LaricitrinCAS# 53472-37-0 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 53472-37-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5282154 | Appearance | Powder |
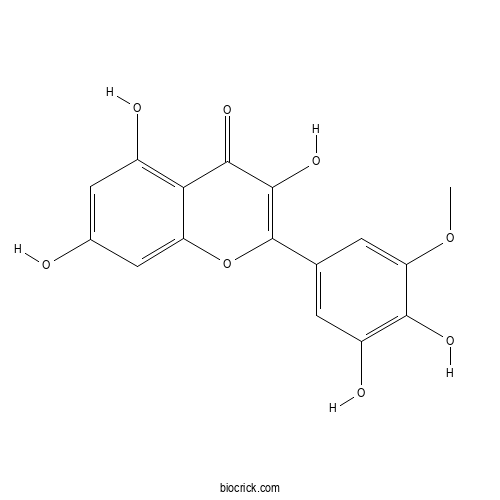
| Formula | C16H12O8 | M.Wt | 332.3 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-methoxyphenyl)-3,5,7-trihydroxychromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=CC(=CC(=C1O)O)C2=C(C(=O)C3=C(C=C(C=C3O2)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | CFYMYCCYMJIYAB-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C16H12O8/c1-23-11-3-6(2-9(19)13(11)20)16-15(22)14(21)12-8(18)4-7(17)5-10(12)24-16/h2-5,17-20,22H,1H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Laricitrin is a novel flavonoid ABCG2 inhibitor, it suppresses certain factors and decreases the progression of lung cancer cells that are promoted by BaP in the lung cancer tumor microenvironment. Laricitrin could be an efficacious immunoadjuvant and have a synergistic effect when combined with chemotherapy. | |||||

Laricitrin Dilution Calculator

Laricitrin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.0093 mL | 15.0466 mL | 30.0933 mL | 60.1866 mL | 75.2332 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6019 mL | 3.0093 mL | 6.0187 mL | 12.0373 mL | 15.0466 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3009 mL | 1.5047 mL | 3.0093 mL | 6.0187 mL | 7.5233 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0602 mL | 0.3009 mL | 0.6019 mL | 1.2037 mL | 1.5047 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0301 mL | 0.1505 mL | 0.3009 mL | 0.6019 mL | 0.7523 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Undecanolactone
Catalog No.:BCN0068
CAS No.:710-04-3
- (R)-(+)-Limonene
Catalog No.:BCN0067
CAS No.:5989-27-5
- 1,4-Cineole
Catalog No.:BCN0066
CAS No.:470-67-7
- Delta-Nonalactone
Catalog No.:BCN0065
CAS No.:3301-94-8
- Kaempferol 3,4'-diglucoside 7-rhamnoside
Catalog No.:BCN0064
CAS No.:1131009-93-2
- Acetic acid m-cresyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN0063
CAS No.:122-46-3
- 2',6'-Dihydroxy-4,4'-dimethoxychalcone
Catalog No.:BCN0062
CAS No.:20621-49-2
- 4-Isopropylbenzaldehyde
Catalog No.:BCN0061
CAS No.:122-03-2
- Dihydroxyfumaric acid
Catalog No.:BCN0060
CAS No.:133-38-0
- Apigenin 4'-O-(2'',6''-di-O-E-p-coumaroyl)glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN0059
CAS No.:71781-79-8
- Myosmine
Catalog No.:BCN0058
CAS No.:532-12-7
- Hippuric acid
Catalog No.:BCN0057
CAS No.:495-69-2
- Peucenidin
Catalog No.:BCN0070
CAS No.:33044-93-8
- Homobutein
Catalog No.:BCN0071
CAS No.:34000-39-0
- Undecanoic gamma-lactone
Catalog No.:BCN0072
CAS No.:104-67-6
- Procyanidin B4
Catalog No.:BCN0073
CAS No.:29106-51-2
- Gitoxin
Catalog No.:BCN0074
CAS No.:4562-36-1
- Isoarundinin II
Catalog No.:BCN0075
CAS No.:151538-56-6
- 3,4-Dihydroxy-5-methoxybenzoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN0076
CAS No.:3934-84-7
- Cimiaceroside A
Catalog No.:BCN0077
CAS No.:210643-83-7
- 2-Octanone
Catalog No.:BCN0078
CAS No.:111-13-7
- 3,5,7-Trihydroxy-3',4',5'-trimethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN0079
CAS No.:146132-95-8
- 3,5-Dihydroxy-4-methylbenzoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN0080
CAS No.:28026-96-2
- Sabinyl acetate
Catalog No.:BCN0081
CAS No.:53833-85-5
Phenolics profiling by HPLC-DAD-ESI-MS(n) aided by principal component analysis to classify Rabbiteye and Highbush blueberries.[Pubmed:32916406]
Food Chem. 2021 Mar 15;340:127958.
Although blueberries are widely studied, little information exists on their composition and content of flavonol glycosides. Most studies identify only a few flavonols in blueberries due to separation and identification issues. In the present study, we identified 44 flavonols and chlorogenic acid in 30 samples of Highbush and Rabbiteye blueberry, using HPLC-DAD-ESI-MS(n). Highbush group fruits presented mainly quercetin-3-galactoside in their composition, while Rabbiteye group fruits exhibited higher levels of quercetin-3-rhamnoside and quercetin-3-glucuronide. Among the identified flavonols, 8 acylates (acetyl and hydroxymethylglutaroyl) were found, of which quercetin-3-O-[4''-(3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaroyl)]-alpha-rhamnoside was found for the first time in blueberries. This compound is exclusive to the cultivars Florida and Powderblue, where it is present in high quantities. Glucuronides of syringetin and Laricitrin, and rhamnosyl-galactosides of myricetin, quercetin and isorhamnetin were also found for the first time in blueberries. The Principal Component Analysis showed that blueberry groups can be distinguished based on their phenolic compound profile.
Untargeted profiling of field cultivated bush tea (Athrixia phylicoides DC.) based on metabolite analysis.[Pubmed:32583775]
Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2020 Jun 25;66(4):104-109.
Bush tea (Athrixia phylicoides DC.) is an aromatic South African indigenous plant used for many decades as a health beverage and medicine. Several studies have extensively investigated wild bush tea's secondary metabolites, but the entire profiling of cultivated bush tea's metabolites is limited in the literature. Thus, the objective of this study was to profile cultivated bush tea metabolites using liquid chromatography-quadrupole time of flight-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-QTOF-MS). The 31 metabolites profiled included; benjaminamide, chlorogenate, chrysosplenetin, coumarin, 6Z-docosenamide, naringenin 7-O-beta-d-glucoside, 5-p-coumaroylquinic acid, integrastatin A, luteolin 7-O-(6-O-malonyl-beta-d-glucoside), 1,3-dicaffeoylquinic acid, magnoshinin, okanin, (2S)-5-hydroxy-7-methoxy-6,8-dimethylflavanone, (9Z,12Z,15Z)-octadecatrienoic acid, 2''-deamino-2''-hydroxy-6''-dehydroparomamine, O-butanoylcarnitine, myricitrin, gorlic acid, tetracenomycin X, sakuranin, d-tryptophan, linoleamide, Laricitrin 7-monoglucoside, l-beta-phenylalanine, l-proline, pheophytin A, pheophorbide A, PI(18:0/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z), stearidonic acid, and gibberellin A14 aldehyde. These annotated metabolites included phenolics, flavonoids, and quinic acids, indicating that bush tea is rich in metabolites, which have a potential wide range of health benefits.
High-resolution mass spectrometry metabolomics of grape chemical markers to reveal use of not-allowed varieties in the production of Amarone and Recioto wines.[Pubmed:30830408]
Metabolomics. 2018 Sep 17;14(10):124.
INTRODUCTION: Grape varieties allowed to produce Amarone della Valpolicella and Recioto DOCG wines are strictly regulated by their disciplinary of production. These are Corvina Veronese and Corvinone grapes, to a lesser extent also Rondinella can be used. The use of other varieties, is not allowed. OBJECTIVES: To identify chemical markers suitable to reveal addition of two not allowed grape varieties to the Corvina/Corvinone blend, such as Primitivo or Negro Amaro. METHODS: The identification of the secondary metabolites of the four grape varieties was conducted by high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) metabolomics. By using the signals of these metabolites the indexes able to identify the presence of Primitivo or Negro Amaro grapes in the Corvina/Corvinone 1:1 blend were calculated. RESULTS: Indexes of Laricitrin (Lr), delphinidin (Dp), and petunidin (Pt) signals were effective to identify the use of 10% Primitivo, while alpha-terpineol pentosyl-hexoside and linalool pentosyl-hexoside reveal the presence of Negro Amaro in the grape blend. CONCLUSIONS: Varietal markers useful to detect the presence of Primitivo and Negro Amaro in the grape blend were identified by HRMS metabolomics, a method suitable to check the identity of grapes on arrival at the winery, as well as the fermenting musts. The effectiveness of the identified markers in the final wines have to be confirmed. Potentially, a similar approach can be used to reveal analogous frauds performed on other high-quality wines.
New acylated flavonols identified in Vitis vinifera grapes and wines.[Pubmed:30131163]
Food Res Int. 2018 Oct;112:98-107.
Flavonols are a class of polyphenol compounds whose importance for wine quality has increased as their structures and properties have become better understood. Here, the acetylated and p-coumaroylated derivatives of the flavonol 3-O-glucosides of isorhamnetin, Laricitrin and syringetin have been identified for the first time in Vitis vinifera grape skins and wines. First, the MS(2) fragmentation patterns of the new flavonol derivatives showed a main signal attributable to the expected flavonol aglycone. In the p-coumaroylated derivatives, the signal corresponding to the intermediate loss of the phenolic acid was also observed. The structures of the aglycones were confirmed by their respective MS(3) experiments that matched with those obtained from authentic standards of the aglycones. In addition, the fragmentation signals corresponding to the aglycone radical ions generated through homolytic cleavage assisted identification, and could support future studies of flavonoid compounds by ESI-MS. Using an HPLC-ESI-Q-ToF system, the observed m/z values of the compounds being studied were successfully matched with the expected formula. Surprisingly, just the minority methoxylated flavonol glucosides presented acylation, suggesting a high substrate specificity of the acyltransferases implicated in their synthesis. These findings show higher diversity of grape and wine flavonols. Additional studies and isolation strategies need to be followed to further characterize these metabolites as to test their presence in other grape varieties and it wines.
Laricitrin ameliorates lung cancer-mediated dendritic cell suppression by inhibiting signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.[Pubmed:27833081]
Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 20;7(51):85220-85234.
Natural polyphenolic compounds of grapes and their seeds are thought to be therapeutic adjuvants in a variety of diseases, including cancer prevention. This study was carried out to investigate the effect of grape phenolic compounds on the regulation of cancer-mediated immune suppression. Laricitrin exhibits the greatest potential to ameliorate the suppressive effects of lung cancer on dendritic cells' (DCs') differentiation, maturation and function. Human lung cancer A549 and CL1-5 cells change the phenotype of DCs that express to high levels of IL-10 and prime T cells towards an immune suppression type-2 response (Th2). Laricitrin treatment stimulated DC differentiation and maturation in the condition media of cancer cells, a finding supported by monocyte marker CD14's disappearance and DC marker CD1a's upregulation. Laricitrin decreases expression of IL-10 in cancer-conditioned DCs, and subsequently switches CD4+ T cell response from Th2 to Th1 in vitro and in vivo. Reversal of Laricitrin on lung cancer-induced DCs' paralysis was via inhibiting the phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3). Laricitrin also potentiated the anticancer activity of cisplatin in mouse models. Thus, Laricitrin could be an efficacious immunoadjuvant and have a synergistic effect when combined with chemotherapy.
[Flavonoids from leaves of Psidum littorale].[Pubmed:29908132]
Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2016 Nov;51(11):1745-50.
We investigated the chemical constituents of the leaves of Psidum littorale, which include 16 flavonoids, including seven flavonols, six flavonoid glycosides and three flavonones. The compounds were isolated by silica gel column chromatography. Their structures were elucidated on the basis of spectral analysis and by comparison with published data. Seven flavonols were kaempferol (1), isorhamnetin (2), myricetin- 3,7,3'-trimethyl ether(3), Laricitrin (4), quercetin (5), myricetin (6) and quercein-3,4'-dimethyl ether (7), six flavonoid glycosides were guaijaverin (8), hyperoside (9), 5,4'-dyhydroxy-3,7,5'-methoxyflavone-3'-O-beta-D- glucoside (10), Laricitrin-3-O-xyloside (11), myricetin-3-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranoside (12) and myricetin-3-O-beta-D- xyloside (13). Three flavonones were 4'-O-methyldihydroquercetin (14), dihydroapigenin (15) and ampelopsin 4'-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (16). Compound 10 is a new chemical, compounds 2-4, 7, 10-16 were first isolated from this plant. (1)H NMR and (13)C NMR data of compound 11 were not reported in literature.
Mass spectrometric imaging of flavonoid glycosides and biflavonoids in Ginkgo biloba L.[Pubmed:27233155]
Phytochemistry. 2016 Oct;130:201-6.
Ginkgo biloba L. is known to be rich in flavonoids and flavonoid glycosides. However, the distribution within specific plant organs (e.g. within leaves) is not known. By using HPLC-MS and MS/MS we have identified a number of previously known G. biloba flavonoid glycosides and biflavonoids from leaves. Namely, kaempferol, quercetin, isorhamnetin, myricetin, Laricitrin/mearnsetin and apigenin glycosides were identified. Furthermore, biflavonoids like ginkgetin/isoginkgetin were also detected. The application of MALDI mass spectrometric imaging, enabled the compilation of concentration profiles of flavonoid glycosides and biflavonoids in G. biloba L. leaves. Both, flavonoid glycosides and biflavonoids show a distinct distribution in leaf thin sections of G. biloba L.
Laricitrin suppresses increased benzo(a)pyrene-induced lung tumor-associated monocyte-derived dendritic cell cancer progression.[Pubmed:26998077]
Oncol Lett. 2016 Mar;11(3):1783-1790.
Benzo(a)pyrene (BaP) stimulates lung cancer cells, promoting monocyte-derived dendritic cells to secrete soluble factors, including heparin binding-epidermal growth factor and C-X-C motif chemokine 5. The secretions from monocyte-derived dendritic cells stimulate the progression of lung cancer cells, including the migration and invasion of cells. To the best of our knowledge, these secretions remain unknown, and require additional study. The present study identified that treatment with BaP-H1395-tumor-associated dendritic cell-conditioned medium had the most marked effect on cell migration and invasion. This result may be associated with the female gender, stage 2 adenocarcinoma or mutation of the proto-oncogene B-Raf (BRAF), according to the cell line background. Laricitrin, a dietary flavonoid derivative present in grapes and red wine, suppresses certain factors and decreases the progression of lung cancer cells that are promoted by BaP in the lung cancer tumor microenvironment. The results of the present study suggest that prolonged exposure to BaP exacerbates lung cancer, particularly in female lung cancer patients with the BRAF mutation, but that Laricitrin may ameliorate this effect.
Characterization of Non-Anthocyanic Flavonoids in Some Hybrid Red Grape Extracts Potentially Interesting for Industrial Uses.[Pubmed:26445038]
Molecules. 2015 Oct 2;20(10):18095-106.
Previous studies showed that hybrid grapes often have qualitatively and quantitatively higher polyphenolic contents than the common V. vinifera grape varieties. In general, these compounds are studied for grape chemotaxonomy and for nutraceutical purposes due to their relevant antioxidant activity. Non-anthocyanic flavonoid composition of five red hybrid grape varieties produced by crossing of V. vinifera, V. aestivalis, V. cinerea, V. berlandieri, V. labrusca, V. lincecumii, and V. rupestris were studied by liquid chromatography/high-resolution mass spectrometry. Thirty-one compounds were identified, including methylnaringenin, a tetrahydroxy-dimethoxyflavanone-hexoside, two flavonols (quercetin and a pentahydroxyflavone isomer), 20 glycoside flavonols (four quercetin, two myricetin, two kaempferol, three isorhamnetin, one Laricitrin, two syringetin, one kaempferide and two dihydroflavonol derivatives; myricetin-glucoside-glucuronide; myricetin-diglucoside; syringetin-dihexoside), three flavan-3-ols (-)-epicatechin, (+)-catechin, (-)-epicatechin gallate) and four proantocyanidins (procyanidin B1, procyanidin B2, procyanidin B3 or B4/B5, procyanidin T2 or T3/T4/C1). Seibel 19881, Seyve Villard 12-347 and Seyve Villard 29-399 were particularly rich in polyphenols. These findings emphasize that these grapes are especially interesting for the production of antioxidant extracts for nutraceutical and pharmaceutical uses.
Methylated derivatives of myricetin enhance life span in Caenorhabditis elegans dependent on the transcription factor DAF-16.[Pubmed:26281763]
Food Funct. 2015 Oct;6(10):3383-92.
Only certain flavonoids have been shown to enhance life span. This was pointed out for e.g. myricetin in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. However, the structural requirements responsible for this effect are not known. We used methylated derivatives of myricetin (Laricitrin, syringetin, myricetintrimethylether) to investigate if free OH moieties in the B-ring are necessary for the life span extending effect. In analogy to myricetin, all derivatives increased the life span, decreased oxidative stress (DCF) and decreased the accumulation of lipofuscin. In contrast to myricetin, the methylated compounds strongly enhanced the resistance against thermal stress. Furthermore, treatment with the derivatives induced a much stronger nuclear localization of the DAF-16 transcription factor (FoxO homologue). Additionally, no antioxidant effects and only minor effects on life span prolongation and stress resistance were detectable for the methylated compounds in a DAF-16 deficient nematode strain. Comparable to the dietary flavonoid myricetin, the methylated myricetin derivatives Laricitrin, syringetin and myricetintrimethylether strongly enhance the life span of C. elegans. Therefore, OH groups of ring B are not necessary for this effect. Only the methylated compounds increase the stress resistance of the nematode which was dependent on DAF-16. These findings suggest that methylation of myricetin increases the biofunctionality.
Application of recombinant Pediococcus acidilactici BD16 (fcs(+)/ech(+)) in malolactic fermentation.[Pubmed:25650327]
Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015 Apr;99(7):3015-28.
This study was conducted to enhance flavor characteristics of wine by malolactic fermentation using recombinant Pediococcus acidilactici BD16 (fcs (+)/ech (+)) encoding synthetic genes of feruloyl-CoA synthetase and enoyl-CoA hydratase. After malolactic fermentation, wine phenolics were characterized using LCMS-ESI technique and a significant improvement in the antioxidant activity and flavor characteristics of wine was observed due to increased concentration of cinnamic acid derivatives. This proof of concept study highlights the role of recombinant P. acidilactici BD16 (fcs (+)/ech (+)) in improving flavor as well as aroma of wine due to production of several phenolic derivatives during secondary fermentation. A novel metabolic pathway was predicted from mass spectral analysis data that indicates biotransformation of cinnamic acid and derivatives into apigenin, catechin, coniferyl aldehyde, cyanidin, hydroxybenzoic acids, Laricitrin, luteolin, malvidin 3-glucoside, myricetin, naringenin, pelargonin, piceatannol, querecitin, and vanillin that not only increased the overall consumer appreciation but also improved nutritional and probably the therapeutic properties of wines. This is a first evidence-based study where role of recombinant P. acidilactici BD16 (fcs (+)/ech (+)) in the wine secondary fermentation has been elucidated.


