ArctiinCAS# 20362-31-6 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 20362-31-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 330034 | Appearance | White powder |
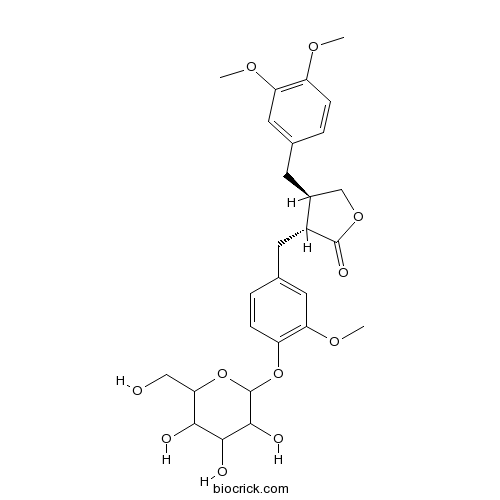
| Formula | C27H34O11 | M.Wt | 534.55 |
| Type of Compound | Lignans | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Arctii; NSC 315527; Arctigenin-4-glucoside | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 250 mg/mL (467.68 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
| Chemical Name | (3R,4R)-4-[(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)methyl]-3-[[3-methoxy-4-[3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxyphenyl]methyl]oxolan-2-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C=C(C=C1)CC2COC(=O)C2CC3=CC(=C(C=C3)OC4C(C(C(C(O4)CO)O)O)O)OC)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | XOJVHLIYNSOZOO-RVDKUWPISA-N | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Arctiin(NSC 315527), a plant lignan that can be extracted from the Arctium lappa (burdock) seeds, is a possible environmental endocrine disruptor compounds and have been shown to influence sex hormone metabolism as well as protein synthesis, steroid biosynthesis. Arctiin has been reported to have preventing obesity, antibacterial, antiviral, anti-inflammatory, and anti-oxidant effects in vitro. Arctiin inhibits adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes through the inhibition of PPARγ and C/EBPα and the activation of AMPK signaling pathways. Arctiin also has a protective effect on ROS-induced cell dysfunction in HHDPCs and may therefore be useful for alopecia prevention and treatment strategies. |
| Targets | PPAR | Fatty Acid Synthase | AMPK | ROS | MAPK | TNF-α | IL Receptor | p65 | NF-kB | IkB | PGE | NO | IKK |
| In vitro | Arctiin blocks hydrogen peroxide-induced senescence and cell death though microRNA expression changes in human dermal papilla cells.[Pubmed: 25299961]Biol Res. 2014 Sep 30;47(1):50.Accumulating evidence indicates that reactive oxygen species (ROS) are an important etiological factor for the induction of dermal papilla cell senescence and hair loss, which is also known alopecia. Arctiin is an active lignin isolated from Arctium lappa and has anti-inflammation, anti-microbial, and anti-carcinogenic effects. In the present study, we found that Arctiin exerts anti-oxidative effects on human hair dermal papilla cells (HHDPCs).
|
| In vivo | Arctiin inhibits adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells and decreases adiposity and body weight in mice fed a high-fat diet.[Pubmed: 25489405]Nutr Res Pract. 2014 Dec;8(6):655-61.The purpose of this study was to examine the effects and associated mechanisms of Arctiin, a lignan compound found in burdock, on adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells. Also, the effects of Arctiin supplementation in obese mice fed a high-fat diet on adiposity were examined.
|
| Kinase Assay | Anti-inflammatory function of arctiin by inhibiting COX-2 expression via NF-κB pathways.[Pubmed: 21733191 ]J Inflamm (Lond). 2011 Jul 7;8(1):16.Arctiin, isolated from Forsythia suspensa has been reported to have anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, antibacterial, and antiviral effects in vitro. However, there has been a lack of studies regarding its effects on immunological activity. The aim of this study is to investigate the anti-inflammatory potential and possible mechanisms of Arctiin in LPS-induced macrophages.
|
| Cell Research | Arctiin induces cell growth inhibition through the down-regulation of cyclin D1 expression.[Pubmed: 18288407]Photoprotective effect of arctiin against ultraviolet B-induced damage in HaCaT keratinocytes is mediated by microRNA expression changes.[Pubmed: 24926940]Mol Med Rep. 2014 Sep;10(3):1363-70.Human keratinocytes are located in the outermost skin layer and thus particularly vulnerable to ultraviolet B (UVB) radiation exposure. Previous studies have focused on the cellular and molecular perspectives of UVB-induced keratinocyte damage.
Oncol Rep. 2008 Mar;19(3):721-7.Arctiin is a major lignan constituent of Arctium lappa and has anti-cancer properties in animal models. It was recently reported that Arctiin induces growth inhibition in human prostate cancer PC-3 cells. However, the growth inhibitory mechanism of Arctiin remains unknown.
|
| Animal Research | Arctigenin but not arctiin acts as the major effective constituent of Arctium lappa L. fruit for attenuating colonic inflammatory response induced by dextran sulfate sodium in mice.[Pubmed: 25284342]Int Immunopharmacol. 2014 Dec;23(2):505-15.The crude powder of the fruit of Arctium lappa L. (ALF) has previously been reported to attenuate experimental colitis in mice. But, its main effective ingredient and underlying mechanisms remain to be identified. In this study, ALF was extracted with ethanol, and then successively fractionated into petroleum ether, ethyl acetate, n-butanol and water fraction.
|

Arctiin Dilution Calculator

Arctiin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8707 mL | 9.3537 mL | 18.7073 mL | 37.4146 mL | 46.7683 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3741 mL | 1.8707 mL | 3.7415 mL | 7.4829 mL | 9.3537 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1871 mL | 0.9354 mL | 1.8707 mL | 3.7415 mL | 4.6768 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0374 mL | 0.1871 mL | 0.3741 mL | 0.7483 mL | 0.9354 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0187 mL | 0.0935 mL | 0.1871 mL | 0.3741 mL | 0.4677 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Arctiin(NSC 315527), a plant lignan that can be extracted from the Arctium lappa (burdock) seeds, is a possible environmental endocrine disruptor compounds and have been shown to influence sex hormone metabolism as well as protein synthesis, steroid biosynthesis. IC50 Value: Target: Others in vitro: Treatment of PC-3 cells with arctiin decreased the cell number in a concentration- and time-dependent manner in serum-containing condition. Arctiin preferentially induced cell detachment, but did not have anti-proliferation or cytotoxic effects in PC-3 cells. The arctiin-induced effect was inhibited by cycloheximide, indicating that protein synthesis was required [1]. Although arctiin, the active component of AL that has been described in the literature, was not able to reduce degranulation in RBL-2H3 cells, a single high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) fraction from the AL extract inhibited beta-hexosaminidase release (IC(50) = 22.2 microg/ml) [2]. The growth inhibition caused by arctiin is associated with the down-regulation of cyclin D1 protein expression. Furthermore, thearctiin-induced suppression of cyclin D1 protein expression occurs in various types of human tumor cells, including osteosarcoma, lung, colorectal, cervical and breast cancer, melanoma, transformed renal cells and prostate cancer. Depletion of the cyclin D1 protein using small interfering RNA-rendered human breast cancer MCF-7 cells insensitive to the growth inhibitory effects of arctiin, implicates cyclin D1 as an important target of arctiin [6]. in vivo: Histopathological evaluation of prostate revealed that all the rats in any group developed adenocarcinoma in dorsolateral lobe of prostate, except two rats in 0.1% arctiin treated and one rat in 0.002% arctiin treated groups without prostate adenocarcinoma development [3]. After oral administration of arctiin (30, 60, 120 mg/kgd) for three weeks, the levels of serum creatinine (Scr) and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and 24-h urine protein content markedly decreased, while endogenous creatinine clearance rate (ECcr) significantly increased [4]. STZ-induced diabetic rats were treated witharctiin at the dosage of 60 or 40 mg/kg/day via intraperitoneal injection for 8 weeks. Blood glucose and 24-h urinary albumin content were measured, and kidney histopathological changes were monitored [5].
References:
[1]. Huang DM, et al. Modulation of anti-adhesion molecule MUC-1 is associated with arctiin-induced growth inhibition in PC-3 cells. Prostate. 2004 May 15;59(3):260-7.
[2]. Knipping K, et al. In vitro and in vivo anti-allergic effects of Arctium lappa L. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2008 Nov;233(11):1469-77.
[3]. Zeng Y, et al. Lack of significant modifying effect of arctiin on prostate carcinogenesis in probasin/SV40 T antigen transgenic rats. Cancer Lett. 2005 May 26;222(2):145-51.
[4]. Wu JG, et al. Ameliorative effects of arctiin from Arctium lappa on experimental glomerulonephritis in rats. Phytomedicine. 2009 Nov;16(11):1033-41.
[5]. Ma ST, et al. Effect of arctiin on glomerular filtration barrier damage in STZ-induced diabetic nephropathy rats. Phytother Res. 2013 Oct;27(10):1474-80.
[6]. Matsuzaki Y, et al. Arctiin induces cell growth inhibition through the down-regulation of cyclin D1 expression. Oncol Rep. 2008 Mar;19(3):721-7.
- Hastacine
Catalog No.:BCN2086
CAS No.:20361-77-7
- DMNB
Catalog No.:BCC7259
CAS No.:20357-25-9
- 2,4,6,6-Tetramethyl-3(6H)-pyridinone
Catalog No.:BCN4893
CAS No.:203524-64-5
- Brefeldin A
Catalog No.:BCC4387
CAS No.:20350-15-6
- (-)-Maackiain
Catalog No.:BCN4892
CAS No.:2035-15-6
- (+)-Bornyl acetate
Catalog No.:BCN8317
CAS No.:20347-65-3
- SNX 482
Catalog No.:BCC5952
CAS No.:203460-30-4
- 18-Norabieta-8,11,13-triene-4,15-diol
Catalog No.:BCN1504
CAS No.:203455-81-6
- Luteollin 5-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN5391
CAS No.:20344-46-1
- 7-Oxo-beta-sitosterol
Catalog No.:BCN4891
CAS No.:2034-74-4
- Daphnoretin
Catalog No.:BCN2473
CAS No.:2034-69-7
- H-D-Arg-NH2.2HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2870
CAS No.:203308-91-2
- Istaroxime
Catalog No.:BCC1660
CAS No.:203737-93-3
- 27-Hydroxycholesterol
Catalog No.:BCN2750
CAS No.:20380-11-4
- MMAD
Catalog No.:BCC1774
CAS No.:203849-91-6
- Fmoc-ß-HoGlu(OtBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3234
CAS No.:203854-49-3
- Helioxanthin derivative 5-4-2
Catalog No.:BCC5414
CAS No.:203935-39-1
- SU5416
Catalog No.:BCC1974
CAS No.:204005-46-9
- PD 176252
Catalog No.:BCC7426
CAS No.:204067-01-6
- (2-Aminoethyl)phosphonic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1762
CAS No.:2041-14-7
- Anabasamine
Catalog No.:BCN2148
CAS No.:20410-87-1
- 4'-Hydroxy-2-O-methylanigorufone
Catalog No.:BCN7179
CAS No.:204134-70-3
- Caesalmin E
Catalog No.:BCN7247
CAS No.:204185-91-1
- Boc-Ser-OH.H2O
Catalog No.:BCC2599
CAS No.:204191-40-2
Arctiin induces cell growth inhibition through the down-regulation of cyclin D1 expression.[Pubmed:18288407]
Oncol Rep. 2008 Mar;19(3):721-7.
Arctiin is a major lignan constituent of Arctium lappa and has anti-cancer properties in animal models. It was recently reported that Arctiin induces growth inhibition in human prostate cancer PC-3 cells. However, the growth inhibitory mechanism of Arctiin remains unknown. Herein we report that Arctiin induces growth inhibition and dephosphorylates the tumor-suppressor retinoblastoma protein in human immortalized keratinocyte HaCaT cells. We also show that the growth inhibition caused by Arctiin is associated with the down-regulation of cyclin D1 protein expression. Furthermore, the Arctiin-induced suppression of cyclin D1 protein expression occurs in various types of human tumor cells, including osteosarcoma, lung, colorectal, cervical and breast cancer, melanoma, transformed renal cells and prostate cancer. Depletion of the cyclin D1 protein using small interfering RNA-rendered human breast cancer MCF-7 cells insensitive to the growth inhibitory effects of Arctiin, implicates cyclin D1 as an important target of Arctiin. Taken together, these results suggest that Arctiin down-regulates cyclin D1 protein expression and that this at least partially contributes to the anti-proliferative effect of Arctiin.
Arctiin inhibits adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells and decreases adiposity and body weight in mice fed a high-fat diet.[Pubmed:25489405]
Nutr Res Pract. 2014 Dec;8(6):655-61.
BACKGROUND/OBJECTIVES: The purpose of this study was to examine the effects and associated mechanisms of Arctiin, a lignan compound found in burdock, on adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells. Also, the effects of Arctiin supplementation in obese mice fed a high-fat diet on adiposity were examined. MATERIALS/METHODS: 3T3-L1 cells were treated with Arctiin (12.5 to 100 microM) during differentiation for 8 days. The accumulation of lipid droplets was determined by Oil Red O staining and intracellular triglyceride contents. The expressions of genes related to adipogenesis were measured by real-time RT-PCR and Western blot analyses. For in vivo study, C57BL/6J mice were first fed either a control diet (CON) or high-fat diet (HF) to induce obesity, and then fed CON, HF, or HF with 500 mg/kg BW Arctiin (HF + AC) for four weeks. RESULTS: Arctiin treatment to 3T3-L1 pre-adipocytes markedly decreased adipogenesis in a dose-dependent manner. The Arctiin treatment significantly decreased the protein levels of the key adipogenic regulators PPARgamma and C/EBPalpha, and also significantly inhibited the expression of SREBP-1c, fatty acid synthase, fatty acid-binding protein and lipoprotein lipase. Also, Arctiin greatly increased the phosphorylation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and its downstream target phosphorylated-acetyl CoA carboxylase. Furthermore, administration of Arctiin significantly decreased the body weight in obese mice fed with the high-fat diet. The epididymal, perirenal or total visceral adipose tissue weights of mice were all significantly lower in the HF + AC than in the HF. Arctiin administration also decreased the sizes of lipid droplets in the epididymal adipose tissue. CONCLUSIONS: Arctiin inhibited adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes through the inhibition of PPARgamma and C/EBPalpha and the activation of AMPK signaling pathways. These findings suggest that Arctiin has a potential benefit in preventing obesity.
Arctigenin but not arctiin acts as the major effective constituent of Arctium lappa L. fruit for attenuating colonic inflammatory response induced by dextran sulfate sodium in mice.[Pubmed:25284342]
Int Immunopharmacol. 2014 Dec;23(2):505-15.
The crude powder of the fruit of Arctium lappa L. (ALF) has previously been reported to attenuate experimental colitis in mice. But, its main effective ingredient and underlying mechanisms remain to be identified. In this study, ALF was extracted with ethanol, and then successively fractionated into petroleum ether, ethyl acetate, n-butanol and water fraction. Experimental colitis was induced by dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) in mice. Among the four fractions of ALF, the ethyl acetate fraction showed the most significant inhibition of DSS-induced colitis in mice. The comparative studies of arctigenin and Arctiin (the two main ingredients of ethyl acetate fraction) indicated that arctigenin rather than Arctiin could reduce the loss of body weight, disease activity index and histological damage in the colon. Arctigenin markedly recovered the loss of intestinal epithelial cells (E-cadherin-positive cells) and decreased the infiltration of neutrophils (MPO-positive cells) and macrophages (CD68-positive cells). Arctigenin could down-regulate the expressions of TNF-alpha, IL-6, MIP-2, MCP-1, MAdCAM-1, ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 at both protein and mRNA levels in colonic tissues. Also, it markedly decreased the MDA level, but increased SOD activity and the GSH level. Of note, the efficacy of arctigenin was comparable or even superior to that of the positive control mesalazine. Moreover, it significantly suppressed the phosphorylation of MAPKs and the activation of NF-kappaB, including phosphorylation of IkappaBalpha and p65, p65 translocation and DNA binding activity. In conclusion, arctigenin but not Arctiin is the main active ingredient of ALF for attenuating colitis via down-regulating the activation of MAPK and NF-kappaB pathways.
Photoprotective effect of arctiin against ultraviolet B-induced damage in HaCaT keratinocytes is mediated by microRNA expression changes.[Pubmed:24926940]
Mol Med Rep. 2014 Sep;10(3):1363-70.
Human keratinocytes are located in the outermost skin layer and thus particularly vulnerable to ultraviolet B (UVB) radiation exposure. Previous studies have focused on the cellular and molecular perspectives of UVB-induced keratinocyte damage. In the present study, it was demonstrated that pretreatment with the phytochemical Arctiin, one of the lignin compounds, protects human HaCaT keratinocytes from UVB-mediated damage. Biochemical assays revealed that UVB-induced cytotoxicity and cell death were significantly reduced in Arctiin-pretreated HaCaT cells. In addition, Arctiin promoted the wound healing and DNA repair properties of keratinocytes. The photoprotective effects of Arctiin were associated with changes in the expression levels of specific microRNAs (miRNAs) in HaCaT cells. A bioinformatics analysis demonstrated that the miRNAs were functionally involved in cancer, cell cycle, and Wnt and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways. In the present study, the results from the cellular and molecular assays demonstrated a novel role for Arctiin in UVB protection in keratinocytes, which is mediated by miRNA responses and the suppression of UVB-induced cell death. Furthermore, Arctiin is implicated as a potential chemopreventive agent through UVB protection of keratinocytes.
Anti-inflammatory function of arctiin by inhibiting COX-2 expression via NF-kappaB pathways.[Pubmed:21733191]
J Inflamm (Lond). 2011 Jul 7;8(1):16.
BACKGROUND: Arctiin, isolated from Forsythia suspensa has been reported to have anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, antibacterial, and antiviral effects in vitro. However, there has been a lack of studies regarding its effects on immunological activity. The aim of this study is to investigate the anti-inflammatory potential and possible mechanisms of Arctiin in LPS-induced macrophages. METHODS: We investigated the mRNA and protein levels of proinflammatory cytokines through RT-PCR and western blot analysis, followed by a FACS analysis for surface molecule changes. RESULTS: Arctiin dose dependently decreased the production of NO and proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-1beta, IL-6, TNF-alpha, and PGE2, and it reduced the gene and protein levels as determined by RT-PCR and western blot analysis, respectively. The expression of co-stimulatory molecules such as B7-1 and B7-2 were also inhibited by Arctiin. Furthermore, the activation of the nuclear transcription factor, NF-kappaB in macrophages was inhibited by Arctiin. CONCLUSION: Taken together these results provide evidence of the bioactivity of Arctiin in inflammatory diseases and suggest that Arctiin may exert anti-inflammatory effect by inhibiting the pro-inflammatory mediators through the inactivation of NF-kB.
Arctiin blocks hydrogen peroxide-induced senescence and cell death though microRNA expression changes in human dermal papilla cells.[Pubmed:25299961]
Biol Res. 2014 Sep 30;47:50.
BACKGROUND: Accumulating evidence indicates that reactive oxygen species (ROS) are an important etiological factor for the induction of dermal papilla cell senescence and hair loss, which is also known alopecia. Arctiin is an active lignin isolated from Arctium lappa and has anti-inflammation, anti-microbial, and anti-carcinogenic effects. In the present study, we found that Arctiin exerts anti-oxidative effects on human hair dermal papilla cells (HHDPCs). RESULTS: To better understand the mechanism, we analyzed the level of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-induced cytotoxicity, cell death, ROS production and senescence after Arctiin pretreatment of HHDPCs. The results showed that Arctiin pretreatment significantly inhibited the H2O2-induced reduction in cell viability. Moreover, H2O2-induced sub-G1 phase accumulation and G2 cell cycle arrest were also downregulated by Arctiin pretreatment. Interestingly, the increase in intracellular ROS mediated by H2O2 was drastically decreased in HHDPCs cultured in the presence of Arctiin. This effect was confirmed by senescence associated-beta galactosidase (SA-beta-gal) assay results; we found that Arctiin pretreatment impaired H2O2-induced senescence in HHDPCs. Using microRNA (miRNA) microarray and bioinformatic analysis, we showed that this anti-oxidative effect of Arctiin in HHDPCs was related with mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and Wnt signaling pathways. CONCLUSIONS: Taken together, our data suggest that Arctiin has a protective effect on ROS-induced cell dysfunction in HHDPCs and may therefore be useful for alopecia prevention and treatment strategies.


