SU5416VEGF receptor inhibitor and AHR agonist CAS# 204005-46-9 |
- ZM323881
Catalog No.:BCC2073
CAS No.:193001-14-8
- Ki8751
Catalog No.:BCC1116
CAS No.:228559-41-9
- Pazopanib (GW-786034)
Catalog No.:BCC1286
CAS No.:444731-52-6
- Motesanib
Catalog No.:BCC1776
CAS No.:453562-69-1
- Nintedanib (BIBF 1120)
Catalog No.:BCC3661
CAS No.:656247-17-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 204005-46-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5329098 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C15H14N2O | M.Wt | 238.28 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Semaxinib;194413-58-6 | ||
| Solubility | DMF : ≥ 50 mg/mL (209.84 mM) DMSO : 22.5 mg/mL (94.43 mM; Need ultrasonic and warming) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
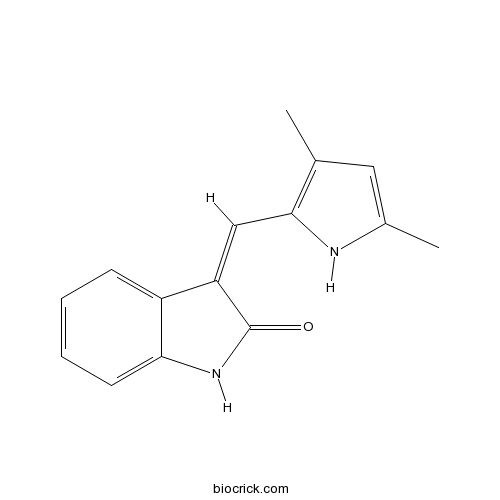
| Chemical Name | (3Z)-3-[(3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylidene]-1H-indol-2-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1=CC(=C(N1)C=C2C3=CC=CC=C3NC2=O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | WUWDLXZGHZSWQZ-WQLSENKSSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H14N2O/c1-9-7-10(2)16-14(9)8-12-11-5-3-4-6-13(11)17-15(12)18/h3-8,16H,1-2H3,(H,17,18)/b12-8- | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) that also inhibits other tyrosine kinases KIT, MET, FLT3 and RET. Displays no activity against EGFR, HER2, IGF1R and PDGFR. Inhibits tumor vascularization and growth of multiple tumor types. |

SU5416 Dilution Calculator

SU5416 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.1967 mL | 20.9837 mL | 41.9674 mL | 83.9349 mL | 104.9186 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8393 mL | 4.1967 mL | 8.3935 mL | 16.787 mL | 20.9837 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4197 mL | 2.0984 mL | 4.1967 mL | 8.3935 mL | 10.4919 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0839 mL | 0.4197 mL | 0.8393 mL | 1.6787 mL | 2.0984 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.042 mL | 0.2098 mL | 0.4197 mL | 0.8393 mL | 1.0492 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Description: SU5416 was found to inhibit VEGF-dependent phosphorylation of the Flk-1 receptor in Flk-1-overexpressing NIH 3T3 cells with an IC50 of 1.04±0.53 mM
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which stimulates vasculogenesis and angiogenesis, is able to create new blood vessels during embryonic development, new blood vessels after injury, muscle following exercise, and new vessels (collateral circulation) to bypass blocked vessels. Semaxanib (SU5416), a tyrosine-kinase inhibitor drug designed by SUGEN as a cancer therapeutic, is a potent and selective synthetic inhibitor of the Flk-1/KDR VEGF receptor tyrosine kinase demonstrating antiangiogenic effects.
Preclinical study: SU5416 was found to inhibit vascular endothelial growth factor-dependent mitogenesis of human endothelial cells. Moreover, systemic administration of SU5416 at nontoxic doses in mice resulted in the inhibition of subcutaneous tumor growth of cells derived from various tissue origins. The antitumor effect of SU5416 was accompanied by the appearance of pale white tumors, supporting its antiangiogenic property [1].
Another study showed that SU5416 was also an aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) agonist with unique properties. Like TCDD, SU5416 favors induction of indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase (IDO) in immunologically relevant populations such as dendritic cells in an AHR-dependent manner, leading to generation of regulatory T-cells in vitro. These characteristics lead us to suggest that SU5416 may be an ideal clinical agent for treatment of autoimmune diseases and prevention of transplant rejection, two areas where regulatory ligands of the AHR have shown promise [2].
Clinical trial: As an anticancer agent, SU5416 went as far as Phase III clinical trials, but showed poor results. Its clical termination is based on the results from a planned interim efficacy and safety analyses of a large phase III study of standard chemotherapy with or without SU5416 in the treatment of patients with advanced stage colorectal cancer, which shows that the study will not achieve the defined trial endpoints due to a lack of clinical benefit.
References:
[1] Fong TA, Shawver LK, Sun L, Tang C, App H, Powell TJ, Kim YH, Schreck R, Wang X, Risau W, Ullrich A, Hirth KP, McMahon G. SU5416 is a potent and selective inhibitor of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (Flk-1/KDR) that inhibits tyrosine kinase catalysis, tumor vascularization, and growth of multiple tumor types. Cancer Res. 1999;59(1):99-106.
[2] Mezrich JD, Nguyen LP, Kennedy G, Nukaya M, Fechner JH, Zhang X, Xing Y, Bradfield CA. SU5416, a VEGF receptor inhibitor and ligand of the AHR, represents a new alternative for immunomodulation. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e44547. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044547.
Semaxanib (SU5416) is a potent and selective VEGFR(Flk-1/KDR) inhibitor with IC50 of 1.23 μM, 20-fold more selective for VEGFR than PDGFRβ, lack of activity against EGFR, InsR and FGFR. Phase 3.
- Helioxanthin derivative 5-4-2
Catalog No.:BCC5414
CAS No.:203935-39-1
- Fmoc-ß-HoGlu(OtBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3234
CAS No.:203854-49-3
- MMAD
Catalog No.:BCC1774
CAS No.:203849-91-6
- 27-Hydroxycholesterol
Catalog No.:BCN2750
CAS No.:20380-11-4
- Istaroxime
Catalog No.:BCC1660
CAS No.:203737-93-3
- Arctiin
Catalog No.:BCN1090
CAS No.:20362-31-6
- Hastacine
Catalog No.:BCN2086
CAS No.:20361-77-7
- DMNB
Catalog No.:BCC7259
CAS No.:20357-25-9
- 2,4,6,6-Tetramethyl-3(6H)-pyridinone
Catalog No.:BCN4893
CAS No.:203524-64-5
- Brefeldin A
Catalog No.:BCC4387
CAS No.:20350-15-6
- (-)-Maackiain
Catalog No.:BCN4892
CAS No.:2035-15-6
- (+)-Bornyl acetate
Catalog No.:BCN8317
CAS No.:20347-65-3
- PD 176252
Catalog No.:BCC7426
CAS No.:204067-01-6
- (2-Aminoethyl)phosphonic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1762
CAS No.:2041-14-7
- Anabasamine
Catalog No.:BCN2148
CAS No.:20410-87-1
- 4'-Hydroxy-2-O-methylanigorufone
Catalog No.:BCN7179
CAS No.:204134-70-3
- Caesalmin E
Catalog No.:BCN7247
CAS No.:204185-91-1
- Boc-Ser-OH.H2O
Catalog No.:BCC2599
CAS No.:204191-40-2
- Oseltamivir phosphate
Catalog No.:BCC4690
CAS No.:204255-11-8
- RS 45041-190 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5682
CAS No.:204274-74-8
- NS 2028
Catalog No.:BCC6212
CAS No.:204326-43-2
- Fmoc-β-Homo-Phe-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2629
CAS No.:204384-69-0
- BCH
Catalog No.:BCC7993
CAS No.:20448-79-7
- Talnetant hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1982
CAS No.:204519-66-4
Detrimental Impact of Vasopressin V2 Receptor Antagonism in a SU5416/Hypoxia/Normoxia-Exposed Rat Model of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.[Pubmed:26924211]
Circ J. 2016;80(4):989-97.
BACKGROUND: The expression of vasopressin type 2 receptor (V2R) in the lung, and the long-term effects of tolvaptan, a selective V2R antagonist, on pulmonary circulation and right ventricular (RV) remodeling in a pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) rat model were evaluated. METHODS AND RESULTS: Six-week-old male Sprague-Dawley rats were injected subcutaneously with 20 mg/kg of SU5416 and were exposed to hypoxia for 3 weeks followed by re-exposure to normoxia for 7 weeks. These rats showed signs of RV failure and upregulation of V2R and cAMP in the lung tissue at 10 weeks after SU5416 injection. They were then treated with either 0.05% tolvaptan in diet (SUHx+Tolv) or normal diet (SUHx) during 5-10 weeks of SU5416 injection. Normal control rats (Cont) were also used for comparison. SUHx+Tolv had significantly higher pulmonary arterial pressure, more progressive pulmonary arterial remodeling, and more severe myocyte hypertrophy and interstitial myocardial fibrosis in the right ventricle compared with SUHx despite achieving successful preload reduction. CONCLUSIONS: Chronic vasopressin V2R antagonism may contribute to the worsening of PAH and the development of RV remodeling.
Complete radiological and metabolic response of metastatic renal cell carcinoma to SU5416 (semaxanib) in a patient with probable von Hippel-Lindau syndrome.[Pubmed:15271314]
Urol Oncol. 2004 May-Jun;22(3):193-6.
We report a case of a patient with probable von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) syndrome and metastatic renal cell cancer (RCC) who had a complete radiological and metabolic response to SU5416 (semaxanib). The patient was enrolled on a clinical study examining the efficacy of SU5416 in patients with metastatic cancer. Treatment with SU5416 was given at a dose of 145 mg/m2 intravenously twice-weekly for 11 doses. The patient achieved an early metabolic response on an F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) Positron Emission Tomographic (PET) scan within 2 weeks of therapy. Subsequent computerized tomography (CT) and PET scans (9 and 12 months after treatment, respectively) confirmed ongoing complete radiological and metabolic response. He remains tumor-free 18 months after treatment. This is the first documented report of metastatic RCC in the setting of presumed VHL syndrome responding to treatment with SU5416. While vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) inhibitors have been shown to produce a modest response in sporadic metastatic RCC, further studies utilizing VEGF inhibitors in patients with VHL syndrome and RCC warrants exploration.
A Phase I study of the angiogenesis inhibitor SU5416 (semaxanib) in solid tumours, incorporating dynamic contrast MR pharmacodynamic end points.[Pubmed:16222321]
Br J Cancer. 2005 Oct 17;93(8):876-83.
SU5416 (Z-3-[(2,4-dimethylpyrrol-5-yl)methylidenyl]-2-indolinone; semaxanib) is a small molecule inhibitor of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR2). A Phase I dose escalation study was performed. Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) was used as a pharmacodynamic assessment tool. In all, 27 patients were recruited. SU5416 was administered twice weekly by fixed rate intravenous infusion. Patients were treated in sequential cohorts of three patients at 48, 65, 85 110 and 145 mg m-2. A further dose level of 190 mg m-2 after a 2-week lead in period at a lower dose was completed; thereafter, the cohort at 145 mg m-2 was expanded. SU5416 showed linear pharmacokinetics to 145 mg m-2 with a large volume of distribution and rapid clearance. A significant degree of interpatient variability was seen. SU5416 was well tolerated, by definition a maximum-tolerated dose was not defined. No reproducible changes were seen in DCE-MRI end points. Serial assessments of VEGF in a cohort of patients treated at 145 mg m-2 did not show a statistically significant treatment-related change. Parallel assessments of the impact of SU5416 on coagulation profiles in six patients showed a transient effect within the fibrinolytic pathway. Clinical experience showed that patients who had breaks of therapy longer than a week could not have treatment reinitiated at a dose of 190 mg m-2 without unacceptable toxicity. The 145 mg m-2 dose level is thus the recommended dose for future study.
A phase I dose escalation and pharmacodynamic study of SU5416 (semaxanib) combined with weekly cisplatin and irinotecan in patients with advanced solid tumors.[Pubmed:24192770]
Onkologie. 2013;36(11):657-60.
BACKGROUND: This phase I study evaluated the safety of SU5416, a potent and selective inhibitor of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor tyrosine kinase Flk-1, in combination with weekly cisplatin and irinotecan in patients with advanced solid tumors. METHODS: The patients received cisplatin 30 mg/m(2) and irinotecan 50 mg/m(2) weekly from week 1 to week 4, with SU5416 at either 65 mg/m(2) (dose level (DL)1) or 85 mg/m(2) (DL2) twice weekly for 6 weeks (1 cycle). Serial (1)(8)fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography ((1)(8)FDG-PET) and (1)(5)O-H(2)O-PET scans were obtained. RESULTS: 13 patients were treated (7 on DL1, 6 on DL2); 7 patients completed at least 1 cycle of treatment. 3 patients experienced dose-limiting toxicity (DLT) at DL2 (grade 3 neutropenia and grade 3 thrombocytopenia causing treatment delay, grade 3 nausea/vomiting). No objective responses were observed at DL1, which was determined to be the maximum tolerated dose (MTD). 1 partial response (PR) was observed at DL2. (1)(8)FDG-PET responses were documented but did not predict response according to the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST). CONCLUSIONS: SU5416 at 65 mg/m(2) twice weekly combined with cisplatin and irinotecan weekly for 4 of 6 weeks is well tolerated but without evidence of clinical activity. (1)(8)FDG-PET may be a useful pharmacodynamic marker of SU5416 bioactivity but requires additional development.
Pneumonectomy combined with SU5416 induces severe pulmonary hypertension in rats.[Pubmed:27036867]
Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2016 Jun 1;310(11):L1088-97.
The SU5416 + hypoxia (SuHx) rat model is a commonly used model of severe pulmonary arterial hypertension. While it is known that exposure to hypoxia can be replaced by another type of hit (e.g., ovalbumin sensitization) it is unknown whether abnormal pulmonary blood flow (PBF), which has long been known to invoke pathological changes in the pulmonary vasculature, can replace the hypoxic exposure. Here we studied if a combination of SU5416 administration combined with pneumonectomy (PNx), to induce abnormal PBF in the contralateral lung, is sufficient to induce severe pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) in rats. Sprague Dawley rats were subjected to SuPNx protocol (SU5416 + combined with left pneumonectomy) or standard SuHx protocol, and comparisons between models were made at week 2 and 6 postinitiation. Both SuHx and SuPNx models displayed extensive obliterative vascular remodeling leading to an increased right ventricular systolic pressure at week 6 Similar inflammatory response in the lung vasculature of both models was observed alongside increased endothelial cell proliferation and apoptosis. This study describes the SuPNx model, which features severe PAH at 6 wk and could serve as an alternative to the SuHx model. Our study, together with previous studies on experimental models of pulmonary hypertension, shows that the typical histopathological findings of PAH, including obliterative lesions, inflammation, increased cell turnover, and ongoing apoptosis, represent a final common pathway of a disease that can evolve as a consequence of a variety of insults to the lung vasculature.
Mechanisms of SU5416, an inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor, as a radiosensitizer for colon cancer cells.[Pubmed:27373272]
Oncol Rep. 2016 Aug;36(2):763-70.
Colorectal cancer is one of the most common cancers worldwide. Previous studies suggest that chemoradiotherapy is more effective for the treatment of colorectal cancer than is radiotherapy or chemotherapy alone. To enhance the radiosensitivity of tumor cells, several investigators have used targeted therapeutic agents that act as radiosensitizers. In the present study, we provide a scientific rationale for the clinical application of SU5416, an inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2, as a radiosensitizer for colorectal cancer. Two human colorectal adenocarcinoma cell lines, HCT116 and HT-29, were treated with SU5416 and radiation alone or radiation followed by SU5416. In vitro tests were performed using colony forming assays, flow cytometric analysis, immunohistochemistry, senescence-associated beta-galactosidase, tumor cell motility and invasion assays. The combination of radiation and SU5416 synergistically inhibited cell survival and induced apoptosis through reactive oxygen species, enhanced IR-induced premature senescence, and inhibited DNA repair activity, cell migration and invasion. Collectively, our results favor the use of SU5416 and radiotherapy as a combination therapy for the treatment of colon cancer and it can be combined successfully with a radiation regimen to potentiate its antitumor and antimetastatic activities for future clinical trials.
A Phase I study of escalating doses of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor semaxanib (SU5416) in combination with irinotecan in patients with advanced colorectal carcinoma.[Pubmed:16449240]
Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2006 Feb;36(2):100-3.
BACKGROUND: One of the most studied pro-angiogenic factors involved in the development of colorectal cancer is the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). The small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitor semaxanib (SU5416) is one of the several agents targeting the VEGF signaling pathway, and its development centered mostly in the treatment of colorectal cancer. METHODS: We designed and conducted an NCI-sponsored trial to determine the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) and dose-limiting toxicities (DLTs) of semaxanib given twice weekly in combination with weekly irinotecan in patients with advanced colorectal cancer who had failed at least one prior treatment. The irinotecan dose was fixed at 125 mg/m(2) given weekly for 4 weeks followed by 2 weeks of rest. Patients with prior pelvic irradiation received a reduced dose of 100 mg/m(2). The semaxanib dose was escalated, going from 85 to 110 mg/m(2) and finally to 145 mg/m(2). RESULTS: Ten patients were treated in our study and all were evaluable for toxicity. There were no drug-related Grade 4 toxicities. There was one episode of Grade 3 headache and one episode of Grade 3 vomiting. The most common Grades 1 and 2 toxicities included diarrhea, abdominal cramping, anemia and nausea. Nine patients completed at least one 6 week cycle of treatment and were considered evaluable for response. Among those nine, two had a partial response, three had stable disease and four had progressive disease after the first cycle. CONCLUSIONS: Both irinotecan and semaxanib could be given at their full single-agent recommended doses without significant toxicity, and the combination showed signs of clinical activity. However, owing to discouraging results from Phase III trials, it is unlikely that this combination will be further explored.
Mechanisms for SU5416 as a radiosensitizer of endothelial cells.[Pubmed:26314590]
Int J Oncol. 2015 Oct;47(4):1440-50.
Endothelial cells (ECs), that comprise the tumor vasculature, are critical targets for anticancer radiotherapy. The aim of this work was to study the mechanism by which SU5416, a known anti-angiogenesis inhibitor, modifies the radiation responses of human vascular ECs. Two human endothelial cell lines (HUVEC and 2H11) were treated with SU5416 alone, radiation alone, or a combination of both. In vitro tests were performed using colony forming assays, FACS analysis, western blotting, immunohistochemistry, migration assay, invasion assays and endothelial tube formation assays. The combination of radiation and SU5416 significantly inhibited cell survival, the repair of radiation-induced DNA damage, and induced apoptosis. It also caused cell cycle arrest, inhibited cell migration and invasion, and suppressed angiogenesis. In this study, our results first provide a scientific rationale to combine SU5416 with radiotherapy to target ECs and suggest its clinical application in combination cancer treatment with radiotherapy.
Inhibition of RET tyrosine kinase by SU5416.[Pubmed:17032739]
J Mol Endocrinol. 2006 Oct;37(2):199-212.
Thyroid neoplasia is frequently associated with rearranged during transfection (RET) proto-oncogene mutations that cause hyperactivation of RET kinase activity. Selective inhibition of RET-mediated signaling should lead to an efficacious therapy. SU5416 is a potent inhibitor of vascular endothelial cell growth factor receptor, c-Kit, and FLT-3 receptor tyrosine kinases presently used in clinical trials. We found that SU5416 inhibits RET with similar potency, both in cell-free assays and in cells, thus causing proliferation arrest in oncogenic RET-transfected cells and in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) cells expressing the RET/PTC1 oncogene, but not in RET-negative control cells. SU5416 inhibited RET-mediated signaling through the extracellular signal regulated kinase (ERK) and JNK pathways. In addition, we show that a naturally occurring MEN2 mutation at codon 804 confers resistance to SU5416, but not to the related compound SU4984. We provide a possible explanation to these results by using molecular docking. Finally, SU5416 was also assessed against an array of 52 tyrosine and serine/threonine kinases.
The antiangiogenic protein kinase inhibitors SU5416 and SU6668 inhibit the SCF receptor (c-kit) in a human myeloid leukemia cell line and in acute myeloid leukemia blasts.[Pubmed:11222388]
Blood. 2001 Mar 1;97(5):1413-21.
SU5416 and SU6668 are potent antiangiogenic small-molecule inhibitors of receptor tyrosine kinases, including those of the vascular endothelial growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor receptor families. The stem cell factor (SCF) receptor, c-kit, is structurally related to these receptors and, although not expressed on mature peripheral blood cells, is expressed in leukemic blasts derived from 60% to 80% of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients. The c-kit kinase inhibitory activity of SU5416 and SU6668 was evaluated in MO7E cells, a human myeloid leukemia cell line. Tyrosine autophosphorylation of the receptor, induced by SCF, was inhibited in these cells by SU5416 and SU6668 in a dose-dependent manner (inhibitory concentration of 50% [IC(50)] 0.1-1 microM). Inhibition of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) phosphorylation, a signaling event downstream of c-kit activation, was also inhibited in a dose-dependent manner. Both compounds also inhibited SCF-induced proliferation of MO7E cells (IC(50) 0.1 microM for SU5416; 0.29 microM for SU6668). Furthermore, both SU5416 and SU6668 induced apoptosis in a dose- and time-dependent manner as measured by the increase in activated caspase-3 and the enhanced cleavage of its substrate poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. These findings with MO7E cells were extended to leukemic blasts from c-kit(+) patients. In patient blasts, both SU5416 and SU6668 inhibited SCF-induced phosphorylation of c-kit and ERK1/2 and induced apoptosis. These studies indicate that SU5416 and SU6668 inhibit biologic functions of c-kit in addition to exhibiting antiangiogenic properties and suggest that the combination of these activities may provide a novel therapeutic approach for the treatment of AML.
SU5416 is a potent and selective inhibitor of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (Flk-1/KDR) that inhibits tyrosine kinase catalysis, tumor vascularization, and growth of multiple tumor types.[Pubmed:9892193]
Cancer Res. 1999 Jan 1;59(1):99-106.
SU5416, a novel synthetic compound, is a potent and selective inhibitor of the Flk-1/KDR receptor tyrosine kinase that is presently under evaluation in Phase I clinical studies for the treatment of human cancers. SU5416 was shown to inhibit vascular endothelial growth factor-dependent mitogenesis of human endothelial cells without inhibiting the growth of a variety of tumor cells in vitro. In contrast, systemic administration of SU5416 at nontoxic doses in mice resulted in inhibition of subcutaneous tumor growth of cells derived from various tissue origins. The antitumor effect of SU5416 was accompanied by the appearance of pale white tumors that were resected from drug-treated animals, supporting the antiangiogenic property of this agent. These findings support that pharmacological inhibition of the enzymatic activity of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor represents a novel strategy for limiting the growth of a wide variety of tumor types.


