LigustilideCAS# 4431-01-0 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 4431-01-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5319022 | Appearance | Oil |
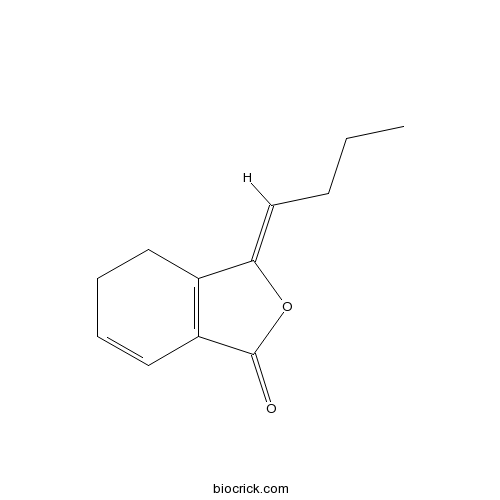
| Formula | C12H14O2 | M.Wt | 190.24 |
| Type of Compound | Miscellaneous | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 50 mg/mL (262.83 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
| Chemical Name | (3Z)-3-butylidene-4,5-dihydro-2-benzofuran-1-one | ||
| SMILES | CCCC=C1C2=C(C=CCC2)C(=O)O1 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | IQVQXVFMNOFTMU-FLIBITNWSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C12H14O2/c1-2-3-8-11-9-6-4-5-7-10(9)12(13)14-11/h5,7-8H,2-4,6H2,1H3/b11-8- | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Ligustilide possesses neuroprotective, vasorelaxation, antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities, it blocked the activation of MAPKs/IKK and the downstream transcription factors AP-1 and NF-κB. It has the potential to be developed into an effective drug for the treatment of various pain syndromes including primary dysmenorrhoea. |
| Targets | IGF-1R | Akt | ERK | Caspase | TNF-α | Sodium Channel | ATPase | Potassium Channel | GABA Receptor | NO | PGE | AP-1 | NOS | NF-kB | IkB | p38MAPK | JNK | ROS | Beta Amyloid | IKK |
| In vitro | [Protective effect of ligustilide against low potassium induced apoptosis in cultured rat cerebellar granule neurons].[Pubmed: 25807794]Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2015 Jan;46(1):42-6. To investigate the effect of Ligustilide (LIG) on low potassium-induced apoptosis in primary cultured cerebellar granule neurons (CGN). Relaxation effects of ligustilide and senkyunolide A, two main constituents of Ligusticum chuanxiong, in rat isolated aorta.[Pubmed: 17222996 ]J Ethnopharmacol. 2007 May 22;111(3):677-80.Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort. (Umbelliferae) is a widely prescribed traditional Chinese medicinal herb for cardiovascular diseases in China. However, the cardiovascular actions of Ligustilide and senkyunolide A, two of the most abundant Ligusticum chuanxiong constituents, have yet to be examined.
|
| In vivo | Ligustilide prevents cognitive impairment and attenuates neurotoxicity in D-galactose induced aging mice brain.[Pubmed: 25446001]Brain Res. 2015 Jan 21;1595:19-28.Ligustilide (LIG) is a principal active ingredient of traditional Chinese medicine, Radix Angelica sinensis, which has versatile pharmacological activities including neuroprotection. Previous studies have demonstrated that Ligustilide has beneficial effects on cognition deficits associated with cerebral damage or neurodegenerative disorders. In present study, we investigated the neuroprotective effect of Ligustilide on cognitive impairment and neurotoxicity in the brain of aging mouse induced by d-galactose (d-gal).
|
| Kinase Assay | Ligustilide inhibits tumour necrosis factor-alpha-induced autophagy during C2C12 cells differentiation.[Pubmed: 25661336]Biomed Pharmacother. 2015 Feb;69:42-6.Ligustilide is widely thought to be the most potent bioactive constituent of Angelica sinensis. We have previously reported the role of Ligustilide in preventing TNF-α-induced apoptosis and identified the presence of autophagosome clusters. Then, we hypothesised that autophagy may contribute to muscle loss and that Ligustilide could protect cell fibres by regulating the autophagic process. The aim of this study was to identify the effects of Ligustilide on autophagy regulation during cell differentiation in the presence of TNF-α.
|
| Cell Research | Ligustilide prevents LPS-induced iNOS expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages by preventing ROS production and down-regulating the MAPK, NF-κB and AP-1 signaling pathways.[Pubmed: 21457761 ]Int Immunopharmacol. 2011 Sep;11(9):1166-72.Angelica sinensis (AS), an herb used in traditional Chinese medicine, is thought to have anti-inflammatory activities. Ligustilide is its most abundant ingredient.
This study sought to determine Ligustilide's effects on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammation in RAW 264.7 macrophages.
|
| Animal Research | Klotho upregulation contributes to the neuroprotection of ligustilide in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model.[Pubmed: 23973442 ]Neurobiol.Aging, 2014, 35(1):169-78.Klotho, an aging-suppressor gene, encodes a protein that potentially acts as a neuroprotective factor by modulating insulin-like growth factor 1 signaling and oxidative stress. In the present study, we investigated the potential role of Klotho in the therapeutic effect of Ligustilide against Alzheimer's disease (AD)-like neuropathologies and memory impairment in aged senescence-accelerated mouse prone-8 (SAMP8) mice.
|

Ligustilide Dilution Calculator

Ligustilide Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.2565 mL | 26.2826 mL | 52.5652 mL | 105.1304 mL | 131.413 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.0513 mL | 5.2565 mL | 10.513 mL | 21.0261 mL | 26.2826 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5257 mL | 2.6283 mL | 5.2565 mL | 10.513 mL | 13.1413 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1051 mL | 0.5257 mL | 1.0513 mL | 2.1026 mL | 2.6283 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0526 mL | 0.2628 mL | 0.5257 mL | 1.0513 mL | 1.3141 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Ligustilide is an effective constituent extracted from Angelica sinensis. IC50 value: Target: In vitro: To investigate the neuroprotective of ligustilide (LIG) against glutamate-induced apoptosis of PC12 cells, cell viability were examined by MTT assay. Pretreatment with ligustilide (1, 5, 15 μmol · L(-1)) significantly improved cell viability. The apoptosis rate in glutamate-induced PC12 cells was 13.39%, and decreased in the presence of ligustilide (1, 5, 15 μmol · L(-1)) by 9.06%, 6.48%, 3.82%, separately. Extracellular accumulation of Ca2+ induced by glutamate were significantly reduced by ligustilide [1]. In vivo:
References:
[1]. Wu Q, et al. Protective effect of ligustilide against glutamate-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2015 Feb;50(2):162-8.
[2]. Du H, et al. A cell membrane chromatography method for investigation of 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor-ligustilide interaction. Se Pu. 2015 May;33(5):530-4.
- Metronidazole
Catalog No.:BCC9046
CAS No.:443-48-1
- Tabersonine
Catalog No.:BCN5496
CAS No.:4429-63-4
- Methyl isodrimeninol
Catalog No.:BCN5495
CAS No.:442851-27-6
- Anguizole
Catalog No.:BCC1365
CAS No.:442666-98-0
- JW 67
Catalog No.:BCC6251
CAS No.:442644-28-2
- CK 666
Catalog No.:BCC6088
CAS No.:442633-00-3
- CK-636
Catalog No.:BCC5107
CAS No.:442632-72-6
- Aspertine C
Catalog No.:BCN2153
CAS No.:442155-62-6
- Clemizole
Catalog No.:BCC1485
CAS No.:442-52-4
- Harmine
Catalog No.:BCN5494
CAS No.:442-51-3
- Macitentan
Catalog No.:BCC1142
CAS No.:441798-33-0
- 6-Acetylacteoside
Catalog No.:BCC8109
CAS No.:441769-43-3
- Isopedicin
Catalog No.:BCN4633
CAS No.:4431-42-9
- SF 11
Catalog No.:BCC7805
CAS No.:443292-81-7
- Z-DL-Met-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2759
CAS No.:4434-61-1
- BC 11 hydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCC2381
CAS No.:443776-49-6
- JNJ-7706621
Catalog No.:BCC2171
CAS No.:443797-96-4
- 3-Chloro-4-(3-fluorobenzyloxy)nitrobenzene
Catalog No.:BCC8626
CAS No.:443882-99-3
- Norkhellol
Catalog No.:BCN5497
CAS No.:4439-68-3
- Glycosmisic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3650
CAS No.:443908-19-8
- Vandetanib (ZD6474)
Catalog No.:BCC3883
CAS No.:443913-73-3
- 1,4-Benzodioxane-6-carboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8422
CAS No.:4442-54-0
- 2-Cyclohexylethylamine
Catalog No.:BCN1794
CAS No.:4442-85-7
- Norwogonin
Catalog No.:BCN3190
CAS No.:4443-09-8
Klotho upregulation contributes to the neuroprotection of ligustilide in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model.[Pubmed:23973442]
Neurobiol Aging. 2014 Jan;35(1):169-78.
Klotho, an aging-suppressor gene, encodes a protein that potentially acts as a neuroprotective factor by modulating insulin-like growth factor 1 signaling and oxidative stress. In the present study, we investigated the potential role of Klotho in the therapeutic effect of Ligustilide against Alzheimer's disease (AD)-like neuropathologies and memory impairment in aged senescence-accelerated mouse prone-8 (SAMP8) mice. Ligustilide treatment (10 and 40 mg/kg for 8 weeks, intragastrically) in 10-month-old SAMP8 mice reduced memory deficits, amyloid-beta(1)-42 accumulation, tau phosphorylation, and neuron loss, increased mitochondrial manganese-superoxide dismutase and catalase expression and activity, and decreased malondialdehyde, protein carbonyl, and 8-hydroxydesoxyguanosine levels in the brain. Ligustilide upregulated Klotho expression in the cerebral choroid plexus and serum, decreased Akt and Forkhead box class O1 phosphorylation. Moreover, Ligustilide inhibited the insulin-like growth factor 1 pathway and induced Forkhead box class O1 activation in 293T cells along with Klotho upregulation. An inverse correlation was found between Klotho expression and the AD phenotype, suggesting that Klotho might be a novel therapeutic target for age-related AD, and Klotho upregulation might contribute to the neuroprotective effect of Ligustilide against AD.
Relaxation effects of ligustilide and senkyunolide A, two main constituents of Ligusticum chuanxiong, in rat isolated aorta.[Pubmed:17222996]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2007 May 22;111(3):677-80.
Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort. (Umbelliferae) is a widely prescribed traditional Chinese medicinal herb for cardiovascular diseases in China. However, the cardiovascular actions of Ligustilide and senkyunolide A, two of the most abundant Ligusticum chuanxiong constituents, have yet to be examined. The objective of the present study was to investigate the vasorelaxation effects of Ligustilide and senkyunolide A and their underlying mechanisms in rat isolated aorta. Both constituents had similar relaxation potencies against contractions to 9,11-dideoxy-9alpha,11alpha-methanoepoxyprostaglandin F(2alpha), phenylephrine, 5-hydroxytryptamine and KCl. Their vasorelaxation effects were not affected by endothelium removal, the adenylate cyclase inhibitor 9-(tetrahydro-2-furanyl)-9H-purin-6-amine, the soluble guanylate cyclase inhibitor 1H-[1,2,4]oxadiazolo[4,3-a]quinoxalin-1-one, or the non-selective K+ channel blocker tetraethylammonium. This is the first report to demonstrate the vasorelaxation activities of Ligustilide and senkyunolide A in contractions to various contractile agents in rat isolated aorta. The underlying mechanisms await further investigations.
Ligustilide prevents cognitive impairment and attenuates neurotoxicity in D-galactose induced aging mice brain.[Pubmed:25446001]
Brain Res. 2015 Jan 21;1595:19-28.
Ligustilide (LIG) is a principal active ingredient of traditional Chinese medicine, Radix Angelica sinensis, which has versatile pharmacological activities including neuroprotection. Previous studies have demonstrated that LIG has beneficial effects on cognition deficits associated with cerebral damage or neurodegenerative disorders. In present study, we investigated the neuroprotective effect of LIG on cognitive impairment and neurotoxicity in the brain of aging mouse induced by d-galactose (d-gal). The aging model mice were induced by subcutaneous (S.C.) injection of d-gal once daily for 8 weeks and LIG (80 mg/kg) was simultaneously administered orally. The Morris water maze (MWM) test was used to assess the spatial learning and memory abilities. The activity of Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase and the content of lipid peroxidation product malondialdehyde (MDA) in brain were examined. The levels of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), growth-associated protein GAP-43, and cleaved caspase-3 in brain were also determined by immunohistochemistry. The MWM test showed that LIG administration markedly improved behavioral performance of d-gal treated mice. This action could be partly explained by the results that LIG reduced the level of MDA as well as increased the activity of Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase in the brain of d-gal induced aging mice. Moreover, LIG significantly raised the expression of GAP-43 and reduced cleaved caspase-3 and GFAP levels in the brain of d-gal treated mice. These results demonstrated that LIG improves d-gal-induced cognitive dysfunction and brain toxicity, which suggests that LIG may be developed as a new medicine for the treatment of aged-related conditions.
Ligustilide prevents LPS-induced iNOS expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages by preventing ROS production and down-regulating the MAPK, NF-kappaB and AP-1 signaling pathways.[Pubmed:21457761]
Int Immunopharmacol. 2011 Sep;11(9):1166-72.
Angelica sinensis (AS), an herb used in traditional Chinese medicine, is thought to have anti-inflammatory activities. Ligustilide is its most abundant ingredient. This study sought to determine Ligustilide's effects on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammation in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Ligustilide significantly suppressed the production of nitric oxide (NO), prostaglandin E(2) (PGE(2)) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha). The inhibition of NO was concomitant with a decrease in the protein and mRNA levels of LPS-induced nitric oxide synthase (iNOS). Furthermore, activation of activator protein-1 (AP-1) and nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) in the nucleus and the cytosolic degradation of IkappaBalpha were abrogated by Ligustilide. Ligustilide also inhibited the phosphorylation of IkappaB kinase (IKK) and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), including p38 MAPK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK1/2) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). The intracellular reactive oxygen species (iROS) level was also significantly decreased. These results suggest that Ligustilide exhibits anti-inflammatory activities by blocking the activation of MAPKs/IKK and the downstream transcription factors AP-1 and NF-kappaB, which may result from Ligustilide's down-regulation of iROS production.
[Protective effect of ligustilide against low potassium induced apoptosis in cultured rat cerebellar granule neurons].[Pubmed:25807794]
Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2015 Jan;46(1):42-6.
OBJECTIVE: To investigate the effect of Ligustilide (LIG) on low potassium-induced apoptosis in primary cultured cerebellar granule neurons (CGN). METHODS: Apoptosis was induced by low potassium in cultured neonatal rat CGN in vitro. The CGN was divided into control/model/CGP54626 + LIG and LIG group. The neuronal viability of each group was measured by MTT assay. The protein expression levels of the key insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF)-1 signaling effectors,including the phosphorylated IGF-1 receptor (IGF-1R), Akt, ERK1/2, CREB and activated caspase 3 were examined by Western blot analysis. RESULTS: LIG ranging from 2.5 to 20 micromol/L could protect against low potassium-induced apoptosis of CGN ini a concentration-dependent manner. 20 micromol/L LIG significantly induced upregulation of the phosphorylated levels of IGF-1, Akt, ERK1/2 and CREB, and downregulation of cleaved-caspase 3 expression, which could be blocked by a selective gamma-aminobutyric acid B (GABAs) receptor antagonist CGP54626. CONCLUSION: LIG concentration-dependently protects against low potassium-induced apoptosis in CGN at least partly through GABAa receptor activation and its downstream IGF-1 signaling pathway.
Ligustilide inhibits tumour necrosis factor-alpha-induced autophagy during C2C12 cells differentiation.[Pubmed:25661336]
Biomed Pharmacother. 2015 Feb;69:42-6.
Ligustilide is widely thought to be the most potent bioactive constituent of Angelica sinensis. We have previously reported the role of Ligustilide in preventing TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis and identified the presence of autophagosome clusters. Then, we hypothesised that autophagy may contribute to muscle loss and that Ligustilide could protect cell fibres by regulating the autophagic process. The aim of this study was to identify the effects of Ligustilide on autophagy regulation during cell differentiation in the presence of TNF-alpha. We then observed intracellular morphologic changes and autophagosome formation using transmission electron microscopy. LC3B expression was assessed by immunofluorescence and Atg-7, Atg-5, Atg-12 and LC3B expression levels were detected by western blot. The results revealed a reduction in the number of TNF-alpha-induced autophagosomes after Ligustilide treatment accompanied by a decrease in Atg-7, Atg-5, Atg-12 and LC3B expression, as well as a reduction of the LC3BII/I ratio in a concentration-dependent manner. Our findings provide evidence supporting a protective effect of Ligustilide against TNF-alpha-induced autophagy during myotubes formation.


