L-Dihydroorotic acidCAS# 5988-19-2 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 5988-19-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 439216 | Appearance | Powder |
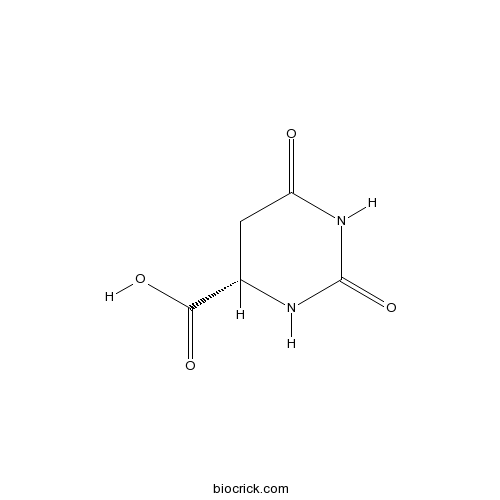
| Formula | C5H6N2O4 | M.Wt | 158 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 100 mg/mL (632.47 mM; Need ultrasonic) DMF : 33.33 mg/mL (210.80 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : 5 mg/mL (31.62 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
| Chemical Name | (4S)-2,6-dioxo-1,3-diazinane-4-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1C(NC(=O)NC1=O)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | UFIVEPVSAGBUSI-REOHCLBHSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C5H6N2O4/c8-3-1-2(4(9)10)6-5(11)7-3/h2H,1H2,(H,9,10)(H2,6,7,8,11)/t2-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

L-Dihydroorotic acid Dilution Calculator

L-Dihydroorotic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 6.3291 mL | 31.6456 mL | 63.2911 mL | 126.5823 mL | 158.2278 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.2658 mL | 6.3291 mL | 12.6582 mL | 25.3165 mL | 31.6456 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.6329 mL | 3.1646 mL | 6.3291 mL | 12.6582 mL | 15.8228 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1266 mL | 0.6329 mL | 1.2658 mL | 2.5316 mL | 3.1646 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0633 mL | 0.3165 mL | 0.6329 mL | 1.2658 mL | 1.5823 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Glabridin
Catalog No.:BCN1221
CAS No.:59870-68-7
- Oxybuprocaine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4691
CAS No.:5987-82-6
- Cyclosporin A
Catalog No.:BCC4773
CAS No.:59865-13-3
- Patchouli alcohol
Catalog No.:BCN4966
CAS No.:5986-55-0
- Palustrol
Catalog No.:BCN4100
CAS No.:5986-49-2
- Synephrine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4359
CAS No.:5985-28-4
- Ajmalimine
Catalog No.:BCN3420
CAS No.:59846-31-0
- Tenoxicam
Catalog No.:BCC4733
CAS No.:59804-37-4
- UK 14,304
Catalog No.:BCC5226
CAS No.:59803-98-4
- Vindolinine
Catalog No.:BCN7822
CAS No.:5980-02-9
- Cyclosporin C
Catalog No.:BCC8160
CAS No.:59787-61-0
- 6beta-Angeloyloxy-1beta,10beta-epoxy-9-oxofuranoeremophilane
Catalog No.:BCN7600
CAS No.:59780-08-4
- N-Formyl-Met-Leu-Phe
Catalog No.:BCC7205
CAS No.:59880-97-6
- ent-7alpha,9-Dihydroxy-15-oxokaur-16-en-19,6bet-olide
Catalog No.:BCN7401
CAS No.:59885-89-1
- 7-hydroxy-4-benzopyrone
Catalog No.:BCC9209
CAS No.:59887-89-7
- Loliolid
Catalog No.:BCN3655
CAS No.:5989-02-6
- Mesopsin
Catalog No.:BCN8050
CAS No.:5989-16-2
- Medicagenic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3893
CAS No.:599-07-5
- 3,3'-Sulfonyldianiline
Catalog No.:BCC8595
CAS No.:599-61-1
- Sulfasalazine
Catalog No.:BCC2545
CAS No.:599-79-1
- 3-Hydroxy-8,9-methylenedioxypterocarpene
Catalog No.:BCN1407
CAS No.:59901-98-3
- Vicenin -3
Catalog No.:BCN3014
CAS No.:59914-91-9
- HPI 1
Catalog No.:BCC3938
CAS No.:599150-20-6
- Vindesine sulfate
Catalog No.:BCC8266
CAS No.:59917-39-4
Bovine liver dihydropyrimidine amidohydrolase: pH dependencies of inactivation by chelators and steady-state kinetic properties.[Pubmed:3089167]
Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Jul;248(1):368-78.
Dihydropyrimidine amidohydrolase (EC 3.5.2.2) catalyzes the reversible hydrolysis of 5,6-dihydropyrimidines to the corresponding beta-ureido acids. Previous work has shown that incubation of this Zn2+ metalloenzyme with 2,6-dipicolinic acid, 8-hydroxyquinoline-5-sulfonic acid, or o-phenanthroline results in inactivation by Zn2+ removal by a reaction pathway involving formation of a ternary enzyme-Zn2+-chelator complex which subsequently dissociates to yield apoenzyme and the Zn2+-chelate (K. P. Brooks, E. A. Jones, B. D. Kim, and E. G. Sander, (1983) Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 226, 469-483). In the present work, the pH dependence of chelator inactivation is studied. The equilibrium constant for formation of the ternary complex is strongly pH dependent and increases with decreasing pH for all three chelators. There is a positive correlation between the value of the equilibrium constant observed for each chelator and the value of its stability constant for formation of Zn2+-chelate. The affinity of the chelators for the enzyme increases in the order 8-hydroxyquinoline-5-sulfonic acid greater than o-phenanthroline greater than 2,6-dipicolinic acid. The first-order rate constant for breakdown of the ternary complex to yield apoenzyme and Zn2+-chelate is invariant with pH for a given chelator but is different for each chelator, increasing in the reverse order. The pH dependence of the inactivation shows that two ionizable groups on the enzyme are involved in the inactivation. On the other hand, the steady-state kinetic behavior of the enzyme is well-described by ionization of a single group with a pK of 6.0 in the free enzyme. The basic form of the group is required for catalysis; protonation of the group decreases both Vmax and the apparent affinity for substrate. Conversely, binding of substrate decreases the pK of this group to about 5. L-Dihydroorotic acid is shown to be a competitive inhibitor of dihydropyrimidine amidohydrolase. Binding of L-Dihydroorotic acid increases the pK of the ionizable group to 6.5. The agreement between the pK in the enzyme-L-Dihydroorotic acid complex and the higher pK observed in the pH dependence of inactivation by chelators suggests that the same group is involved in the binding of acid, and chelators. The different effects of substrate and L-Dihydroorotic acid on the pK suggest that the binding modes of these two ligands may be different and suggest a structural basis for the mutally exclusive substrate specificities of dihydropyrimidine amidohydrolase and dihydroorotase.


