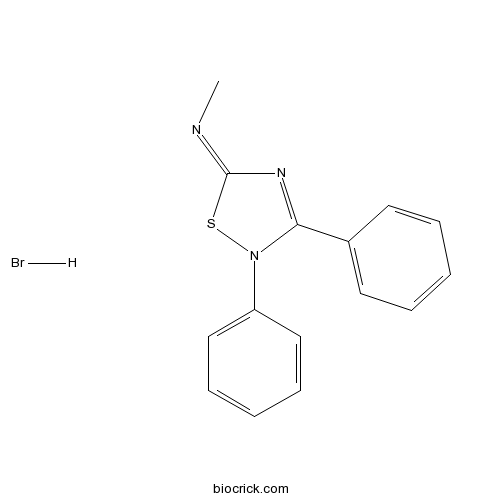
SCH 202676 hydrobromideInhibitor of ligand binding to G-protein-coupled receptors CAS# 265980-25-4 |
- MLN8237 (Alisertib)
Catalog No.:BCC2166
CAS No.:1028486-01-2
- VX-680 (MK-0457,Tozasertib)
Catalog No.:BCC2167
CAS No.:639089-54-6
- Reversine
Catalog No.:BCC1892
CAS No.:656820-32-5
- AZD1152
Catalog No.:BCC1393
CAS No.:722543-31-9
- XL228
Catalog No.:BCC2058
CAS No.:898280-07-4
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 265980-25-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 11957689 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C15H14BrN3S | M.Wt | 348.26 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 25 mM in DMSO with gentle warming | ||
| Chemical Name | N-methyl-2,3-diphenyl-1,2,4-thiadiazol-5-imine;hydrobromide | ||
| SMILES | CN=C1N=C(N(S1)C2=CC=CC=C2)C3=CC=CC=C3.Br | ||
| Standard InChIKey | YJYGOWVFDGULLL-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H13N3S.BrH/c1-16-15-17-14(12-8-4-2-5-9-12)18(19-15)13-10-6-3-7-11-13;/h2-11H,1H3;1H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Sulphydryl-reactive compound that inhibits agonist and antagonist binding to G-protein-coupled receptors. Inhibits a variety of GPCRs including adenosine, opioid, muscarinic, adrenergic and dopaminergic receptors (IC50 values are 0.1-1.8 μM). |

SCH 202676 hydrobromide Dilution Calculator

SCH 202676 hydrobromide Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8714 mL | 14.3571 mL | 28.7142 mL | 57.4284 mL | 71.7854 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5743 mL | 2.8714 mL | 5.7428 mL | 11.4857 mL | 14.3571 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2871 mL | 1.4357 mL | 2.8714 mL | 5.7428 mL | 7.1785 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0574 mL | 0.2871 mL | 0.5743 mL | 1.1486 mL | 1.4357 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0287 mL | 0.1436 mL | 0.2871 mL | 0.5743 mL | 0.7179 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Crenatine
Catalog No.:BCN5148
CAS No.:26585-14-8
- Dehydrocrenatine
Catalog No.:BCN5147
CAS No.:26585-13-7
- Harmalacidine
Catalog No.:BCN8033
CAS No.:26579-69-1
- 5-Acetoacetlamino benzimdazolone
Catalog No.:BCC8725
CAS No.:26576-46-5
- Alisol B 23-acetate
Catalog No.:BCN1243
CAS No.:26575-95-1
- Alisol C monoacetate
Catalog No.:BCN2345
CAS No.:26575-93-9
- Z-D-Glu-OMe
Catalog No.:BCC2773
CAS No.:26566-11-0
- 3-Hydroxycatalponol
Catalog No.:BCN5146
CAS No.:265644-24-4
- 2,3-Dihydroxy-12-oleanen-28-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5145
CAS No.:26563-68-8
- 8-Phenyloctanoic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8790
CAS No.:26547-51-3
- Apiin
Catalog No.:BCN2311
CAS No.:26544-34-3
- (-)-Hinokinin
Catalog No.:BCN3227
CAS No.:26543-89-5
- Z-D-Ala-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3059
CAS No.:26607-51-2
- 3-Ethoxyandrosta-3,5-dien-17β-ol
Catalog No.:BCC8631
CAS No.:26614-48-2
- Zotepine
Catalog No.:BCC7838
CAS No.:26615-21-4
- Fmoc-β-Homo-Met-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2630
CAS No.:266359-48-2
- Reparixin
Catalog No.:BCC1885
CAS No.:266359-83-5
- Reparixin L-lysine salt
Catalog No.:BCC1886
CAS No.:266359-93-7
- Conodurine
Catalog No.:BCN7463
CAS No.:2665-57-8
- Salirepin
Catalog No.:BCN5149
CAS No.:26652-12-0
- Dipalmitin
Catalog No.:BCN2214
CAS No.:26657-95-4
- N4-Benzoylcytosine
Catalog No.:BCC9073
CAS No.:26661-13-2
- 6'-O-beta-D-Apiofuranosylsweroside
Catalog No.:BCN2876
CAS No.:266678-59-5
- Boc-Glycinol
Catalog No.:BCC3093
CAS No.:26690-80-2
Investigation of the interaction of a putative allosteric modulator, N-(2,3-diphenyl-1,2,4-thiadiazole-5-(2H)-ylidene) methanamine hydrobromide (SCH-202676), with M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors.[Pubmed:14617684]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004 Mar;308(3):830-7.
The interaction between a novel G protein-coupled receptor modulator, N-(2,3-diphenyl-1,2,4-thiadiazole-5-(2H)-ylidene) methanamine hydrobromide (SCH-202676), and the M(1) muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (mAChR) was investigated. In contrast to the prototypical mAChR allosteric modulator, heptane 1,7-bis-(dimethyl-3'-phthalimidopropyl)-ammonium bromide (C(7)/3-phth), SCH-202676 had no effect on the dissociation kinetics of [(3)H]N-methylscopolamine ([(3)H]NMS) at M(1) mAChRs stably expressed in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell membranes. However, SCH-202676 completely inhibited the binding of [(3)H]NMS in membrane preparations, with a Hill slope significantly greater than unity, indicative of positive cooperativity in the binding of the inhibitor. Moreover, SCH-202676 caused dextral shifts of the [(3)H]NMS saturation binding curve that were greater than expected for a competitive interaction. The addition of C(7)/3-phth (100 microM) had no significant effect on the inhibitory potency of SCH-202676. In contrast to the findings in cell membranes, the interaction between SCH-202676 and [(3)H]NMS in intact M(1) CHO cells yielded saturation and inhibition isotherms that were compatible with the predictions for a competitive interaction. Intact cell assays of acetylcholine-mediated phosphoinositide hydrolysis in the absence or presence of SCH-202676 revealed a mixed competitive/noncompetitive mode of interaction that was dependent on the concentration of SCH-202676. These data reveal that the nature of the interaction between SCH-202676 and the M(1) mAChR is dependent on whether it is studied using intact versus broken cell preparations. It is proposed that SCH-202676 uses a dual mode of ligand-receptor interaction involving both extra- and intracellular attachment points on the M(1) mAChR that are distinct from the allosteric binding site recognized by prototypical mAChR modulators such as C(7)/3-phth.
The 'allosteric modulator' SCH-202676 disrupts G protein-coupled receptor function via sulphydryl-sensitive mechanisms.[Pubmed:16402041]
Br J Pharmacol. 2006 Feb;147(4):422-9.
1. Previous studies suggest that the thiadiazole compound SCH-202676 (N-(2,3-diphenyl-1,2,4-thiadiazol-5-(2H)-ylidene)methanamine) acts as an allosteric modulator of a variety of structurally distinct G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). It was postulated that SCH-202676 would directly bind a structural motif in the receptor molecule common to divergent members of the GPCR family. The molecular mechanisms of such a promiscuous action, however, remain obscure. 2. To clarify the mechanism of SCH-202676 action, we used the functional approach of [35S]GTPgammaS autoradiography with rat brain cryostat sections together with classical membrane [35S]GTPgammaS binding assays to evaluate how the thiadiazole affects G protein activity mediated by various receptors linked to the Gi-family of G proteins. 3. We found that in the absence of dithiotreitol (DTT), SCH-202676 (10(-7)-10(-5) M) elicits nonspecific effects in the [35S]GTPgammaS-based G protein activation assays, thereby severely compromising interpretations on the compounds ability to allosterically inhibit receptor-mediated G protein activity. Such a nonspecific behaviour was fully reversed upon addition of DTT (1 mM), revealing thiol-based mechanism of action. 4. In routine incubations containing DTT, SCH-202676 had no effect on receptor-driven G protein activity, as assessed for adenosine A1, alpha2-adrenergic, cannabinoid CB1, lysophosphatidic acid LPA1, muscarinic M2/M4, purinergic P2Y12 or sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors, suggesting that the thiadiazole does not act as an allosteric modulator of GPCR function. 5. 1H NMR analysis indicated that SCH-202676 underwent structural changes after incubation with the reducing agent DTT or with brain tissue. 6. We conclude that SCH-202676 modulates GPCRs via thiol modification rather than via true allosteric mechanisms.
Effects of the allosteric modulator SCH-202676 on adenosine and P2Y receptors.[Pubmed:15081581]
Life Sci. 2004 May 7;74(25):3173-80.
The G protein-coupled receptor allosteric modulator SCH-202676 (N-(2,3-diphenyl-1,2,4-thiadiazol-5-(2H)-ylidene)methanamine), which affects a wide range of structurally unrelated G protein-coupled receptors, has highly divergent effects on purine receptors. SCH-202676 inhibited radioligand binding to human adenosine A(1), A(2A), and A(3) receptors (IC(50) = 0.5-0.8 microM) and affected dissociation kinetics, but at the human P2Y(1) nucleotide receptor it had no effect. SCH-202676 (10 microM) selectively accelerated agonist dissociation at adenosine A(3) receptors and either slowed (adenosine A(1) receptors) or accelerated (adenosine A(2A) receptors) antagonist dissociation. Thus, SCH-202676 differentially modulated A(1), A(2A), and A(3) receptors as well as agonist- and antagonist-occupied receptors.
SCH-202676: An allosteric modulator of both agonist and antagonist binding to G protein-coupled receptors.[Pubmed:11125021]
Mol Pharmacol. 2001 Jan;59(1):30-7.
A novel thiadiazole compound, SCH-202676 (N-(2,3-diphenyl-1,2, 4-thiadiazol-5-(2H)-ylidene)methanamine), has been identified as an inhibitor of both agonist and antagonist binding to G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). SCH-202676 inhibited radioligand binding to a number of structurally distinct, heterologously expressed GPCRs, including the human mu-, delta-, and kappa-opioid, alpha- and beta-adrenergic, muscarinic M1 and M2, and dopaminergic D1 and D2 receptors, but not to the tyrosine kinase epidermal growth factor receptor. SCH-202676 had no direct effect on G protein activity as assessed by [35S]guanosine-5'-O-(gamma-thio)triphosphate binding to purified recombinant G(oalpha)- or G(betagamma)-stimulated ADP-ribosylation of G(oalpha) by pertussis toxin. In addition, SCH-202676 inhibited antagonist binding to the beta2-adrenergic receptor expressed in Escherichia coli, a system devoid of classical heterotrimeric G proteins. SCH-202676 inhibited radiolabeled agonist and antagonist binding to the alpha2a-adrenergic receptor with an IC50 value of 0.5 microM, decreased the Bmax value of the binding sites with a slight increase in the KD value, and inhibited agonist-induced activation of the receptor. The effects of SCH-202676 were reversible. Incubation of plasma membranes with 10 microM SCH-202676 did not alter subsequent radioligand binding to the alpha2a-adrenergic receptor and the dopaminergic D1 receptor. Taken together, our data suggest that SCH-202676 has the unique ability to allosterically regulate agonist and antagonist binding to GPCRs in a manner that is both selective and reversible. The scope of the data presented suggests this occurs by direct interaction with a structural motif common to a large number of GPCRs or by activation/inhibition of an unidentified accessory protein that regulates GPCR function.


