Methyl cinnamateCAS# 103-26-4 |
Quality Control & MSDS
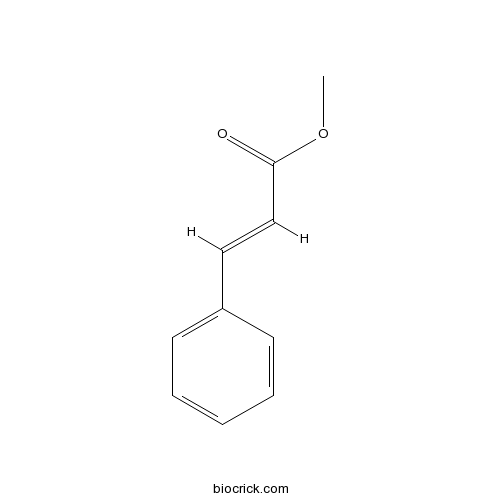
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 103-26-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 637520 | Appearance | Cryst. |
| Formula | C10H10O2 | M.Wt | 162.19 |
| Type of Compound | Phenylpropanoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | methyl (E)-3-phenylprop-2-enoate | ||
| SMILES | COC(=O)C=CC1=CC=CC=C1 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | CCRCUPLGCSFEDV-BQYQJAHWSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C10H10O2/c1-12-10(11)8-7-9-5-3-2-4-6-9/h2-8H,1H3/b8-7+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Methyl cinnamate, a tyrosinase inhibitor and a flavoring compound, which has antimicrobial, antiadipogenic, vasorelaxant, and anti-inflammatory effects. It has a wide spectrum of targets including CaMKK2-AMPK, Ca(2+) channels. |
| Targets | Calcium Channel | Potassium Channel | Antifection | PPAR | AMPK | Tyrosinase |
| In vitro | Vasorelaxation induced by methyl cinnamate, the major constituent of the essential oil of Ocimum micranthum, in rat isolated aorta.[Pubmed: 25115734]Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2014 Oct;41(10):755-62.The aim of the present study was to investigate the vascular effects of the E-isomer of Methyl cinnamate (E-MC) in rat isolated aortic rings and the putative mechanisms underlying these effects. Optimization of antimicrobial and physical properties of alginate coatings containing carvacrol and methyl cinnamate for strawberry application.[Pubmed: 24405047]J Agric Food Chem. 2014 Jan 29;62(4):984-90.Increasing strawberry consumption has led to a growing safety concern because they are not washed after harvest. Increasing strawberry shelf-life with carvacrol and methyl cinnamate antimicrobial vapors released from edible films.[Reference: WebLink]Postharvest Biol. Tec., 2014, 89(3):11-8.
The effect of carvacrol and Methyl cinnamate vapors incorporated into strawberry puree edible films on the postharvest quality of strawberry fruit (Fragaria × ananassa) was investigated. Myorelaxant effects of methyl cinnamate, the major constituent of the essential oil of Ocimum micranthum, on smooth muscle of the gastrointestinal tract of rats.[Reference: WebLink]Planta Med., 2013, 79(13):PF5-6.Methyl cinnamate (MC) is a flavoring compound naturally found in the essential oil of Ocimum micranthum Willd. (EOOM), but its effects on gastrointestinal tract are not known. This study aimed to characterize the pharmacological actions of the EOOM (˜40% of MC) and MC on the contractile behavior of strips from rat gastrointestinal smooth muscle disposed in bath chambers. |
| Kinase Assay | Methyl cinnamate inhibits adipocyte differentiation via activation of the CaMKK2-AMPK pathway in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes.[Pubmed: 22273148]J Agric Food Chem. 2012 Feb 1;60(4):955-63.Methyl cinnamate, an active component of Zanthoxylum armatum , is a widely used natural flavor compound with antimicrobial and tyrosinase inhibitor activities. However, the underlying bioactivity and molecular mechanisms of Methyl cinnamate on adipocyte function and metabolism remain unclear. The aim of this study was to investigate the inhibitory effect of Methyl cinnamate on adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. |

Methyl cinnamate Dilution Calculator

Methyl cinnamate Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 6.1656 mL | 30.828 mL | 61.6561 mL | 123.3122 mL | 154.1402 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.2331 mL | 6.1656 mL | 12.3312 mL | 24.6624 mL | 30.828 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.6166 mL | 3.0828 mL | 6.1656 mL | 12.3312 mL | 15.414 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1233 mL | 0.6166 mL | 1.2331 mL | 2.4662 mL | 3.0828 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0617 mL | 0.3083 mL | 0.6166 mL | 1.2331 mL | 1.5414 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Monobenzone
Catalog No.:BCC3818
CAS No.:103-16-2
- H-DL-Phg-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3317
CAS No.:103-01-5
- Trelagliptin succinate
Catalog No.:BCC2015
CAS No.:1029877-94-8
- INCB28060
Catalog No.:BCC3793
CAS No.:1029712-80-8
- Scutellaric acid
Catalog No.:BCN5843
CAS No.:102919-76-6
- MDL 73005EF hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6636
CAS No.:102908-60-1
- Pexidartinib (PLX3397)
Catalog No.:BCC6405
CAS No.:1029044-16-3
- 17-Hydroxy sprengerinin C
Catalog No.:BCN2755
CAS No.:1029017-75-1
- Lycopsamine
Catalog No.:BCN1999
CAS No.:10285-07-1
- Intermedine
Catalog No.:BCN1997
CAS No.:10285-06-0
- MLN8237 (Alisertib)
Catalog No.:BCC2166
CAS No.:1028486-01-2
- Ganolactone B
Catalog No.:BCN2872
CAS No.:1028449-53-7
- Ethyl cinnamate
Catalog No.:BCN5044
CAS No.:103-36-6
- Benzyl cinnamate
Catalog No.:BCN5042
CAS No.:103-41-3
- Scutebarbatine M
Catalog No.:BCN8327
CAS No.:960302-92-5
- N-Methylbenzylamine
Catalog No.:BCN1790
CAS No.:103-67-3
- Phenylacetic Acid
Catalog No.:BCC8349
CAS No.:103-82-2
- 4'-Methylacetanilide
Catalog No.:BCC8714
CAS No.:103-89-9
- Acetaminophen
Catalog No.:BCC5269
CAS No.:103-90-2
- Dehydroheliobuphthalmin
Catalog No.:BCN5844
CAS No.:103001-05-4
- Alterlactone
Catalog No.:BCN7261
CAS No.:1030376-89-6
- MK-4305
Catalog No.:BCC1760
CAS No.:1030377-33-3
- CTCE 9908
Catalog No.:BCC6366
CAS No.:1030384-98-5
- Ethyl 3-(pyridin-2-ylamino)propanoate
Catalog No.:BCC8973
CAS No.:103041-38-9
Methyl cinnamate inhibits adipocyte differentiation via activation of the CaMKK2-AMPK pathway in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes.[Pubmed:22273148]
J Agric Food Chem. 2012 Feb 1;60(4):955-63.
Methyl cinnamate, an active component of Zanthoxylum armatum , is a widely used natural flavor compound with antimicrobial and tyrosinase inhibitor activities. However, the underlying bioactivity and molecular mechanisms of Methyl cinnamate on adipocyte function and metabolism remain unclear. The aim of this study was to investigate the inhibitory effect of Methyl cinnamate on adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Methyl cinnamate markedly suppressed triglyceride accumulation associated with down-regulation of adipogenic transcription factor expression, including sterol regulatory element binding protein-1 (SREBP-1), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma), and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha (C/EBPalpha). Additionally, Methyl cinnamate-inhibited PPARgamma activity and adipocyte differentiation were partially reversed by the PPARgamma agonist troglitazone. Furthermore, Methyl cinnamate stimulated Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2 (CaMKK2) and phospho-AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) expression during adipogenesis. This study first revealed Methyl cinnamate has antiadipogenic activity through mechanisms mediated, in part, by the CaMKK2-AMPK signaling pathway in 3T3-L1 cells.
Optimization of antimicrobial and physical properties of alginate coatings containing carvacrol and methyl cinnamate for strawberry application.[Pubmed:24405047]
J Agric Food Chem. 2014 Jan 29;62(4):984-90.
Increasing strawberry consumption has led to a growing safety concern because they are not washed after harvest. An antimicrobial edible coating could be an effective postharvest technique to ensure microbial safety and, at the same time, retain overall quality of the fruits. Response surface methodology was used to optimize the antimicrobial activity against Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Botrytis cinerea and several physical properties (turbidity, viscosity, and whitish index) of an alginate coating. A full factorial design was used to select the concentrations of carvacrol and Methyl cinnamate on the basis of their effect against E. coli and B. cinerea. A central composite design was then performed to evaluate the effects/interactions of the two antimicrobials on the coating characteristics. The results from analysis of variance showed the significant fitting of all responses to the quadratic model. To attain the desirable responses, the optimal concentrations were 0.98% (w/w) carvacrol and 1.45% (w/w) Methyl cinnamate.
Vasorelaxation induced by methyl cinnamate, the major constituent of the essential oil of Ocimum micranthum, in rat isolated aorta.[Pubmed:25115734]
Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2014 Oct;41(10):755-62.
The aim of the present study was to investigate the vascular effects of the E-isomer of Methyl cinnamate (E-MC) in rat isolated aortic rings and the putative mechanisms underlying these effects. At 1-3000 mumol/L, E-MC concentration-dependently relaxed endothelium-intact aortic preparations that had been precontracted with phenylephrine (PHE; 1 mumol/L), with an IC50 value (geometric mean) of 877.6 mumol/L (95% confidence interval (CI) 784.1-982.2 mumol/L). These vasorelaxant effects of E-MC remained unchanged after removal of the vascular endothelium (IC50 725.5 mumol/L; 95% CI 546.4-963.6 mumol/L) and pretreatment with 100 mumol/L N(G) -nitro-l-arginine methyl ester (IC50 749.0 mumol/L; 95% CI 557.8-1005.7 mumol/L) or 10 mumol/L 1H-[1,2,4]oxadiazolo[4,3-a]quinoxalin-1-one (IC50 837.2 mumol/L; 95% CI 511.4-1370.5 mumol/L). Over the concentration range 1-3000 mumol/L, E-MC relaxed K(+) -induced contractions in mesenteric artery preparations (IC50 314.5 mumol/L; 95% CI 141.9-697.0 mumol/L) with greater potency than in aortic preparations (IC50 1144.7 mumol/L; 95% CI 823.2-1591.9 mumol/L). In the presence of a saturating contractile concentration of K(+) (150 mmol/L) in Ca(2+) -containing medium combined with 3 mumol/L PHE, 1000 mumol/L E-MC only partially reversed the contractile response. In contrast, under similar conditions, E-MC nearly fully relaxed PHE-induced contractions in aortic rings in a Ba(2+) -containing medium. In preparations that were maintained under Ca(2+) -free conditions, 600 and 1000 mumol/L E-MC significantly reduced the contractions induced by exogenous Ca(2+) or Ba(2+) in KCl-precontracted preparations, but not in PHE-precontracted preparations (in the presence of 1 mumol/L verapamil). In addition, E-MC (1-3000 mumol/L) concentration-dependently relaxed the contractions induced by 2 mmol/L sodium orthovanadate. Based on these observations, E-MC-induced endothelium-independent vasorelaxant effects appear to be preferentially mediated by inhibition of plasmalemmal Ca(2+) influx through voltage-dependent Ca(2+) channels. However, the involvement of a myogenic mechanism in the effects of E-MC is also possible.


