Kushenol WCAS# 254886-76-5 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 254886-76-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 10834013 | Appearance | Powder |
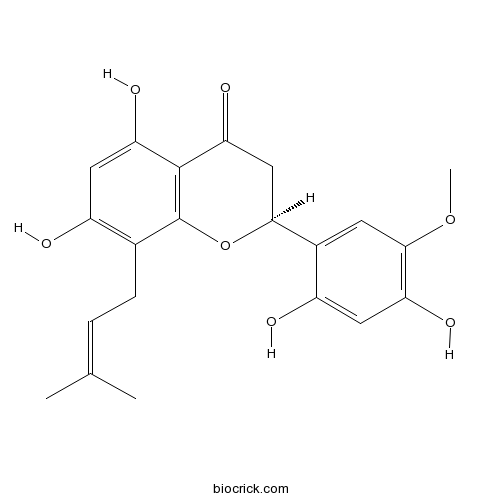
| Formula | C21H22O7 | M.Wt | 386.4 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (2S)-2-(2,4-dihydroxy-5-methoxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-8-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)-2,3-dihydrochromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | CC(=CCC1=C(C=C(C2=C1OC(CC2=O)C3=CC(=C(C=C3O)O)OC)O)O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | IPQQRODECSTJDH-SFHVURJKSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C21H22O7/c1-10(2)4-5-11-13(22)8-16(25)20-17(26)9-18(28-21(11)20)12-6-19(27-3)15(24)7-14(12)23/h4,6-8,18,22-25H,5,9H2,1-3H3/t18-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Targets | ROS | NF-kB | HSV |

Kushenol W Dilution Calculator

Kushenol W Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.588 mL | 12.94 mL | 25.8799 mL | 51.7598 mL | 64.6998 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5176 mL | 2.588 mL | 5.176 mL | 10.352 mL | 12.94 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2588 mL | 1.294 mL | 2.588 mL | 5.176 mL | 6.47 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0518 mL | 0.2588 mL | 0.5176 mL | 1.0352 mL | 1.294 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0259 mL | 0.1294 mL | 0.2588 mL | 0.5176 mL | 0.647 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 2,3-Bis(3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)butyrolactone
Catalog No.:BCN1473
CAS No.:25488-59-9
- Curryangine
Catalog No.:BCN7907
CAS No.:25488-37-3
- Talsupram hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7924
CAS No.:25487-28-9
- Emricasan
Catalog No.:BCC5367
CAS No.:254750-02-2
- 2-MPPA
Catalog No.:BCC7995
CAS No.:254737-29-6
- Demethyleneberberine
Catalog No.:BCN2829
CAS No.:25459-91-0
- H-Asn-OtBu
Catalog No.:BCC2877
CAS No.:25456-86-4
- H-D-Glu-OtBu
Catalog No.:BCC2938
CAS No.:25456-76-2
- Felbamate
Catalog No.:BCC4904
CAS No.:25451-15-4
- (+)-Afzelechin
Catalog No.:BCN5121
CAS No.:2545-00-8
- Dehydropitavastatin ethyl ester
Catalog No.:BCC8931
CAS No.:254452-91-0
- H-Cys(pMeOBzl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2909
CAS No.:2544-31-2
- Kushenol X
Catalog No.:BCN3350
CAS No.:254886-77-6
- 4-Allyloxy-2-hydroxybenzophenone
Catalog No.:BCC8675
CAS No.:2549-87-3
- Tasquinimod
Catalog No.:BCC1987
CAS No.:254964-60-8
- 3-Epioleanolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3050
CAS No.:25499-90-5
- 4-Phenylbutan-2-one
Catalog No.:BCN3808
CAS No.:2550-26-7
- 1-Acetyl-4-piperidinecarboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8447
CAS No.:25503-90-6
- Bruceine B
Catalog No.:BCN7615
CAS No.:25514-29-8
- Bruceine C
Catalog No.:BCN8000
CAS No.:25514-30-1
- Bruceine A
Catalog No.:BCC5311
CAS No.:25514-31-2
- Ibotenic acid
Catalog No.:BCC6591
CAS No.:2552-55-8
- Isoferulic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5122
CAS No.:25522-33-2
- Z-Ile-Glu-Pro-Phe-Ome
Catalog No.:BCC5526
CAS No.:255257-97-4
Nonlinear pulse compression to 43 W GW-class few-cycle pulses at 2 mum wavelength.[Pubmed:29028042]
Opt Lett. 2017 Oct 15;42(20):4179-4182.
High-average power laser sources delivering intense few-cycle pulses in wavelength regions beyond the near infrared are promising tools for driving the next generation of high-flux strong-field experiments. In this work, we report on nonlinear pulse compression to 34.4 muJ-, 2.1-cycle pulses with 1.4 GW peak power at a central wavelength of 1.82 mum and an average power of 43 W. This performance level was enabled by the combination of a high-repetition-rate ultrafast thulium-doped fiber laser system and a gas-filled antiresonant hollow-core fiber.
THE 2017 13(TH) ANNUAL DAVID W. KENNEDY, MD, LECTURE The evolution of outcomes in sinus surgery for chronic rhinosinusitis: past, present, and future.[Pubmed:29028274]
Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2017 Dec;7(12):1121-1126.
This is an edited transcript from the 2017 13th Annual David W. Kennedy, MD, Lecture, presented to the American Rhinologic Society during the 63rd Annual Meeting.
Kit (W-sh) Mutation Prevents Cancellous Bone Loss during Calcium Deprivation.[Pubmed:29032463]
Calcif Tissue Int. 2018 Jan;102(1):93-104.
Calcium is essential for normal bone growth and development. Inadequate calcium intake increases the risk of osteoporosis and fractures. Kit ligand/c-Kit signaling plays an important role in regulating bone homeostasis. Mice with c-Kit mutations are osteopenic. The present study aimed to investigate whether impairment of or reduction in c-Kit signaling affects bone turnover during calcium deprivation. Three-week-old male WBB6F1/J-Kit (W) /Kit (W-v) /J (W/W (v) ) mice with c-Kit point mutation, Kit (W-sh) /HNihrJaeBsmJ (W (sh) /W (sh) ) mice with an inversion mutation in the regulatory elements upstream of the c-Kit promoter region, and their wild-type controls (WT) were fed either a normal (0.6% calcium) or a low calcium diet (0.02% calcium) for 3 weeks. muCT analysis indicated that both mutants fed normal calcium diet had significantly decreased cortical thickness and cancellous bone volume compared to WT. The low calcium diet resulted in a comparable reduction in cortical bone volume and cortical thickness in the W/W (v) and W (sh) /W (sh) mice, and their corresponding controls. As expected, the low calcium diet induced cancellous bone loss in the W/W (v) mice. In contrast, W (sh) /W (sh) cancellous bone did not respond to this diet. This c-Kit mutation prevented cancellous bone loss by antagonizing the low calcium diet-induced increase in osteoblast and osteoclast numbers in the W (sh) /W (sh) mice. Gene expression profiling showed that calcium deficiency increased Osx, Ocn, Alp, type I collagen, c-Fms, M-CSF, and RANKL/OPG mRNA expression in controls; however, the W (sh) mutation suppressed these effects. Our findings indicate that although calcium restriction increased bone turnover, leading to osteopenia, the decreased c-Kit expression levels in the W (sh) /W (sh) mice prevented the low calcium diet-induced increase in cancellous bone turnover and bone loss but not the cortical bone loss.
The first anion-exchange membrane fuel cell to exceed 1 W cm(-2) at 70 degrees C with a non-Pt-group (O2) cathode.[Pubmed:29034381]
Chem Commun (Camb). 2017 Aug 22;53(86):11771-11773.
Anion-exchange membrane fuel cells face two challenges: performance and durability. Addressing the first, we demonstrate high performance with both O2 and CO2-free air supplies, even when using a Ag/C cathode. This was enabled by the development of a radiation-grafted anion-exchange membrane that was less than 30 mum thick when hydrated.
Accuracy of W' Recovery Kinetics in High Performance Cyclists-Modeling Intermittent Work Capacity.[Pubmed:29035607]
Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2018 Jul 1;13(6):724-728.
PURPOSE: With knowledge of an individual's critical power and W', the SKIBA 2 model provides a framework with which to track W' balance during intermittent high-intensity work bouts. There are fears that the time constant controlling the recovery rate of W' (tauW') may require refinement to enable effective use in an elite population. METHODS: Four elite endurance cyclists completed an array of intermittent exercise protocols to volitional exhaustion. Each protocol lasted approximately 3.5-6 min and featured a range of recovery intensities, set in relation to the athlete's critical power (DCP). Using the framework of the SKIBA 2 model, the tauW' values were modified for each protocol to achieve an accurate W' at volitional exhaustion. Modified tauW' values were compared with equivalent SKIBA 2 tauW' values to assess the difference in recovery rates for this population. Plotting modified tauW' values against DCP showed the adjusted relationship between work rate and recovery rate. RESULTS: Comparing modified tauW' values against the SKIBA 2 tauW' values showed a negative bias of 112 (46) s (mean +/- 95% confidence limits), suggesting that athletes recovered W' faster than predicted by SKIBA 2 (P = .0001). The modified tauW'-DCP relationship was best described by a power function: tauW' = 2287.2 x DCP(-0.688) (R(2) = .433). CONCLUSIONS: The current SKIBA 2 model is not appropriate for use in elite cyclists, as it underpredicts the recovery rate of W'. The modified tauW' equation presented will require validation but appears more appropriate for high-performance athletes. Individual tauW' relationships may be necessary to maximize the model's validity.


