Shatavarin IVCAS# 84633-34-1 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

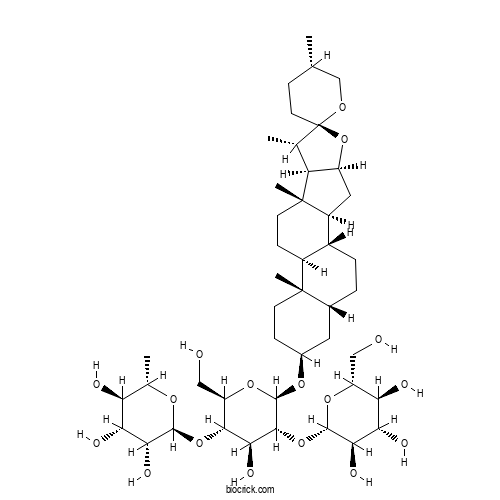
| Cas No. | 84633-34-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 441896 | Appearance | White powder |
| Formula | C45H74O17 | M.Wt | 887.1 |
| Type of Compound | Steroids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Asparanin B; Curillin H | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in methan | ||
| Chemical Name | (2S,3R,4R,5R,6S)-2-[(2R,3S,4S,5R,6R)-4-hydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)-6-[(1R,2S,4S,5'S,6R,7S,8R,9S,12S,13S,16S,18R)-5',7,9,13-tetramethylspiro[5-oxapentacyclo[10.8.0.02,9.04,8.013,18]icosane-6,2'-oxane]-16-yl]oxy-5-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxyoxan-3-yl]oxy-6-methyloxane-3,4,5-triol | ||
| SMILES | CC1CCC2(C(C3C(O2)CC4C3(CCC5C4CCC6C5(CCC(C6)OC7C(C(C(C(O7)CO)OC8C(C(C(C(O8)C)O)O)O)O)OC9C(C(C(C(O9)CO)O)O)O)C)C)C)OC1 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | BCUDKRWNGQAFLF-PJFZGHSASA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C45H74O17/c1-19-8-13-45(55-18-19)20(2)30-27(62-45)15-26-24-7-6-22-14-23(9-11-43(22,4)25(24)10-12-44(26,30)5)57-42-39(61-41-36(53)34(51)32(49)28(16-46)58-41)37(54)38(29(17-47)59-42)60-40-35(52)33(50)31(48)21(3)56-40/h19-42,46-54H,6-18H2,1-5H3/t19-,20-,21-,22+,23-,24+,25-,26-,27-,28+,29+,30-,31-,32+,33+,34-,35+,36+,37-,38+,39+,40-,41-,42+,43-,44-,45+/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Shatavarin IV shows in vitro anti-malassezia activity. Shatavarins (containing shatavarin IV) rich fraction (AR-2B) exhibits significant anticancer activity in both in vitro and in vivo experimental models. | |||||

Shatavarin IV Dilution Calculator

Shatavarin IV Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.1273 mL | 5.6363 mL | 11.2727 mL | 22.5454 mL | 28.1817 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.2255 mL | 1.1273 mL | 2.2545 mL | 4.5091 mL | 5.6363 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1127 mL | 0.5636 mL | 1.1273 mL | 2.2545 mL | 2.8182 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0225 mL | 0.1127 mL | 0.2255 mL | 0.4509 mL | 0.5636 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0113 mL | 0.0564 mL | 0.1127 mL | 0.2255 mL | 0.2818 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 8-Acetyl-7-methoxycoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN0004
CAS No.:89019-07-8
- Hydrocotarnine hydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCN0003
CAS No.:5985-00-2
- N-Methylcolchicine
Catalog No.:BCN0002
CAS No.:7336-40-5
- 2-(4-Methoxybenzal)acetophenone
Catalog No.:BCN0001
CAS No.:959-33-1
- 8-p-Coumaroylharpagide
Catalog No.:BCN0152
CAS No.:87686-74-6
- trans-5-Hydroxyferulic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9999
CAS No.:110642-42-7
- 7-Methoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN9998
CAS No.:22395-22-8
- Oxyacanthine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN9997
CAS No.:15352-74-6
- 3,4-Dimethoxychalcone
Catalog No.:BCN9996
CAS No.:5416-71-7
- 2',3,5,7-Tetrahydroxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN9995
CAS No.:480-15-9
- 4-Hydroxyquinoline
Catalog No.:BCN9994
CAS No.:611-36-9
- Cytochalasin C
Catalog No.:BCN9993
CAS No.:22144-76-9
- N-trans-p-Coumaroyltyrosine
Catalog No.:BCN0006
CAS No.:77201-66-2
- Chamigrenol
Catalog No.:BCN0007
CAS No.:19822-80-1
- Harmol hydrochloride monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCN0008
CAS No.:40580-83-4
- Daidzein 7-O-glucuronide
Catalog No.:BCN0009
CAS No.:38482-80-3
- Chamaemeloside
Catalog No.:BCN0010
CAS No.:173356-77-9
- Withanoside IV
Catalog No.:BCN0011
CAS No.:362472-81-9
- Phyllanthusiin C
Catalog No.:BCN0012
CAS No.:142674-52-0
- beta-Cryptoxanthin
Catalog No.:BCN0013
CAS No.:472-70-8
- Cyanidin-3-O-rhamnoside chloride
Catalog No.:BCN0014
CAS No.:38533-30-1
- Phloroglucinol dihydrate
Catalog No.:BCN0015
CAS No.:6099-90-7
- 3-Methoxyflavon
Catalog No.:BCN0016
CAS No.:7245-02-5
- Luteolin 7-diglucuronide
Catalog No.:BCN0017
CAS No.:96400-45-2
A Bioactive compound Shatavarin IV-mediated longevity as revealed by dietary restriction-induced autophagy in Caenorhabditis elegans.[Pubmed:32888154]
Biogerontology. 2020 Dec;21(6):827-844.
Plant-based dietary supplements that delay aging are of significant interest now a days because these naturally occurring bioactive molecules effectively provide pharmaceuticals/neutraceuticals to deal with diseases related to the advanced life expectancy. In this paper, we aimed to investigate the effect of Shatavarin IV (SIV), a steroidal saponin isolated from Asparagus racemosus Willd. on dietary restriction (DR) induced longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans. SIV significantly increased the lifespan to 18% which is independent of antimicrobial activity and reduced the aging by-product, lipofuscin along with increased locomotion, and chemotaxis behavior in wild type worms. The longevity effect has been dependent on eat-2, which was further validated via reduced pharyngeal pumping rate that established the effect similar to DR induced longevity. Moreover, like eat-2 mutant worms, SIV reduces the total progeny number of wild type worm along with a significant alleviation of stored fat, which reconfirms the involvement of eat-2 mediated longevity. Further, it was also observed that DR induced longevity mechanism by SIV requires mTOR which works in PHA-4/FOXA dependent manner. In addition to this, the role of autophagy mechanism concerning SIV mediated DR was confirmed via bec-1, unc-51, and lgg-1. The longevity effect achieved by SIV was also dependent on SKN-1/NRF-2 and partially dependent on DAF-16/FOXO. Furthermore, the DR-induced longevity by SIV was found to be independent of hsf-1 exhibiting non-significant alteration in the mRNA expression of downstream target genes hsp-16.2 and hsp-70. Altogether, this study provides first-hand information on the pro-longevity effect of SIV in worms that have been mediated by the DR-regulating gene induced autophagy.
Shatavarin IV elicits lifespan extension and alleviates Parkinsonism in Caenorhabditis elegans.[Pubmed:29069955]
Free Radic Res. 2017 Dec;51(11-12):954-969.
Shatavarin IV (SIV), a steroidal saponin, is a major bioactive phytomolecule present in roots of Asparagus racemosus (Liliaceae) known for its anticancer activity. Age-associated neurodegenerative Parkinson's disease (PD) is characterised by alpha-synuclein aggregation in dopaminergic neuron resulting in neurodegeneration. The invention of bioactive molecules that delay aging and age-associated disorders endorses development of natural phytomolecule as a therapeutic agent for curing age-related diseases. Therefore, the present study for the first time explores the potential of SIV against aging and Parkinsonism utilising Caenorhabditis elegans model system. SIV significantly attenuated oxidative stress in terms of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) as well as oxidative damage including protein carbonylation and also promotes longevity. SIV also significantly increased the mRNA expression of stress responsive genes namely sod-1, sod-2, sod-3, gst-4, gst-7 and ctl-2 suggesting its anti-oxidant property that might be contributed in the modulation of oxidative stress and promoting lifespan. Additionally, SIV improved PD symptoms by reducing the alpha-synuclein aggregation, lipid accumulation and enhancing dopamine level. Altogether, present findings indicate that SIV possibly utilising ubiquitin-mediated proteasomal system and attenuating oxidative stress by up-regulating PD-associated genes pdr-1, ubc-12 and pink-1. Therefore, this study is a forward step in exploring the anti-aging and anti-Parkinsonism potential of bioactive compound SIV in C. elegans.
Immunoaffinity Knockout of Saponin Glycosides from Asparagus racemosus to Assess Anti-lipid Peroxidation.[Pubmed:28198114]
Phytochem Anal. 2017 Jul;28(4):316-323.
INTRODUCTION: Asparagus racemosus Willd (Asparagaceae family), known as Shatavari, is important in Ayurveda and traditional Thai medicines. The saponin glycosides, shatavarin I and IV are major constituents in its roots and may be responsible for their actions including protection against lipid peroxidation and carcinogenesis. OBJECTIVE: To develop an immunoaffinity column for isolating compounds with structures related to Shatavarin IV from crude extracts of A. racemosus root. METHODOLOGY: The monoclonal antibody recognising Shatavarin IV (mAbShavIV) was coupled to an Affi-Gel Hz gel to isolate compounds with structures related to Shatavarin IV from the other components of crude extracts of A. racemosus root. The saponin glycosides in each fraction were analysed by mAbShavIV ELISA and LC-MS/MS. RESULTS: The pooled wash-through fractions contained 3% of loaded mAbShavIV reactive saponin glycosides, while eluted fractions released ~ 90% of shatavarin saponin glycosides in a single step. Using thiobarbiturate (TBARs) to measure lipid-peroxidation, the extract, and the pooled wash-through fractions showed moderate protection against Cu(+) -induced oxidation of human low density lipoprotein (LDL) (IC50 11.3 +/- 1.4 and 12.6 +/- 0.9 mug/mL, respectively). In contrast, the saponin glycosides eluted from the mAbShavIV-column had weaker protectant (IC50 29.7 +/- 1.8 mug/mL) suggesting that A. racemosus shatavarins do not inhibit carcinogenesis through preventing lipid peroxidation. CONCLUSION: The strategy described here demonstrates its utility for isolating a group of related compounds from the rest of the extract with selectivity and recovery rate. Pharmacological efficacy and synergistic effects of the components obtained can be further investigated. Copyright (c) 2017 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Quantification of Saponins in Asparagus racemosus by HPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS.[Pubmed:30549812]
Nat Prod Commun. 2017 Jan;12(1):7-10.
Asparagus racemosus Willd. or Shatavari (Asparagaccae family) is an important medicinal plant in Ayurvedic medicine as a rejuvenate for women A method - for quantitative analysis of saponin glycosides bioactive constituents in A. racemosus is reported. A high performance liquid chromatography quadrupole time of flight mass spectrometry (HPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS) method was developed and validated for simultaneous determination of five saponin glycosides, asparacoside, shatavarin IX, Shatavarin IV, asparanin A and shatavarin V in A. racemosus extracted with 70% MeOH. The method was validated through intra- and inter-day precision, with the relative standard deviation (RSD) less than 6%, limits of detection (LOD) and limits of quantification (LOQ) <10 and 50 ng, respectively. Overall recoveries ranged from 95% to 105%, with RSD ranging from 0.7% to 4.5%. The method was applied to saponin glycoside contents in the leaves, stems, and roots of A. racemosus sourced from different geographical locations, including four provinces in Thailand, and a sample from India. Saponin glycosides were detected predominantly in the roots, the part used in traditional medicines and these showed wide variations in saponin glycoside profiles from undetectable to 12 mg/g dry weight. The quality control of A. raceinosus is crucial for reliable and predictable therapies and only methods like the one developed has the necessary flexibility, sensitivity, accuracy, and selectivity for reliable routine quality control.
Spirostanol steroids from the roots of Allium tuberosum.[Pubmed:25836597]
Steroids. 2015 Aug;100:1-4.
Three new spirostanol saponins named tuberosines A-C (1-3), together with three known ones tuberoside O (4), 25(S)-Schidigera-saponin D5 (5), and Shatavarin IV (6) were isolated from the roots of Allium tuberosum. Their structures were established on the basis of extensive spectroscopic analyses. Whereas compounds 5 and 6 exhibited potent antibacterial activities against Bacillus subtilis (32 mug/mL) and Escherichia coli (16 mug/mL), the new saponin 2 showed only moderate antibacterial activities against these pathogens. The relationship between the antibacterial activities and the structures of these saponins are described.
HPLC/tandem mass spectrometric studies on steroidal saponins: an example of quantitative determination of Shatavarin IV from dietary supplements containing Asparagus racemosus.[Pubmed:25632427]
J AOAC Int. 2014 Nov-Dec;97(6):1497-502.
Asparagus racemosus (AR) is a popular botanical present in several Ayurvedic medicines and nutritional and dietary supplements with immunomodulatory, galactogogue, and anticancer activity. A steroidal saponin known as Shatavarin IV is one of the active constituents of AR. A new, selective, and rapid HPLC/MSIMS method has been developed and validated for quantitative estimation of Shatavarin IV in crude, processed, and marketed samples of AR. The analytes were separated on a Luna C18 column using simple isocratic elution with water (0.1% acetic acid)-acetonitrie;(0.1% acetic acid; 70 + 30, vIv) at a flow rate of 0.8 mLlmin. The analytes were detected by electrospray ionization (ESI)-MS/MS and quantified using multiple reaction monitoring techniques in the positive ion mode. The method showed excellent linearity (r2 > 0.998) over the concentration range of 7.5 to 254 ng/mL with LOD of 2.5 ng/mL. Precision (RSD) and accuracy (recovery) were found in the ranges of 2.00 to 5.15 and 102 to 110%, respectively. The validated HPLC/ESI-MS/MS method was successfully applied to the quantification of Shatavarin IV in crude, processed, and marketed (single or multiherb) AR samples. Therefore, this method could be used for QC and standardization of pharmaceutical or nutritional products containing AR.
In vitro anti-Malassezia activity and potential use in anti-dandruff formulation of Asparagus racemosus.[Pubmed:24117781]
Int J Cosmet Sci. 2014 Feb;36(1):74-8.
OBJECTIVE: Malassezia species are frequently associated with dandruff and seborrhoeic dermatitis. The study was conducted to evaluate anti-fungal activities of the extracts obtained from the roots of Asparagus racemosus Willd against Malassezia furfur and M. globosa. METHODS: Asparagus racemosus roots were successively extracted with the series of solvents, that is, hexane, ethanol and water, and also a saponin-enriched fraction was prepared. The amounts of saponin (equivalent to Shatavarin IV) in the extracts were determined using ELISA. The extracts were tested for anti-fungal activity by disc diffusion and broth microdilution methods. RESULTS: By disc diffusion, only the ethanolic and saponin-enriched extracts demonstrated anti-fungal activity against M. furfur and M. globosa at the concentration of 1 mg per disc whereas the extracts with other solvents were ineffective. Multiple concentrations using the broth microdilution method against M. furfur and M. globosa yielded minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of 25 mg mL(-1) for the ethanolic extract but much higher potency for the saponin-enriched extract: MICs to 0.20 and 0.40 mg mL(-1) for M. furfur and M. globosa, respectively. These extracts showed no antagonist effect with the anti-fungal agents, ketoconazole and zinc pyrithione. CONCLUSION: These studies revealed the antifungal activity of A. racemosus roots extracts. Because A. racemosus is also anti-inflammatory agent, it has the potential use as an active ingredient in an anti-dandruff formulation.
Shatavarins (containing Shatavarin IV) with anticancer activity from the roots of Asparagus racemosus.[Pubmed:23248403]
Indian J Pharmacol. 2012 Nov-Dec;44(6):732-6.
OBJECTIVES: The anticancer activity of shatavarins (containing Shatavarin IV) isolated from the roots of Asparagus racemosus (Wild) was evaluated using in vitro and in vivo experimental models. MATERIAL AND METHODS: The Shatavarin IV was isolated from ethyl acetate insoluble fraction (AR-2B) of chloroform:methanol (2:1) (AR-2) extract of A. racemosus roots. The cytotoxicity (in vitro) of Shatavarin IV and other shatavarins rich fraction was carried out using of MTT assay using MCF-7 (human breast cancer), HT-29 (human colon adenocarcinoma), and A-498 (human kidney carcinoma) cell lines. The in vivo anticancer activity of shatavarins (containing Shatavarin IV) was evaluated against Ehrlich ascites carcinoma (EAC) tumor bearing mice. RESULTS: The isolated Shatavarin IV (84.69 %) along with shatavarins rich fraction, coded AR-2B containing 5.05% Shatavarin IV showed potent cytotoxicity. Oral administration of AR-2B to tumor bearing mice at doses of 250 and 500 mg/kg body weight for 10 days, showed significant reduction in percent increase in body weight, tumor volume, packed cell volume, viable tumor cell count, and increased non-viable cell count when compared to the untreated mice of the EAC control group. The restoration of hematological parameters towards normalcy was also observed. CONCLUSION: The result suggests that the shatavarins (containing Shatavarin IV) rich fraction (AR-2B) exhibits significant anticancer activity in both in vitro and in vivo experimental models.
Furostanol saponin and diphenylpentendiol from the roots of Asparagus racemosus.[Pubmed:22978214]
Nat Prod Commun. 2012 Aug;7(8):995-8.
A new furostanol steroidal saponin, shatavaroside C (1), and a new diphenylpentendiol, shatavarol (2), together with five known compounds, Shatavarin IV (3), racemoside A (4), beta-sitosterol (5) stigmasterol (6) and ursolic acid (7), have been isolated from the roots of Asparagus racemosus. This is the first report on the isolation of racemoside A (4) from roots of the plant. Structures of isolated compounds were determined on the basis of detailed analysis of their 1D, 2D NMR and mass spectral data.
Immunomodulatory activity of Asparagus racemosus on systemic Th1/Th2 immunity: implications for immunoadjuvant potential.[Pubmed:19038322]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2009 Jan 21;121(2):241-7.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Roots of Asparagus racemosus Willd (Shatavari in vernacular) are widely used in Ayurveda as Rasayana for immunostimulation, galactogogue as also in treatment of conditions like ulcers and cancer. Various studies have indicated immunomodulatory properties of Shatavari root extracts and formulations. AIM OF THE STUDY: To study the effect of standardized Asparagus racemosus root aqueous extract (ARE) on systemic Th1/Th2 immunity of SRBC sensitized animals. MATERIALS AND METHODS: We used HPTLC to quantify steroidal saponins (Shatavarin IV, Immunoside) and flow cytometry to study effects of ARE on Th1/Th2 immunity. SRBC specific antibody titres and DTH responses were also monitored as markers of Th2 and Th1 responses, respectively. We also studied lymphocyte proliferation. Cyclosporin, cyclophosphamide and levamisole were used as controls. RESULTS: Treatment with ARE (100mg/(kg b.w.p.o.)) resulted in significant increase of CD3(+) and CD4/CD8(+) percentages suggesting its effect on T cell activation. ARE treated animals showed significant up-regulation of Th1 (IL-2, IFN-g) and Th2 (IL-4) cytokines suggesting its mixed Th1/Th2 adjuvant activity. Consistent to this, ARE also showed higher antibody titres and DTH responses. ARE, in combination with LPS, Con A or SRBC, produced a significant proliferation suggesting effect on activated lymphocytes. CONCLUSION: The study suggests mixed Th1/Th2 activity of ARE supports its immunoadjuvant potential.
Steroidal saponins from the roots of Asparagus racemosus.[Pubmed:17936315]
Phytochemistry. 2008 Feb;69(3):796-804.
Five steroidal saponins, shatavarins VI-X, together with five known saponins, shatavarin I (or asparoside B), Shatavarin IV (or asparinin B), shatavarin V, immunoside and schidigerasaponin D5 (or asparanin A), have been isolated from the roots of Asparagus racemosus by RP-HPLC and characterized by spectroscopic (1D and 2D NMR experiments) and spectrometric (LCMS) methods.


