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 106243-16-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 3035905 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C15H24N4S | M.Wt | 292.44 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO and to 100 mM in ethanol | ||
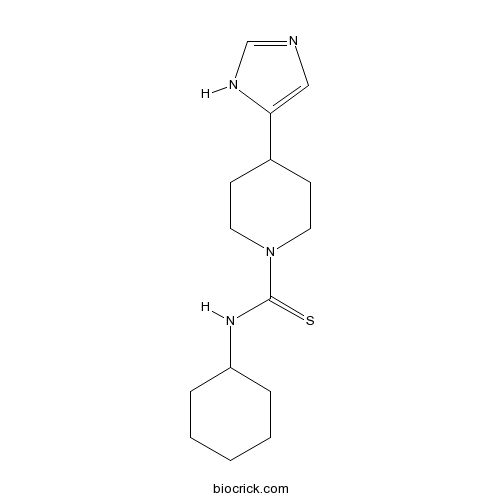
| Chemical Name | N-cyclohexyl-4-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)piperidine-1-carbothioamide | ||
| SMILES | C1CCC(CC1)NC(=S)N2CCC(CC2)C3=CN=CN3 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QKDDJDBFONZGBW-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H24N4S/c20-15(18-13-4-2-1-3-5-13)19-8-6-12(7-9-19)14-10-16-11-17-14/h10-13H,1-9H2,(H,16,17)(H,18,20) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent histamine H3 and H4 antagonist/inverse agonist. Ki values are 25 and 27 nM for human recombinant H3 and H4 receptors respectively. Blocks eosinophil shape change (IC50 = 1.4 μM) and chemotaxis (IC50 = 519 nM) induced by histamine. Freely crosses the blood-brain barrier. Also available as part of the Histamine H3 Receptor. |

Thioperamide Dilution Calculator

Thioperamide Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.4195 mL | 17.0975 mL | 34.195 mL | 68.3901 mL | 85.4876 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6839 mL | 3.4195 mL | 6.839 mL | 13.678 mL | 17.0975 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.342 mL | 1.7098 mL | 3.4195 mL | 6.839 mL | 8.5488 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0684 mL | 0.342 mL | 0.6839 mL | 1.3678 mL | 1.7098 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0342 mL | 0.171 mL | 0.342 mL | 0.6839 mL | 0.8549 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- LDN193189 Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1695
CAS No.:1062368-62-0
- ML347
Catalog No.:BCC5331
CAS No.:1062368-49-3
- LDN-193189
Catalog No.:BCC3687
CAS No.:1062368-24-4
- Ro3280
Catalog No.:BCC3962
CAS No.:1062243-51-9
- WYE-354
Catalog No.:BCC1059
CAS No.:1062169-56-5
- WYE-687
Catalog No.:BCC4604
CAS No.:1062161-90-3
- WAY-600
Catalog No.:BCC4607
CAS No.:1062159-35-6
- TC-G 1004
Catalog No.:BCC6165
CAS No.:1061747-72-5
- PND-1186
Catalog No.:BCC1866
CAS No.:1061353-68-1
- Senktide
Catalog No.:BCC6921
CAS No.:106128-89-6
- Hoechst 33342 analog 2
Catalog No.:BCC1631
CAS No.:106050-84-4
- Palmatine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN5914
CAS No.:10605-02-4
- 4-[(4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) methyl]benzoic acid dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8669
CAS No.:106261-49-8
- Risperidone
Catalog No.:BCC3850
CAS No.:106266-06-2
- Sikokianin A
Catalog No.:BCN3133
CAS No.:106293-99-6
- Nomilin
Catalog No.:BCN1034
CAS No.:1063-77-0
- Rufinamide
Catalog No.:BCC5078
CAS No.:106308-44-5
- DAPTA
Catalog No.:BCC5909
CAS No.:106362-34-9
- ω-Conotoxin GVIA
Catalog No.:BCC5700
CAS No.:106375-28-4
- Boc-D-Alaninol
Catalog No.:BCC2727
CAS No.:106391-86-0
- Boc-D-Valinol
Catalog No.:BCC2692
CAS No.:106391-87-1
- Deoxymorellin
Catalog No.:BCN3067
CAS No.:1064-34-2
- Acid Black 1
Catalog No.:BCC8806
CAS No.:1064-48-8
- Korepimedoside A
Catalog No.:BCN7887
CAS No.:106441-31-0
Low-dose thioperamide injected into the cerebellar vermis of mice immediately after exposure to the elevated plus-maze impairs their avoidance behavior on re-exposure to the apparatus.[Pubmed:24270913]
Braz J Med Biol Res. 2013 Nov;46(11):943-948.
The present study investigated the effect of Thioperamide (THIO), an H3 histaminergic receptor antagonist, microinjected into the cerebellar vermis on emotional memory consolidation in male Swiss albino mice re-exposed to the elevated plus-maze (EPM). We implanted a guide cannula into the cerebellar vermis using stereotactic surgery. On the third day after surgery, we performed behavioral tests for two consecutive days. On the first day (exposure), the mice (n=10/group) were exposed to the EPM and received THIO (0.06, 0.3, or 1.5 ng/0.1 microL) immediately after the end of the session. Twenty-four hours later, the mice were re-exposed to the EPM under the same experimental conditions, but without drug injection. A reduction in the exploration of the open arms upon re-exposure to the EPM (percentage of number of entries and time spent in open arms) compared with the initial exposure was used as an indicator of learning and memory. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by the Duncan post hoc test was used to analyze the data. Upon re-exposure, exploratory activity in the open arms was reduced in the control group, and with the two highest THIO doses: 0.3 and 1.5 ng/0.1 microL. No reduction was seen with the lowest THIO dose (0.06 ng/0.1 microL), indicating inhibition of the consolidation of emotional memory. None of the doses interfered with the animals' locomotor activity. We conclude that THIO at the lowest dose (0.06 ng/0.1 microL) microinjected into the cerebellum impaired emotional memory consolidation in mice.
Thioperamide treats neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy by postsynaptic H1 receptors.[Pubmed:25206478]
Neural Regen Res. 2013 Jul 5;8(19):1814-22.
Thioperamide, a selective histamine H3 receptor antagonist, can increase histamine content in the brain, improve brain edema, and exert a neuroprotective effect. This study aimed to examine the mechanism of action of Thioperamide during brain edema in a rat model of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Our results showed that Thioperamide significantly decreased brain water content and malondialdehyde levels, while significantly increased histamine levels and superoxide dismutase activity in the hippocampus. This evidence demonstrates that Thioperamide could prevent oxidative damage and attenuate brain edema following neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalolopathy. We further observed that changes in the above indexes occurred after combined treatment of Thioperamide with the H1 receptor antagonist, pyrilamine, and the H2 receptor antagonist, tidine. Experimental findings indicated that pyrilamine reversed the effects of Thioperamide; however, cimetidine had no significant influence on the effects of Thioperamide. Our present findings suggest that Thioperamide can increase brain histamine content and attenuate brain edema and oxidative damage by acting in combination with postsynaptic H1 receptors in a rat model of neonatal ic-ischemic encephalopathy.
The prototypical histamine H3 receptor inverse agonist thioperamide improves multiple aspects of memory processing in an inhibitory avoidance task.[Pubmed:23867149]
Behav Brain Res. 2013 Sep 15;253:121-7.
Numerous studies have found that histamine plays a major role in memory and that the histamine H3 receptor (H3R) inverse agonist Thioperamide improves cognitive performance in various animal models. However, little is known about the stages of memory that are specifically affected by Thioperamide. The purpose of the present study was to investigate the effects of Thioperamide on acquisition, consolidation and retrieval processes in a one-trial inhibitory avoidance task in female C57BL/6J mice. In addition, potential state-dependency effects were studied by injecting Thioperamide before the training and the test sessions in order to induce similar physiological states during acquisition and retrieval. Our results indicate that post-training systemic administration of Thioperamide facilitated consolidation. Moreover, the administration of Thioperamide before the training session had no effect on latency to enter the black compartment during training but enhanced memory during the retention test. The administration of Thioperamide before the retention test also increased performance, which indicates that this compound ameliorates memory retrieval. Finally, when animals received Thioperamide before the training session and before the retention test, the cognitive enhancing effects of Thioperamide were not significantly changed. Together, our results show that Thioperamide improves cognitive performance in an inhibitory avoidance task through actions on different memory stages. Furthermore, inducing a similar physiological state with Thioperamide during acquisition and retrieval do not significantly affect cognitive enhancement. Our results suggest that the blockade of H3R can be helpful for the treatment of neuropsychiatric conditions characterized by deficits affecting several stages of memory processing.
The dual H3/4R antagonist thioperamide does not fully mimic the effects of the 'standard' H4R antagonist JNJ 7777120 in experimental murine asthma.[Pubmed:23820873]
Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2013 Nov;386(11):983-90.
Histamine is detected in high concentrations in the airways during an allergic asthma response. In a murine model of allergic asthma, the histamine H4 receptor (H4R)-selective ligand JNJ 7777120 reduces asthma-like symptoms. A sole antagonistic function of JNJ 7777120 at the murine H4R has, however, been questioned in the literature. Therefore, in the present study, we aimed at analyzing the effects of JNJ 7777120 in comparison to that of the H3/4R-selective antagonist Thioperamide. Experimental murine asthma was induced by sensitization and provocation of BALB/c mice with ovalbumine (OVA). JNJ 7777120, Thioperamide, or JNJ 5207852, an H3R-selective antagonist which was used to dissect H3R- and H4R-mediated activities of Thioperamide, were injected subcutaneously during sensitization and effects were analyzed after provocation. Pharmacokinetic analyses revealed shortest t1/2 values in both plasma and lung tissue and lowest maximal concentration in lung tissue for JNJ 7777120 in comparison to Thioperamide and JNJ 5207852. Nevertheless, JNJ 7777120 reduced serum titers of allergen-specific (anti-OVA) IgE, inflammatory infiltrations in lung tissue, and eosinophilia in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. In contrast, Thioperamide reduced only eosinophilia in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, while anti-OVA IgE concentrations and lung infiltrations remained unaffected. JNJ 5207852 had no effect on these parameters. JNJ 7777120 provides beneficial effects in experimental murine asthma, which, however, could only partially be mimicked by Thioperamide, despite more favorable pharmacokinetics. Thus, whether these effects of JNJ 7777120 are entirely attributable to an antagonistic activity at the murine H4R or whether an agonistic activity is also involved has to be reconsidered.
Compared pharmacology of human histamine H3 and H4 receptors: structure-activity relationships of histamine derivatives.[Pubmed:16432504]
Br J Pharmacol. 2006 Apr;147(7):744-54.
Various histamine derivatives were investigated at the human H3 receptor (H3R) and H4 receptor (H4R) stably expressed in human embryonic kidney (HEK)-293 cells using [125I]iodoproxyfan and [3H]histamine binding, respectively. In Tris buffer, [3H]histamine binding to membranes of HEK(hH4R) cells was monophasic (K(D) of 3.8+/-0.8 nM). In phosphate buffer, the Hill coefficient was decreased (n(H) = 0.5+/-0.1) and a large fraction of the binding was converted into a low-affinity component (K(D) = 67+/-27 nM). The inhibition of [3H]histamine binding by two agonists, a protean agonist and five antagonists/inverse agonists confirms that the potency of many H3R ligands is retained or only slightly reduced at the H4R. Histamine derivatives substituted with methyl groups in alpha, beta or N(alpha) position of the side chain retained a nanomolar potency at the H3R, but their affinity was dramatically decreased at the H4R. With relative potencies to histamine of 282 and 0.13% at the H3R and H4R, respectively, (+/-)-alpha,beta-dimethylhistamine is a potent and selective H3R agonist. Chiral alpha-branched analogues exhibited a marked stereoselectivity at the H3R and H4R, the enantiomers with a configuration equivalent to L-histidine being preferred at both receptors. The methylsubstitution of the imidazole ring was also studied. The relative potency to histamine of 4-methylhistamine (4-MeHA) at the H4R (67%) was similar to that reported at H2 receptors but, owing to its high affinity at the H4R (Ki = 7.0+/-1.2 nM) and very low potency at H1- and H3-receptors, it can be considered as a potent and selective H4R agonist. On inhibition of forskolin-induced cAMP formation, all the compounds tested, including 4-MeHA, behaved as full agonists at both receptors. However, the maximal inhibition achieved at the H4R (approximately -30%) was much lower than at the H3R (approximately -80%). Thioperamide behaved as an inverse agonist at both receptors and increased cAMP formation with the same maximal effect (approximately +25%). In conclusion, although the pharmacological profiles of the human H3R and H4R overlap, the structure-activity relationships of histamine derivatives at both receptors strongly differ and lead to the identification of selective compounds.
Histamine H4 receptor mediates eosinophil chemotaxis with cell shape change and adhesion molecule upregulation.[Pubmed:15131002]
Br J Pharmacol. 2004 May;142(1):161-71.
1. During mast cell degranulation, histamine is released in large quantities. Human eosinophils were found to express histamine H(4) but not H(3) receptors. The possible effects of histamine on eosinophils and the receptor mediating these effects were investigated in our studies. 2. Histamine (0.01-30 microm) induced a rapid and transient cell shape change in human eosinophils, but had no effects on neutrophils. The maximal shape change was at 0.3 microm histamine with EC(50) at 19 nm. After 60 min incubation with 1 microm histamine, eosinophils were desensitized and were refractory to shape change response upon histamine restimulation. Histamine (0.01-1 microm) also enhanced the eosinophil shape change induced by other chemokines. 3. Histamine-induced eosinophil shape change was mediated by the H(4) receptor. This effect was completely inhibited by H(4) receptor-specific antagonist JNJ 7777120 (IC(50) 0.3 microm) and H(3)/H(4) receptor antagonist Thioperamide (IC(50) 1.4 microm), but not by selective H(1), H(2) or H(3) receptor antagonists. H(4) receptor agonists imetit (EC(50) 25 nm) and clobenpropit (EC(50) 72 nm) could mimic histamine effect in inducing eosinophil shape change. 4. Histamine (0.01-100 microm) induced upregulation of adhesion molecules CD11b/CD18 (Mac-1) and CD54 (ICAM-1) on eosinophils. This effect was mediated by the H(4) receptor and could be blocked by H(4) receptor antagonists JNJ 7777120 and Thioperamide. 5. Histamine (0.01-10 microm) induced eosinophil chemotaxis with an EC(50) of 83 nm. This effect was mediated by the H(4) receptor and could be blocked by H(4) receptor antagonists JNJ 7777120 (IC(50) 86 nm) and Thioperamide (IC(50) 519 nm). Histamine (0.5 microm) also enhanced the eosinophil shape change induced by other chemokines. 6. In conclusion, we have demonstrated a new mechanism of eosinophil recruitment driven by mast cells via the release of histamine. Using specific histamine receptor ligands, we have provided a definitive proof that the H(4) receptor mediates eosinophil chemotaxis, cell shape change and upregulation of adhesion molecules. The effect of H(4) receptor antagonists in blocking eosinophil infiltration could be valuable for the treatment of allergic diseases. The histamine-induced shape change and upregulation of adhesion molecules on eosinophils can serve as biomarkers for clinical studies of H(4) receptor antagonists.
Cloning and pharmacological characterization of a fourth histamine receptor (H(4)) expressed in bone marrow.[Pubmed:11179434]
Mol Pharmacol. 2001 Mar;59(3):420-6.
Histamine is a multifunctional hormone that regulates smooth muscle contraction in the airways, acid secretion in the gut, and neurotransmitter release in the central nervous system through three well characterized receptor subtypes, H(1), H(2), H(3), respectively. As part of a directed effort to discover novel G-protein-coupled receptors through homology searching of genomic databases, we identified a partial clone (GPCR105) that had significant homology to the recently identified histamine H(3) receptor cDNA. Expression of the full-length human GPCR105 in cells confers the ability to bind [(3)H]histamine with high affinity (K(D) = 5 nM). GPCR105 is pharmacologically similar to the histamine H(3) receptor in that it binds many of the known H(3) agonists and antagonists, albeit with a different rank order of affinity/potency. GPCR105 does not bind (i.e., K(D) > 10 microM) all tested H(1) and H(2) receptor antagonists such as diphenhydramine, loratadine, ranitidine, and cimetidine, but has modest affinity for the H(2) receptor agonist, dimaprit (377 nM). Whereas the H(3) receptor is expressed almost exclusively in nervous tissues, GPRC105 is expressed primarily in bone marrow and eosinophils. Together, these data demonstrate that GPCR105 is a novel histamine receptor structurally and pharmacologically related to the H(3) receptor. However, its unique expression profile and physiological role suggest that GPCR105 is a fourth histamine receptor subtype (H(4)) and may be a therapeutic target for the regulation of immune function, particularly with respect to allergy and asthma.
Characterization of histamine H3-receptors in guinea-pig ileum with H3-selective ligands.[Pubmed:1963802]
Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):621-4.
1. The effect of the selective histamine H3-receptor agonist R-(alpha)-methylhistamine has been investigated on the contractile responses of the longitudinal smooth muscle of guinea-pig ileum elicited by electrical field stimulation of acetylcholine release from myenteric nerve endings. 2. R-(alpha)-methylhistamine produced a concentration-dependent (EC50 = 1.4 +/- 0.2 x 10(-8) M) inhibition of the response to electrical field stimulation which was insensitive to inhibition by mepyramine (1 microM) and tiotidine (2.4 microM). 3. This response to R-(alpha)-methylhistamine could be inhibited in a competitive fashion by a range of H3-receptor antagonists including Thioperamide (KB = 1.1 nM), impromidine (KB = 65 nM), norburimamide (KB = 380 nM) and SKF 91486 (KB = 34 nM). Burimamide was also a potent inhibitor of this response but the Schild slope obtained (1.3) was significantly greater than unity. 4. The estimated KB values were all within a factor of three of those values reported for the histamine H3-receptor mediating inhibition of histamine release in rat cerebral cortex. 5. These data suggest that the histamine receptor mediating inhibition of cholinergic neurotransmission by R-(alpha)-methylhistamine in guinea-pig ileum is the same as the H3-receptor present in rat cerebral cortex.


