TaurineNon-selective, endogenous glycine receptor partial agonist CAS# 107-35-7 |
- Quercetin
Catalog No.:BCN6049
CAS No.:117-39-5
- Lenalidomide (CC-5013)
Catalog No.:BCC2245
CAS No.:191732-72-6
- Carboxypeptidase G2 (CPG2) Inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC1452
CAS No.:192203-60-4
- MEK inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC1738
CAS No.:334951-92-7
- Carboplatin
Catalog No.:BCC1170
CAS No.:41575-94-4
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 107-35-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 1123 | Appearance | Powder |
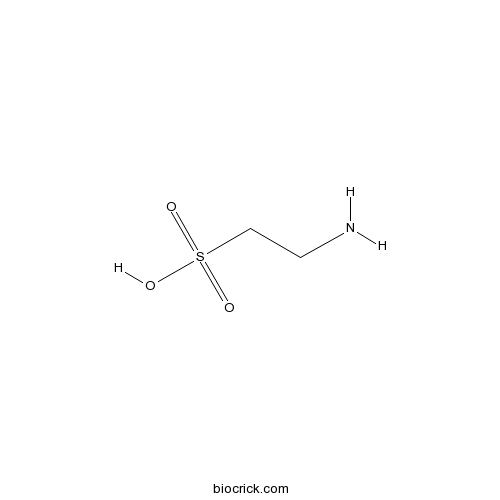
| Formula | C2H7NO3S | M.Wt | 125.15 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | 2-Aminoethanesulfonic acid | ||
| Solubility | H2O : 25 mg/mL (199.76 mM; Need ultrasonic) DMSO : 1 mg/mL (7.99 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-Aminoethylsulfonic acid | ||
| SMILES | NCC[S](O)(=O)=O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | XOAAWQZATWQOTB-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C2H7NO3S/c3-1-2-7(4,5)6/h1-3H2,(H,4,5,6) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Taurine, a free β-amino acid with remarkable antioxidant activity, is used in Taurine-enriched beverages to boost the muscular power of athletes. 2. Taurine can attenuate nandrolone decanoate-induced poor sperm quality and testicular toxicity in rats. 3. Taurine can effectively promote chondrocyte growth and enhance accumulation of glycosaminoglycans and collagens in the conditioned media of chondrocytes, it is effective in proliferation promotion and phenotype maintenance of chondrocytes, thus, taurine may be a useful pro-chondrogenic agent for autologous chondrocyte implantation in the treatment of cartilage repair. |
| Targets | TNF-α | Caspase | MMP(e.g.TIMP) | Calcium Channel | ATPase | Estrogen receptor | Progestogen receptor |

Taurine Dilution Calculator

Taurine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 7.9904 mL | 39.9521 mL | 79.9041 mL | 159.8082 mL | 199.7603 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.5981 mL | 7.9904 mL | 15.9808 mL | 31.9616 mL | 39.9521 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.799 mL | 3.9952 mL | 7.9904 mL | 15.9808 mL | 19.976 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1598 mL | 0.799 mL | 1.5981 mL | 3.1962 mL | 3.9952 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0799 mL | 0.3995 mL | 0.799 mL | 1.5981 mL | 1.9976 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Taurine is an organic acid widely distributed in animal tissues.
- Propylamine
Catalog No.:BCN1814
CAS No.:107-10-8
- Boc-isoleucinol
Catalog No.:BCC3096
CAS No.:106946-74-1
- Adefovir
Catalog No.:BCC8808
CAS No.:106941-25-7
- Boc-D-Leucinol
Catalog No.:BCC2723
CAS No.:106930-51-2
- Valproic acid sodium salt (Sodium valproate)
Catalog No.:BCC2156
CAS No.:1069-66-5
- 5-Allyl-3-methoxy-6-methyl-7-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)bicyclo[3.2.1]oct-3-ene-2,8-dione
Catalog No.:BCN1632
CAS No.:106894-43-3
- BIBP 3226 trifluoroacetate
Catalog No.:BCC7456
CAS No.:1068148-47-9
- Diethyl Acetamidomalonate
Catalog No.:BCC2841
CAS No.:1068-90-2
- Otophylloside B
Catalog No.:BCN7267
CAS No.:106758-54-7
- 24-Deacetylalisol O
Catalog No.:BCN3365
CAS No.:1067510-31-9
- GYY 4137 morpholine salt
Catalog No.:BCC7739
CAS No.:106740-09-4
- Olprinone
Catalog No.:BCC1820
CAS No.:106730-54-5
- Betaine
Catalog No.:BCN6303
CAS No.:107-43-7
- N-Methyltaurine
Catalog No.:BCN1751
CAS No.:107-68-6
- 3-Methyl-1-butylamine
Catalog No.:BCN1810
CAS No.:107-85-7
- H-ß-Ala-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2851
CAS No.:107-95-9
- Sarcosine
Catalog No.:BCN2744
CAS No.:107-97-1
- Granisetron HCl
Catalog No.:BCC1060
CAS No.:107007-99-8
- Amyloid Beta-Peptide (12-28) (human)
Catalog No.:BCC1044
CAS No.:107015-83-8
- O-Phosphorylethanolamine
Catalog No.:BCN1759
CAS No.:1071-23-4
- EIT hydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCC6824
CAS No.:1071-37-0
- Apo-12'-Lycopenal
Catalog No.:BCC8298
CAS No.:1071-52-9
- Adipic dihydrazide
Catalog No.:BCC8810
CAS No.:1071-93-8
- 8,9-Dihydroxy-10-isobutyryloxythymol
Catalog No.:BCN7974
CAS No.:107109-97-7
Chondroprotective effects of taurine in primary cultures of human articular chondrocytes.[Pubmed:25765089]
Tohoku J Exp Med. 2015 Mar;235(3):201-13.
Articular cartilage is characterized by the lack of blood vessels and has a poor self-healing potential. Limited cell numbers and dedifferentiation of chondrocytes when expanded in vitro are the major obstacles of autologous chondrocyte implantation. Autologous chondrocyte implantation is a cell-based treatment that can be used as a second-line measure to regenerate chondral or osteochondral defects in younger, active patients. There is an urgent need to find an effective chondrogenic protection agent alleviating or inhibiting chondrocyte dedifferentiation. In this study, we explored the effect of Taurine (2-aminoethane sulfonic acid) on proliferation and phenotype maintenance of human articular chondrocytes by analyzing the cell proliferation, morphology, viability, and expression of cartilage specific mRNAs and proteins. Primary chondrocytes were isolated from human articular cartilage tissues. Results showed that Taurine effectively promoted chondrocyte growth and enhanced accumulation of glycosaminoglycans and collagens in the conditioned media of chondrocytes. Moreover, Taurine exposure caused significant increases in the relative expression levels of mRNAs for cartilage specific markers, including aggrecan, collagen type II and SOX9. Aggrecan is a cartilage-specific proteoglycan, and SOX9 is a chondrogenic transcription factor. In contrast, the mRNA expression of collagen type I, a marker for chondrocyte dedifferentiation, was significantly decreased in cells treated with Taurine, indicating that Taurine inhibits the chondrocyte dedifferentiation. This study reveals that Taurine is effective in proliferation promotion and phenotype maintenance of chondrocytes. Thus, Taurine may be a useful pro-chondrogenic agent for autologous chondrocyte implantation in the treatment of cartilage repair.
Estradiol decreases taurine level by reducing cysteine sulfinic acid decarboxylase via the estrogen receptor-alpha in female mice liver.[Pubmed:25394658]
Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015 Feb 15;308(4):G277-86.
Cysteine sulfinic acid decarboxylase (CSAD) and cysteine dioxygenase (CDO) are two rate-limiting enzymes in Taurine de novo synthesis, and their expressions are associated with estrogen concentration. The present study was designed to determine the relationship between 17beta-estradiol (E(2)) and Taurine in female mice liver. We initially observed the mice had lower levels of CSAD, CDO, and Taurine during estrus than diestrus. We then, respectively, treated the ovariectomized mice, the cultured hepatocytes, and Hep G2 cells with different doses of E(2), and the CSAD and CDO expressions and Taurine levels were analyzed. The results showed that E(2) decreased Taurine level in the serum and the cultured cells by inhibiting CSAD and CDO expressions. Furthermore, we identified the molecular receptor types through which E(2) plays its role in regulating Taurine synthesis, and our results showed that estrogen receptor-alpha (ERalpha) expression was much higher than estrogen receptor-beta (ERbeta) in the liver and hepatocytes, and the inhibiting effects of E(2) on CSAD, CDO, and Taurine level were partially abrogated in the ICI-182,780-pretreated liver and hepatocytes, and in ERalpha knockout mice. These results indicate that estradiol decreases Taurine content by reducing Taurine biosynthetic enzyme expression in mice liver.
The effects of taurine on vigabatrin, high light intensity and mydriasis induced retinal toxicity in the pigmented rat.[Pubmed:25446799]
Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2015 Jan;67(1):13-20.
The overall purpose of this study was to establish a model that may be used for examining the effect of Vigabatrin-induced retinal toxicity in pigmented rats, and subsequently examine the possible effects of Taurine on the retinal toxicity. In the first part of the study, pigmented Long Evans rats were subjected to combinations of induced mydriasis, low/high light intensities (40/2000 lx) and oral administration of near-MTD (Maximum Tolerated Dose) doses (200 mg/kg/day) of Vigabatrin for up to 6 weeks. The combination of mydriasis and high light intensity applied to Long Evans rats resulted in retinal damage that was increased by the administration of Vigabatrin. In the second part of the study Long Evans rats were subjected to combinations of induced mydriasis and high/low light intensity (40/2000 lx) while being orally administered low (30 mg/kg/day) or high (200 mg/kg/day) doses of Vigabatrin for up to 6 weeks. In addition, selected groups of animals were administered Taurine via the drinking water (20 mg/ml), resulting in systemic Taurine concentrations of approximately threefold the endogenous concentration. The combined results of the studies demonstrate that retinal damage can be induced in pigmented animals when combining mydriasis and high light intensity. Retinal damage was functionally evaluated by electroretinography (ERG), then confirmed by histopathology. While depending on mydriasis and high light intensity, administration of Vigabatrin increased the retinal toxicity and resulted in the formation of rosette-like structures in the retina in a dose-related manner. Administration of Taurine did not alleviate the Vigabatrin-induced retinal toxicity, as demonstrated either functionally by ERG or morphologically, although systemic concentrations of 3-fold the endogenous levels were reached, and it was thus not possible to demonstrate a protective effect of Taurine in these pigmented animals.
Amelioration of nandrolone decanoate-induced testicular and sperm toxicity in rats by taurine: effects on steroidogenesis, redox and inflammatory cascades, and intrinsic apoptotic pathway.[Pubmed:25542992]
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2015 Feb 1;282(3):285-96.
The wide abuse of the anabolic steroid nandrolone decanoate by athletes and adolescents for enhancement of sporting performance and physical appearance may be associated with testicular toxicity and infertility. On the other hand, Taurine; a free beta-amino acid with remarkable antioxidant activity, is used in Taurine-enriched beverages to boost the muscular power of athletes. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to investigate the mechanisms of the possible protective effects of Taurine on nandrolone decanoate-induced testicular and sperm toxicity in rats. To achieve this aim, male Wistar rats were randomly distributed into four groups and administered either vehicle, nandrolone decanoate (10mg/kg/week, I.M.), Taurine (100mg/kg/day, p.o.) or combination of Taurine and nandrolone decanoate, for 8 successive weeks. Results of the present study showed that Taurine reversed nandrolone decanoate-induced perturbations in sperm characteristics, normalized serum testosterone level, and restored the activities of the key steroidogenic enzymes; 3beta-HSD, and 17beta-HSD. Moreover, Taurine prevented nandrolone decanoate-induced testicular toxicity and DNA damage by virtue of its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic effects. This was evidenced by Taurine-induced modulation of testicular LDH-x activity, redox markers (MDA, NO, GSH contents, and SOD activity), inflammatory indices (TNF-alpha, ICAM-1 levels, and MMP-9 gene expression), intrinsic apoptotic pathway (cytochrome c gene expression and caspase-3 content), and oxidative DNA damage markers (8-OHdG level and comet assay). In conclusion, at the biochemical and histological levels, Taurine attenuated nandrolone decanoate-induced poor sperm quality and testicular toxicity in rats.
Role of protein phosphorylation in excitation-contraction coupling in taurine deficient hearts.[Pubmed:25437920]
Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015 Feb 1;308(3):H232-9.
Taurine is a beta-amino acid found in very high concentration in the heart. Depletion of these intracellular stores results in the development of cardiomyopathy, thought to be mediated by abnormal sarcoplasmic reticular (SR) Ca(2+) transport. There is also evidence that Taurine directly alters the Ca(2+) sensitivity of myofibrillar proteins. Major regulators of SR Ca(2+) ATPase (SERCA2a) are the phosphorylation status of a regulatory protein, phospholamban, and SERCA2a expression, which are diminished in the failing heart. The failing heart also exhibits reductions in myofibrillar Ca(2+) sensitivity, a property regulated by the phosphorylation of the muscle protein, troponin I. Therefore, we tested the hypothesis that Taurine deficiency leads to alterations in SR Ca(2+) ATPase activity related to reduced phospholamban phosphorylation and expression of SERCA2a. We found that a sequence of events, which included elevated protein phosphatase 1 activity, reduced autophosphorylation of CaMKII, and reduced phospholamban phosphorylation, supports the reduction in SR Ca(2+) ATPase activity. However, the reduction in SR Ca(2+) ATPase activity was not caused by reduced SERCA2a expression. Taurine transporter knockout (TauTKO) hearts also exhibited a rightward shift in the Ca(2+) dependence of the myofibrillar Ca(2+) ATPase, a property that is associated with an elevation in phosphorylated troponin I. The findings support the observation that Taurine deficient hearts develop systolic and diastolic defects related to reduced SR Ca(2+) ATPase activity, a change mediated in part by reduced phospholamban phosphorylation.
Carnosine and taurine protect rat cerebellar granular cells from free radical damage.[Pubmed:10213162]
Neurosci Lett. 1999 Mar 26;263(2-3):169-72.
Carnosine and Taurine have been suggested to protect excitable tissues against oxidative stress. We have investigated the protection of cerebellar granule cells (neurons) by these compounds against free radicals generated by kainic acid (KA), and 3-morpholinosydnonimine hydrochloride (SIN-1) treatment. Carnosine decreased free radical levels in KA and SIN-1 treated cells, and increased cell viability. The KA effect, but not that of SIN-1, was dependent on the presence of external Ca2+ ions. Taurine increased cell viability, but did not decrease free radical levels. These results suggest that there are multiple pathways leading to cell death, not all of which involve decreases in intracellular free radical levels, and also indicate that multiple mechanisms of cellular defense exist against oxidative stress.
Potentiation of mitochondrial Ca2+ sequestration by taurine.[Pubmed:10484070]
Biochem Pharmacol. 1999 Oct 1;58(7):1123-31.
The effects of Taurine (2-aminoethanesulphonic acid) and its analogues, 2-aminoethylarsonic acid, 2-hydroxyethanesulphonic (isethionic) acid, 3-aminopropanesulphonic acid, 2-aminoethylphosphonic acid, and N,N-dimethylTaurine, were studied on the transport of Ca2+ by mitochondria isolated from rat liver. Taurine enhanced Ca2+ uptake in an apparently saturable process, with a Km value of about 2.63 mM. Taurine behaved as an uncompetitive activator of Ca2+ uptake, increasing both the apparent Km and Vmax values of the process. This effect was not modified in the presence of cyclosporin A (CsA). N,N-DimethylTaurine also stimulated Ca2+ uptake at higher concentrations, but there was no evidence that the process was saturable over the concentration range used (1-10 mM). Aminoethylarsonate was a weak inhibitor of basal Ca2+ uptake, but inhibited that stimulated by Taurine in an apparently competitive fashion (Ki = 0.05 mM). The other analogues had no significant effects on this process. Taurine either in the presence or the absence of CsA had no effect on Ca2+ release induced by 200 nM ruthenium red. Thus, the mechanism of Taurine-enhanced Ca2+ accumulation appears to involve stimulation of Ca2+ uptake via the uniport system rather than inhibition of Ca2+ release via the ion (Na+/Ca2+ and/or H+/Ca2+) exchangers or by Taurine modulating the permeability transition of the mitochondrial inner membrane. Overall, these findings indicate an interaction of Taurine with an as yet unidentified mitochondrial site which might regulate the activity of the uniporter. The unique role of Taurine in modulating mitochondrial Ca2+ homeostasis might be of particular importance under pathological conditions that are characterised by cell Ca2+ overload, such as ischaemia and oxidative stress.
Saturable disposition of taurine in the rat cerebrospinal fluid.[Pubmed:8632336]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1996 Feb;276(2):676-82.
Recently, we described a saturable Na(+)-dependent Taurine transporter in the choroid plexus, the blood-CSF barrier (Chung et al., 1994). The goal of this study was to determine whether this transporter plays a role in the in vivo elimination of Taurine from the CSF. 3H-Taurine and 14C-inulin were injected into the lateral ventricle of anesthetized rats, and the concentrations of the radiolabeled compounds in the CSF were determined. The apparent clearance of Taurine from the CSF was greater than the estimated CSF bulk flow (P < .005), which indicates that there is a clearance process in addition to the CSF bulk flow. Taurine distribution into the choroid plexus was at least 10-fold higher than that found in other brain areas. The apparent clearance of 3H-Taurine and the distribution of Taurine into the choroid plexus and cerebral cortex were dose-dependent. The Michaelis-Menten rate constant estimated from the in vivo elimination study (40 +/- 25 microM) is in the range of that obtained for Taurine uptake in isolated choroid plexus tissue slices (137 +/- 67 microM). Both alpha- and beta-alanine decreased the clearance of Taurine from the CSF as well as the distribution of Taurine into the choroid plexus via inhibitory effects (either direct or indirect) on the Na(+)-Taurine transporter in the choroid plexus. These data suggest that the previously characterized Taurine transporter in the choroid plexus plays a role in the in vivo saturable disposition of Taurine in the CSF.
Pharmacology of the inhibitory glycine receptor: agonist and antagonist actions of amino acids and piperidine carboxylic acid compounds.[Pubmed:7476923]
Mol Pharmacol. 1995 Nov;48(5):919-27.
To define structure-activity relations for ligands binding to the inhibitory glycine receptor (GlyR), the agonistic and antagonistic properties of alpha- and beta-amino acids were analyzed at the recombinant human alpha 1 GlyR expressed in Xenopus oocytes. The agonistic activity of alpha-amino acids exhibited a marked stereoselectivity and was highly susceptible to substitutions at the C alpha-atom. In contrast, alpha-amino acid antagonism was not enantiomer dependent and was influenced little by C alpha-atom substitutions. The beta-amino acids Taurine, beta-aminobutyric acid (beta-ABA), and beta-aminoisobutyric acid (beta-AIBA) are partial agonists at the GlyR. Low concentrations of these compounds competitively inhibited glycine responses, whereas higher concentrations elicited a significant membrane current. Nipecotic acid, which contains a trans-beta-amino acid configuration, behaved as purely competitive GlyR antagonist. Our data are consistent with the existence of a common binding site for all amino acid agonists and antagonists, at which the functional consequences of binding depend on the particular conformation a given ligand adopts within the binding pocket. In the case of beta-amino acids, the trans conformation appears to mediate antagonistic receptor binding, and the cis conformation appears to mediate agonistic receptor binding. This led us to propose that the partial agonist activity of a given beta-amino acid is determined by the relative mole fractions of the respective cis/trans conformers.


