SteviosideCAS# 57817-89-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 57817-89-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 442089 | Appearance | White powder |
| Formula | C38H60O18 | M.Wt | 804.88 |
| Type of Compound | Diterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Steviosin | ||
| Solubility | >80.5mg/ml in DMSO | ||
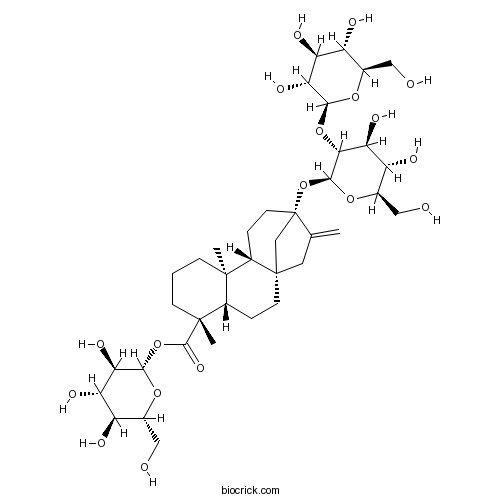
| SMILES | CC12CCCC(C1CCC34C2CCC(C3)(C(=C)C4)OC5C(C(C(C(O5)CO)O)O)OC6C(C(C(C(O6)CO)O)O)O)(C)C(=O)OC7C(C(C(C(O7)CO)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | UEDUENGHJMELGK-HYDKPPNVSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C38H60O18/c1-16-11-37-9-5-20-35(2,7-4-8-36(20,3)34(50)55-32-29(49)26(46)23(43)18(13-40)52-32)21(37)6-10-38(16,15-37)56-33-30(27(47)24(44)19(14-41)53-33)54-31-28(48)25(45)22(42)17(12-39)51-31/h17-33,39-49H,1,4-15H2,2-3H3/t17-,18-,19-,20+,21+,22-,23-,24-,25+,26+,27+,28-,29-,30-,31+,32+,33+,35-,36-,37-,38+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Stevioside is a safe natural sweetener, has no allergic reactions, suited for both diabetics, and PKU patients, as well as for obese persons intending to lose weight by avoiding sugar supplements in the diet. Stevioside enjoys a dual positive effect by acting as an antihyperglycemic and a blood pressure-lowering substance, it may have therapeutic potential in the treatment of type 2 diabetes and the metabolic syndrome.Stevioside exerts anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic properties by inhibiting the release of cytokines and the activation of TLR2 and proteins of the NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways, as well as caspase-3 and Bax. |
| Targets | TLR | NF-kB | TNF-α | IL Receptor | IkB | p38MAPK | ERK | JNK | p65 | Caspase | PDE | IKK |
| In vitro | Stevioside inhibits inflammation and apoptosis by regulating TLR2 and TLR2-related proteins in S. aureus-infected mouse mammary epithelial cells.[Pubmed: 24975657]Int Immunopharmacol. 2014 Sep;22(1):192-9.
|
| In vivo | Effects of lactose-containing stevioside sweeteners on dental biofilm acidogenicity.[Pubmed: 25098824]Braz Oral Res. 2014 Jan-Feb;28(1).The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of a commercial lactose-containing Stevioside sweetener on biofilm acidogenicity in vivo.
Antihyperglycemic and blood pressure-reducing effects of stevioside in the diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rat.[Pubmed: 12647278 ]Metabolism. 2003 Mar;52(3):372-8.Stevioside, a glycoside present in the leaves of the plant, Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni (SrB), has acute insulinotropic effects in vitro. Its potential antihyperglycemic and blood pressure-lowering effects were examined in a long-term study in the type 2 diabetic Goto-Kakizaki (GK) rat.
|
| Cell Research | Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory activities of stevioside and steviol on colonic epithelial cells.[Pubmed: 23794454]J Sci Food Agric. 2013 Dec;93(15):3820-5.Stevioside is a natural non-caloric sweetener isolated from Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni leaves. We have proposed its effect on attenuation of tumour necrosis factor α (TNF-α) and interleukin 1β (IL-1β) release in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated monocytes.
|
| Animal Research | Effect of aqueous solution of stevioside on pharmacological properties of some cardioactive drugs.[Pubmed: 25109114]Vojnosanit Pregl. 2014 Jul;71(7):667-72.Animal Models: Rats |

Stevioside Dilution Calculator

Stevioside Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.2424 mL | 6.2121 mL | 12.4242 mL | 24.8484 mL | 31.0605 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.2485 mL | 1.2424 mL | 2.4848 mL | 4.9697 mL | 6.2121 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1242 mL | 0.6212 mL | 1.2424 mL | 2.4848 mL | 3.1061 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0248 mL | 0.1242 mL | 0.2485 mL | 0.497 mL | 0.6212 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0124 mL | 0.0621 mL | 0.1242 mL | 0.2485 mL | 0.3106 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Domperidone
Catalog No.:BCC4461
CAS No.:57808-66-9
- Liquiritigenin
Catalog No.:BCN5946
CAS No.:578-86-9
- Cosmosiin
Catalog No.:BCN5788
CAS No.:578-74-5
- 8-Aminoquinoline
Catalog No.:BCC8784
CAS No.:578-66-5
- 4-(2-Hydroxy-1-methoxyethyl)-1,2-benzenediol
Catalog No.:BCN1412
CAS No.:577976-26-2
- Topiroxostat
Catalog No.:BCC4202
CAS No.:577778-58-6
- Cardionogen 1
Catalog No.:BCC6199
CAS No.:577696-37-8
- WAY 629 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7271
CAS No.:57756-44-2
- Nisoxetine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6894
CAS No.:57754-86-6
- Equisetin
Catalog No.:BCN1835
CAS No.:57749-43-6
- 4-(Ethoxymethyl)phenol
Catalog No.:BCN4753
CAS No.:57726-26-8
- ent-11alpha-Hydroxy-15-oxokaur-16-en-19-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7372
CAS No.:57719-81-0
- Idarubicin HCl
Catalog No.:BCC1194
CAS No.:57852-57-0
- Clozapine
Catalog No.:BCC5037
CAS No.:5786-21-0
- Myrianthic acid 3,23-acetonide
Catalog No.:BCN7517
CAS No.:578710-52-8
- Oligomycin A
Catalog No.:BCC2530
CAS No.:579-13-5
- Lobelanine
Catalog No.:BCN2156
CAS No.:579-21-5
- o-Anisic acid
Catalog No.:BCC9108
CAS No.:579-75-9
- 19-Nor-4-hydroxyabieta-8,11,13-trien-7-one
Catalog No.:BCN1411
CAS No.:57906-31-7
- Corynoxidine
Catalog No.:BCN6798
CAS No.:57906-85-1
- Z-Cys(Z)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2784
CAS No.:57912-35-3
- L(+)-Asparagine Monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCC8332
CAS No.:5794-13-8
- Officinalisinin I
Catalog No.:BCN2825
CAS No.:57944-18-0
- Bax inhibitor peptide V5
Catalog No.:BCC2394
CAS No.:579492-81-2
Stevioside inhibits inflammation and apoptosis by regulating TLR2 and TLR2-related proteins in S. aureus-infected mouse mammary epithelial cells.[Pubmed:24975657]
Int Immunopharmacol. 2014 Sep;22(1):192-9.
Stevioside is a natural sweetener that is commonly used in traditional medicine and as a food additive. The object of this study was to investigate the anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptosis function of Stevioside and the possible molecular mechanisms for such activity in Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus)-infected mouse mammary epithelial cells (MMECs). The cells were treated with varying doses of Stevioside before infection with S. aureus. The live/dead cells were detected by immunofluorescence microscopy. The pro-inflammatory cytokines were determined by ELISA. The mRNA of TLR2 and proteins related to NF-kappaB, MAPK and apoptosis were analyzed by q-PCR. The relative protein expression levels were determined by Western blot. The results indicated that Stevioside inhibited the mRNA and protein expression of TNF-alpha, IL-6 and IL-1beta dose-dependently in S. aureus-stimulated MMECs. Stevioside suppressed the S. aureus-induced expression of TLR2 and proteins of the NF-kappaB and MAPK pathways as well as apoptosis. The mRNA levels of IkappaBalpha, p38, ERK, JNK, p65, caspase-3 and Bax were not influenced by the Stevioside treatment. Stevioside exerts anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic properties by inhibiting the release of cytokines and the activation of TLR2 and proteins of the NF-kappaB and MAPK signaling pathways, as well as caspase-3 and Bax.
Effect of aqueous solution of stevioside on pharmacological properties of some cardioactive drugs.[Pubmed:25109114]
Vojnosanit Pregl. 2014 Jul;71(7):667-72.
BACKGROUND/AIM: Stevioside is a glycoside that supposedly possesses a number of pharmacodynamic effects such as anti-infective, hypoglycemic, along with the beneficial influence on the cardiovascular system. The aim of this study was to determine the effect of rats pretreatment with aqueous solution of Stevioside on pharmacological actions of adrenaline, metoprolol and verapamil. METHODS: Rats were administered (intraperitoneally 200 mg/kg/day) Stevioside as aqueous solution or physiological saline in the course of 5 days, then anaesthetized with urethane and the first ECG recording was made. The prepared jugular vein was connected to an infusion pump with adrenaline (0.1 mg/mL), verapamil (2.5 mg/mL) or metoprolol (1 mg/mL). Control animals, pretreated with saline, in addition to the mentioned drugs, were also infused with the solution of Stevioside (200 mg/mL) in the course of recording ECG. RESULTS: The infusion of Stevioside produced no significant changes in ECG, even at a dose exceeding 1,600 mg/kg. In the control group, a dose of adrenaline of 0.07 +/- 0.02 mg/kg decreased the heart rate, whereas in the Stevioside-pretreated rats this occurred at a significantly higher dose (0.13 +/- 0.03 mg/kg). In Stevioside-pretreated rats, the amount of verapamil needed to produce the decrease in heart rate was significantly lower compared to the control. The pretreatment with Stevioside caused no significant changes in the parameters registered on ECG during infusion of metoprolol. CONCLUSION: The results suggest that pretreatment with Stevioside may change the effect of adrenaline and verapamile on the heart rate.
Effects of lactose-containing stevioside sweeteners on dental biofilm acidogenicity.[Pubmed:25098824]
Braz Oral Res. 2014;28. pii: S1806-83242014000100237. Epub 2014 Aug 4.
The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of a commercial lactose-containing Stevioside sweetener on biofilm acidogenicity in vivo. Nine volunteers refrained from brushing their teeth for 3 days in five phases. On the 4th day of each phase, the pH of the biofilm was measured by the "Strip method". Interproximal plaque pH was measured before and up to 60 minutes after a 10 mL mouthrinse for 1 minute with the test solutions: I - sweetener with 93% lactose and 7% Stevioside; II - sweetener with 6.8% saccharin, 13.6% cyclamate, and 0.82% Stevioside; III - 18% sucrose solution (positive control); IV - mineral water (negative control); and V- 93% lactose solution. The results revealed that the most pronounced pH fall was found with sucrose (positive control), followed by the 93% lactose solution, the sweetener with lactose + Stevioside, the sweetener with saccharin + cyclamate + Stevioside, and finally water (negative control). According to the area under the curve, the two sweeteners containing Stevioside were significantly different, and the sweetener with lactose + Stevioside was significantly different from water but not from sucrose. The critical pH for dentin demineralization (pH Stevioside + lactose sweetener. Analysis of the data suggests that lactose-containing Stevioside sweeteners may be cariogenic, especially to dentin.
Antihyperglycemic and blood pressure-reducing effects of stevioside in the diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rat.[Pubmed:12647278]
Metabolism. 2003 Mar;52(3):372-8.
Stevioside, a glycoside present in the leaves of the plant, Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni (SrB), has acute insulinotropic effects in vitro. Its potential antihyperglycemic and blood pressure-lowering effects were examined in a long-term study in the type 2 diabetic Goto-Kakizaki (GK) rat. Rats were fed 0.025 g x kg(-1) x d(-1) of Stevioside (purity > 99.6%) for 6 weeks. An intra-arterial catheter was inserted into the rats after 5 weeks, and conscious rats were subjected to arterial glucose tolerance test (2.0 g x kg(-1)) during week 6. Stevioside had an antihyperglycemic effect (incremental area under the glucose response curve [IAUC]): 985 +/- 20 (Stevioside) versus 1,575 +/- 21 (control) mmol/L x 180 minutes, (P <.05), it enhanced the first-phase insulin response (IAUC: 343 +/- 33 [Stevioside] v 136 +/- 24 [control] microU/mL insulin x 30 minutes, P <.05) and concomitantly suppressed the glucagon levels (total AUC: 2,026 +/- 234 [Stevioside] v 3,535 +/- 282 [control] pg/mL x 180 minutes, P <.05). In addition, Stevioside caused a pronounced suppression of both the systolic (135 +/- 2 v 153 +/- 5 mm Hg; P <.001) and the diastolic blood pressure (74 +/- 1 v 83 +/- 1 mm Hg; P <.001). Bolus injections of Stevioside (0.025 g x kg(-1)) did not induce hypoglycemia. Stevioside augmented the insulin content in the beta-cell line, INS-1. Stevioside may increase the insulin secretion, in part, by induction of genes involved in glycolysis. It may also improve the nutrient-sensing mechanisms, increase cytosolic long-chain fatty acyl-coenzyme A (CoA), and downregulate phosphodiesterase 1 (PDE1) estimated by the microarray gene chip technology. In conclusion, Stevioside enjoys a dual positive effect by acting as an antihyperglycemic and a blood pressure-lowering substance; effects that may have therapeutic potential in the treatment of type 2 diabetes and the metabolic syndrome.
Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory activities of stevioside and steviol on colonic epithelial cells.[Pubmed:23794454]
J Sci Food Agric. 2013 Dec;93(15):3820-5.
BACKGROUND: Stevioside is a natural non-caloric sweetener isolated from Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni leaves. We have proposed its effect on attenuation of tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin 1beta (IL-1beta) release in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated monocytes. In this study, the anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory activities of Stevioside and its metabolite, steviol, on human colon carcinoma cell line (Caco-2) were evaluated. RESULTS: Stevioside and steviol, in the doses used in this study, had no cytotoxicity on Caco-2 cells. Anti-inflammatory activities of these two compounds were observed by potentially suppressed LPS-mediated TNF-alpha, IL-1beta and IL-6 release. In addition, Stevioside and steviol showed immunomodulatory effects on IkappaBalpha activation and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB) suppression in western blotting. CONCLUSION: Stevioside and steviol attenuate LPS-induced pro-inflammatory cytokine productions by affecting cytokine gene expression via IkappaBalpha/NF-kappaB signalling pathway.


