PinostrobinCAS# 480-37-5 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 480-37-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 73201 | Appearance | Powder |
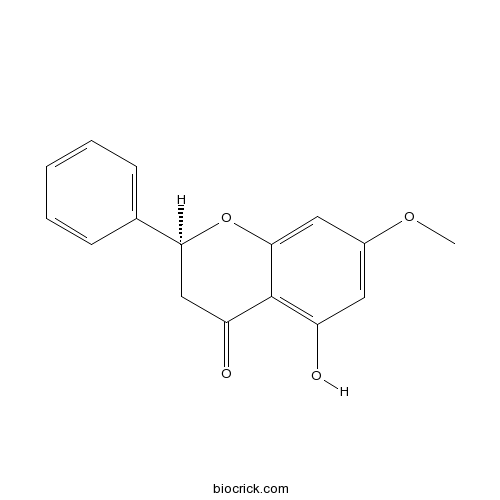
| Formula | C16H14O4 | M.Wt | 270.3 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (2S)-5-hydroxy-7-methoxy-2-phenyl-2,3-dihydrochromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=CC(=C2C(=O)CC(OC2=C1)C3=CC=CC=C3)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ORJDDOBAOGKRJV-AWEZNQCLSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C16H14O4/c1-19-11-7-12(17)16-13(18)9-14(20-15(16)8-11)10-5-3-2-4-6-10/h2-8,14,17H,9H2,1H3/t14-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Pinostrobin, a potent flavonoid inducer, exerts a neuroprotective effect against Aβ(25-35)-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells, at least in part, via inhibiting oxidative damage and calcium overload, as well as suppressing the mitochondrial pathway of cellular apoptosis. Pinostrobin has anti-inflammatory, anti-hemorrhagic and analgesic activity, it can inhibit HSV-1 replication with 50% effective concentration (EC(50)) of 22.71 ± 1.72 ug/ml. |
| Targets | TNF-α | IL Receptor | Beta Amyloid | Bcl-2/Bax | HSV |
| In vitro | Inhibition of the toxic effects of Bothrops asper venom by pinostrobin, a flavanone isolated from Renealmia alpinia (Rottb.) MAAS.[Pubmed: 25138354]J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Sep 29;155(3):1609-15.Renealmia alpinia has been traditionally used to treat snakebites by indigenous Embera-Katíos tribes belonging to the regions of Antioquia and Chocó, Colombia, and it has been shown to inhibit the enzymatic and biological activities of Bothrops venoms and their purified phospholipase A2 (PLA2) toxins. In addition to its common local usage against snakebites, Renealmia alpinia is commonly used to treat pain. To evaluate the inhibitory ability of Pinostrobin, the main compound in the dichloromethane extract of Renealmia alpinia, on the toxic effects of Bothrops asper venom through in vitro and in vivo models and to evaluate its activity against pain and edema.
Protective effects of pinostrobin on β-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells.[Pubmed: 22565301]Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2012 Nov;32(8):1223-30.Pinostrobin, a potent flavonoid inducer, is the major and most active ingredient of Folium cajani. The present study aimed to investigate whether Pinostrobin could provide protective effect against Aβ(25-35)-induced neurotoxicity in cultured rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells. Activity investigation of pinostrobin towards herpes simplex virus-1 as determined by atomic force microscopy.[Pubmed: 20739162]Phytomedicine. 2011 Jan 15;18(2-3):110-8.In the present study, the antiviral activity of Pinostrobin towards herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV-1) was investigated by MTT assay and atomic force microscopy. |
| Kinase Assay | Pinostrobin and Cajanus lactone isolated from Cajanus cajan (L.) leaves inhibits TNF-α and IL-1β production: in vitro and in vivo experimentation.[Pubmed: 24680612]Phytomedicine. 2014 Jun 15;21(7):946-53.The tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin 1 beta (IL-1β) inhibitory activities of Cajanus cajan (leaves) crude methanolic extract, its fractions and its phytochemical constituents were evaluated in lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulated RAW 264.7 and J774A.1 cells. |
| Cell Research | The antiproliferative effect of pinostrobin on human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC).[Pubmed: 23543451]Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2013 Mar;17(5):668-72.Atherosclerosis and stent re-stenosis are problems that are accompanied with high morbidity and mortality. Endothelial cell proliferation plays a role in both diseases, so the quest for potent inhibitors is still ongoing.
The flavonoid Pinostrobin previously showed cytotoxic effects on different cell lines. In this investigation, we tested the antiproliferative effect of Pinostrobin on human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC).
|

Pinostrobin Dilution Calculator

Pinostrobin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.6996 mL | 18.498 mL | 36.9959 mL | 73.9919 mL | 92.4898 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7399 mL | 3.6996 mL | 7.3992 mL | 14.7984 mL | 18.498 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.37 mL | 1.8498 mL | 3.6996 mL | 7.3992 mL | 9.249 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.074 mL | 0.37 mL | 0.7399 mL | 1.4798 mL | 1.8498 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.037 mL | 0.185 mL | 0.37 mL | 0.7399 mL | 0.9249 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Linarin
Catalog No.:BCN5554
CAS No.:480-36-4
- Eugenin
Catalog No.:BCN2921
CAS No.:480-34-2
- Mellein
Catalog No.:BCN4785
CAS No.:480-33-1
- Orobol
Catalog No.:BCN5553
CAS No.:480-23-9
- Aromadendrin
Catalog No.:BCN5552
CAS No.:480-20-6
- Isorhamnetin
Catalog No.:BCN5551
CAS No.:480-19-3
- Taxifolin
Catalog No.:BCN5550
CAS No.:480-18-2
- Morin
Catalog No.:BCN1028
CAS No.:480-16-0
- Izalpinine
Catalog No.:BCN3682
CAS No.:480-14-8
- Oroxylin A
Catalog No.:BCN5363
CAS No.:480-11-5
- Astragalin
Catalog No.:BCN5549
CAS No.:480-10-4
- Eleutherol
Catalog No.:BCN8480
CAS No.:480-00-2
- Pinocembrin
Catalog No.:BCN5556
CAS No.:480-39-7
- Chrysin
Catalog No.:BCN5557
CAS No.:480-40-0
- Naringenin
Catalog No.:BCN5558
CAS No.:480-41-1
- Isosakuranetin
Catalog No.:BCN5559
CAS No.:480-43-3
- Acacetin
Catalog No.:BCN5560
CAS No.:480-44-4
- Hydrangenol
Catalog No.:BCN5561
CAS No.:480-47-7
- Retrorsine
Catalog No.:BCN2119
CAS No.:480-54-6
- Lecanoric acid
Catalog No.:BCN5562
CAS No.:480-56-8
- Orsellinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6574
CAS No.:480-64-8
- 2',4',6'-Trihydroxyacetophenone
Catalog No.:BCN3996
CAS No.:480-66-0
- Jaconine
Catalog No.:BCN2089
CAS No.:480-75-1
- Jacoline
Catalog No.:BCN2088
CAS No.:480-76-2
Inhibition of the toxic effects of Bothrops asper venom by pinostrobin, a flavanone isolated from Renealmia alpinia (Rottb.) MAAS.[Pubmed:25138354]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Sep 29;155(3):1609-15.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Renealmia alpinia has been traditionally used to treat snakebites by indigenous Embera-Katios tribes belonging to the regions of Antioquia and Choco, Colombia, and it has been shown to inhibit the enzymatic and biological activities of Bothrops venoms and their purified phospholipase A2 (PLA2) toxins. In addition to its common local usage against snakebites, Renealmia alpinia is commonly used to treat pain. To evaluate the inhibitory ability of Pinostrobin, the main compound in the dichloromethane extract of Renealmia alpinia, on the toxic effects of Bothrops asper venom through in vitro and in vivo models and to evaluate its activity against pain and edema. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Pinostrobin was isolated from the dichloromethane extract of Renealmia alpinia leaves. The protective properties of the extract and of Pinostrobin against the indirect hemolytic, coagulant and proteolytic effects of Bothrops asper venom were evaluated in vitro, and the anti-hemorrhagic and anti-inflammatory activity were evaluated in vivo. RESULTS: Renealmia alpinia extract significantly inhibited the proteolytic activity and indirect hemolytic activity of Bothrops asper venom at a venom:extract ratio of 1:20. Moreover, the present data demonstrate that Pinostrobin may mitigate some venom-induced local tissue damage due to hemorrhagic effects, and the compound is also responsible for the analgesic and anti-inflammatory activity of the extract from Renealmia alpinia. This is the first report to describe Pinostrobin in the species Renealmia alpinia and its properties in vitro against Bothrops asper venom. CONCLUSION: Our studies of the activity of Renealmia alpinia against the venom of Bothrops asper have confirmed that this species possesses inhibitory effects against Bothrops asper venom in both in vitro and in vivo models and that these effects may be due to Pinostrobin, supporting the traditional usage of the plant. Additionally, Pinostrobin may be responsible for the anti-hemorrhagic and analgesic activity (peripheral analgesic activity) of Renealmia alpinia.
Activity investigation of pinostrobin towards herpes simplex virus-1 as determined by atomic force microscopy.[Pubmed:20739162]
Phytomedicine. 2011 Jan 15;18(2-3):110-8.
In the present study, the antiviral activity of Pinostrobin towards herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV-1) was investigated by MTT assay and atomic force microscopy. Pinostrobin can inhibit HSV-1 replication with 50% effective concentration (EC(50)) of 22.71 +/- 1.72 mug/ml. MTT assay showed HSV-1 was significantly inhibited when pretreated with Pinostrobin, with the inhibition of 85.69 +/- 2.59%. Significant changes in morphology and size of HSV-1 were observed by atomic force microscopy (AFM) in response to Pinostrobin treatment. AFM topography and phase images showed that with increasing time, the envelope was shedded and damaged, finally leading to virus inactivation. With increasing concentration, Pinostrobin caused a gradual leakage, also contributing to breakage of the envelope and virus inactivation. Treatment effect of oral Pinostrobin in vivo showed that Pinostrobin (50mg/kg/dose) possesses definite therapeutical effect in the development of lesion score. In general, the results showed that AFM represents a powerful technique for the investigation of morphology and size of HSV-1 treated by antiviral agents. AFM is applicable to study chemically induced morphological changes at the nanometer level.
Pinostrobin and Cajanus lactone isolated from Cajanus cajan (L.) leaves inhibits TNF-alpha and IL-1beta production: in vitro and in vivo experimentation.[Pubmed:24680612]
Phytomedicine. 2014 Jun 15;21(7):946-53.
The tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin 1 beta (IL-1beta) inhibitory activities of Cajanus cajan (leaves) crude methanolic extract, its fractions and its phytochemical constituents were evaluated in lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulated RAW 264.7 and J774A.1 cells. Phytochemical investigation of the active ethyl acetate (CCE) and n-butanol (CCB) fractions of C. cajan L. leaves yielded 14 compounds. It was observed that both Pinostrobin (9) and cajanus lactone (4) were found to be most active in inhibiting TNF-alpha (IC50<22 muM) and IL-1beta (IC50<40 muM) whereas compounds 2, 3, 5-8, 10 and 14 showed moderate and mild effects (IC50=35.50-81.22 muM for TNF-alpha and 38.23-89.10 muM for IL-1beta) in both the cell lines. Furthermore, at dose of 20mg/kg, both Pinostrobin (9) and cajanus lactone (4) were found to reduce LPS-induced TNF-alpha levels by 48.6% and 55.0% respectively and IL-1beta levels by 53.1% and 41.8% respectively in Sprague Dawley (SD) rats. These findings suggest that C. cajan L. leaves can be developed as an effective herbal remedy for the treatment and prevention of inflammation or associated ailments.
The antiproliferative effect of pinostrobin on human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC).[Pubmed:23543451]
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2013 Mar;17(5):668-72.
BACKGROUND: Atherosclerosis and stent re-stenosis are problems that are accompanied with high morbidity and mortality. Endothelial cell proliferation plays a role in both diseases, so the quest for potent inhibitors is still ongoing. AIM: The flavonoid Pinostrobin previously showed cytotoxic effects on different cell lines. In this investigation, we tested the antiproliferative effect of Pinostrobin on human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC). MATERIALS AND METHODS: The effect of Pinostrobin on human umbilical vein endothelial cells after 1 hour and after 48 hours of treatment was tested. A dose- and time-dependent antiproliferative effect of Pinostrobin was observed. RESULTS: After 1 hour of treatment, no significant differences between the control group and the cells treated with Pinostrobin could be detected. After 48 h of Pinostrobin treatment, the number of cells decreased significantly. Higher doses had stronger inhibitory effects on the proliferation. Furthermore, we tested the change of membrane potential on cells that were treated with different concentrations of Pinostrobin. We could show that the change of membrane potential was also time- as well as dose-dependent. CONCLUSIONS: Our hypothesis is that Pinostrobin leads to depolarisation of the cell potential of endothelial cells. Since the membrane potential remains less negative, this could lead to instability of the membrane, resulting in cell death.
Protective effects of pinostrobin on beta-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells.[Pubmed:22565301]
Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2012 Nov;32(8):1223-30.
Beta-Amyloid peptide (Abeta), a major protein component of brain senile plaques in Alzheimer's disease (AD), has been considered as a critical cause in the pathogenesis of AD. Pinostrobin, a potent flavonoid inducer, is the major and most active ingredient of Folium cajani. The present study aimed to investigate whether Pinostrobin could provide protective effect against Abeta(25-35)-induced neurotoxicity in cultured rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells. The PC12 cells were pretreated with different concentrations of Pinostrobin for 2 h, followed by the challenge with 20 muM Abeta(25-35) for 24 h. The results showed that pretreatment with Pinostrobin significantly elevated cell viability, decreased the lactate dehydrogenase activity, the levels of intracellular reactive oxygen species and calcium, and mitochondrial membrane potential in Abeta(25-35)-treated PC12 cells. In addition, Pinostrobin significantly suppressed the formation of DNA fragmentation and increased the ratio of Bcl-2/Bax. These results indicate that Pinostrobin was able to exert a neuroprotective effect against Abeta(25-35)-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells, at least in part, via inhibiting oxidative damage and calcium overload, as well as suppressing the mitochondrial pathway of cellular apoptosis.


