Isoferulic acidCAS# 25522-33-2 |
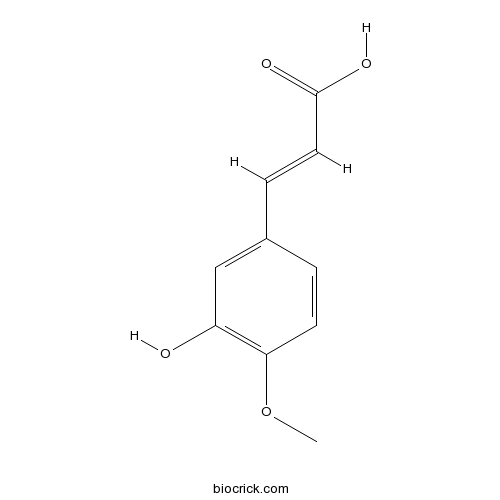
- Isoferulic Acid
Catalog No.:BCX1035
CAS No.:537-73-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 25522-33-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 736186 | Appearance | White-beige powder |
| Formula | C10H10O4 | M.Wt | 194.2 |
| Type of Compound | Phenylpropanoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | 537-73-5;3-Hydroxy-4-methoxycinnamic acid | ||
| Solubility | Sparingly soluble in ethan | ||
| Chemical Name | (E)-3-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-enoic acid | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C=C(C=C1)C=CC(=O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QURCVMIEKCOAJU-HWKANZROSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C10H10O4/c1-14-9-4-2-7(6-8(9)11)3-5-10(12)13/h2-6,11H,1H3,(H,12,13)/b5-3+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Isoferulic acid is an effective natural antioxidant in both lipid and aqueous media, it may be a new promising anti-glycation agent for the prevention of diabetic complications via inhibition of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) formation and oxidation-dependent protein damage. Isoferulic acid is a novel and potent inhibitor of murine IL-8 production, it also has inhibitory effect on mushroom tyrosinase.3-Hydroxy-4-methoxycinnamic acid shows anti-inflammatory, antiviral, antioxidant, and antidiabetic properties, it is an anti-glycation agent, inhibits fructose- and glucose-mediated protein glycation. |
| Targets | HDAC | GLUT | IL Receptor | Antifection |
| In vitro | Isoferulic acid, a new anti-glycation agent, inhibits fructose- and glucose-mediated protein glycation in vitro.[Pubmed: 23722732]Molecules. 2013 May 30;18(6):6439-54.The inhibitory activity of Isoferulic acid (IFA) on fructose- and glucose-mediated protein glycation and oxidation of bovine serum albumin (BSA) was investigated. Evaluation of antioxidant activity of isoferulic acid in vitro.[Pubmed: 21941899]Nat Prod Commun. 2011 Sep;6(9):1285-8.Isoferulic acid (3-hydroxy-4-methoxycinnamic acid, IFA), the isomer of ferulic acid (4-hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamic acid), is a rare phenolic acid occurring in Rhizoma Cimicifugae. Unlike ferulic acid, which has been well investigated, the antioxidant activity of IFA has not been measured. Inhibitory effect of ferulic acid and isoferulic acid on murine interleukin-8 production in response to influenza virus infections in vitro and in vivo.[Pubmed: 7617763 ]Planta Med. 1995 Jun;61(3):221-6.We investigated the effect of ferulic acid (FA) and Isoferulic acid (IFA), which are active components of the rhizoma of Cimicifuga species used frequently as anti-inflammatory drugs in Japanese Oriental medicines, on murine interleukin-8 (IL-8) production in response to influenza virus infections in vitro and in vivo by antibody-sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Anticancer Candidates Derived from Natural Cinnamic Acids.[Pubmed: 25634446]Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2015;15(8):980-7.Cancer is the most dangerous disease that causes deaths all over the world. Natural products have afforded a rich source of drugs in a number of therapeutic fields including anticancer agents. Many significant drugs have been derived from natural sources by structural optimization of natural products. Cinnamic acid has gained great interest due to its antiproliferative, antioxidant, antiangiogenic and antitumorigenic potency. Evaluation of antioxidant activity of isoferulic acid in vitro.[Pubmed: 21941899]Nat Prod Commun. 2011 Sep;6(9):1285-8.Isoferulic acid (3-Hydroxy-4-methoxycinnamic acid, IFA), the isomer of ferulic acid (4-hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamic acid), is a rare phenolic acid occurring in Rhizoma Cimicifugae. Unlike ferulic acid, which has been well investigated, the antioxidant activity of 3-Hydroxy-4-methoxycinnamic acid has not been measured. |
| Kinase Assay | Kinetics governing the inhibitory effect of 3-hydroxy-4-methoxycinnamic acid on tyrosinase-catalyzed reactions[Reference: WebLink]Search for novel histone deacetylase inhibitors. Part II: design and synthesis of novel isoferulic acid derivatives.[Pubmed: 24702857]Kinetics of inhibitory effect of isoferulic acid on mushroom tyrosinase.[Pubmed: 23931087]J Cosmet Sci. 2013 Jul-Aug;64(4):235-41.A study on the kinetics of inhibitory effect of Isoferulic acid on the monophenolase and diphenolase activity of mushroom tyrosinase was carried out using enzymological kinetic analysis method in a Na2HPO4-NaH2PO4 buffer solution (pH = 6.8) at 30°C. Bioorg Med Chem. 2014 May 1;22(9):2707-13.Previously, we described the discovery of potent ferulic acid-based histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACIs) with halogeno-acetanilide as novel surface recognition moiety (SRM). Modern Food Science & Technology, 2015, 31(4):192-6.
|
| Animal Research | Antihyperglycemic action of isoferulic acid in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.[Pubmed: 10683186]Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Feb;129(4):631-6.Wistar rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes (STZ-diabetic rats), which is similar to human insulin-dependent diabetic mellitus (IDDM), were employed to investigate the antihyperglycemic action of Isoferulic acid. |

Isoferulic acid Dilution Calculator

Isoferulic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.1493 mL | 25.7467 mL | 51.4933 mL | 102.9866 mL | 128.7333 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.0299 mL | 5.1493 mL | 10.2987 mL | 20.5973 mL | 25.7467 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5149 mL | 2.5747 mL | 5.1493 mL | 10.2987 mL | 12.8733 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.103 mL | 0.5149 mL | 1.0299 mL | 2.0597 mL | 2.5747 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0515 mL | 0.2575 mL | 0.5149 mL | 1.0299 mL | 1.2873 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Ibotenic acid
Catalog No.:BCC6591
CAS No.:2552-55-8
- Bruceine A
Catalog No.:BCC5311
CAS No.:25514-31-2
- Bruceine C
Catalog No.:BCN8000
CAS No.:25514-30-1
- Bruceine B
Catalog No.:BCN7615
CAS No.:25514-29-8
- 1-Acetyl-4-piperidinecarboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8447
CAS No.:25503-90-6
- 4-Phenylbutan-2-one
Catalog No.:BCN3808
CAS No.:2550-26-7
- 3-Epioleanolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3050
CAS No.:25499-90-5
- Tasquinimod
Catalog No.:BCC1987
CAS No.:254964-60-8
- 4-Allyloxy-2-hydroxybenzophenone
Catalog No.:BCC8675
CAS No.:2549-87-3
- Kushenol X
Catalog No.:BCN3350
CAS No.:254886-77-6
- Kushenol W
Catalog No.:BCN3307
CAS No.:254886-76-5
- 2,3-Bis(3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)butyrolactone
Catalog No.:BCN1473
CAS No.:25488-59-9
- Z-Ile-Glu-Pro-Phe-Ome
Catalog No.:BCC5526
CAS No.:255257-97-4
- Mayumbine
Catalog No.:BCN5123
CAS No.:25532-45-0
- Propidium iodide
Catalog No.:BCC8015
CAS No.:25535-16-4
- 1-(4-Hydroxybenzoyl)glucose
Catalog No.:BCN6900
CAS No.:25545-07-7
- 7-Methoxy-4-methylcoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN6540
CAS No.:2555-28-4
- Efetaal
Catalog No.:BCN8494
CAS No.:2556-10-7
- 1,6,7-Trihydroxyxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN5124
CAS No.:25577-04-2
- Delta-Tocotrienol
Catalog No.:BCN6696
CAS No.:25612-59-3
- 7beta-Acetoxytaxuspine C
Catalog No.:BCN7219
CAS No.:256347-91-8
- BAY 41-2272
Catalog No.:BCC7932
CAS No.:256376-24-6
- SEW 2871
Catalog No.:BCC7312
CAS No.:256414-75-2
- Schleicheol 1
Catalog No.:BCN4661
CAS No.:256445-66-6
Antihyperglycemic action of isoferulic acid in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.[Pubmed:10683186]
Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Feb;129(4):631-6.
Wistar rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes (STZ-diabetic rats), which is similar to human insulin-dependent diabetic mellitus (IDDM), were employed to investigate the antihyperglycemic action of Isoferulic acid. A single intravenous injection of Isoferulic acid decreased the plasma glucose in a dose-dependent manner in the STZ-diabetic rats. Repeated intravenous administration of STZ-diabetic rats with Isoferulic acid (5.0 mg kg(-1)) also resulted in the lowering of plasma glucose after one day. Stimulatory effects of Isoferulic acid on the glucose uptake and glycogen synthesis in soleus muscles isolated from STZ-diabetic rats were also obtained indicating an increase of glucose utilization following Isoferulic acid treatment which was not dependent on insulin. The mRNA level of glucose transporter subtype 4 form (GLUT4) in soleus muscle was raised by Isoferulic acid after repeated treatment for 1 day in STZ-diabetic rats. Similar repeated treatment with Isoferulic acid reversed the elevated mRNA level of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) in liver of STZ-diabetic rats to the normal level. However, expression of GLUT4 and PEPCK genes in nondiabetic rats were not influenced by similar treatment with Isoferulic acid. These results suggest that Isoferulic acid can inhibit hepatic gluconeogenesis and/or increase the glucose utilization in peripheral tissue to lower plasma glucose in diabetic rats lacking insulin.
Inhibitory effect of ferulic acid and isoferulic acid on murine interleukin-8 production in response to influenza virus infections in vitro and in vivo.[Pubmed:7617763]
Planta Med. 1995 Jun;61(3):221-6.
We investigated the effect of ferulic acid (FA) and Isoferulic acid (IFA), which are active components of the rhizoma of Cimicifuga species used frequently as anti-inflammatory drugs in Japanese Oriental medicines, on murine interleukin-8 (IL-8) production in response to influenza virus infections in vitro and in vivo by antibody-sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. In the in vitro study, the murine macrophage cell line RAW 264.7 was infected with influenza virus at a dose of 10 plaque forming units (PFU)/cell and cultured in the presence or absence of drugs. Both FA and IFA reduced the IL-8 levels in the 20-h conditioned medium in comparison with control in a dose-dependent manner. The effect of IFA was greater than that of FA: IL-8 levels were reduced to 43% and 56% of the control in the presence of 100 micrograms/ml of IFA and FA, respectively. In the in vivo study, mice were infected with 1,000 PFU of virus and received daily oral administrations of Cimicifuga heracleifolia extract (5 mg/mouse/day), FA (0.5 mg/mouse/day), IFA (0.125 mg/mouse/day), or phosphate buffered saline. The three drugs showed a tendency to reduce IL-8 levels in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) obtained 2 days after infection. Moreover, both FA and IFA also significantly reduced the number of exuded neutrophils into BAL. However, the drug administrations did not affect the virus yields in BAL. These data suggest that FA and IFA are novel and potent inhibitors of murine IL-8 production and might act as one of the main components of anti-inflammatory rhizoma of Cimicifuga species.
Anticancer agents derived from natural cinnamic acids.[Pubmed:25634446]
Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2015;15(8):980-7.
Cancer is the most dangerous disease that causes deaths all over the world. Natural products have afforded a rich source of drugs in a number of therapeutic fields including anticancer agents. Many significant drugs have been derived from natural sources by structural optimization of natural products. Cinnamic acid has gained great interest due to its antiproliferative, antioxidant, antiangiogenic and antitumorigenic potency. Currently it has been observed that cinnamic acid and its analogs such as caffeic acid, sinapic acid, ferulic acid, and Isoferulic acid display various pharmacological activities, such as immunomodulation, anti-inflammation, anticancer and antioxidant. They have served to be the major sources of potential leading anticancer compounds. In this review, we focus on the anticancer potency of cinnamic acid derivatives and novel strategies to design these derivatives. We hope this review will be useful for researchers who are interested in developing anticancer agents.
Search for novel histone deacetylase inhibitors. Part II: design and synthesis of novel isoferulic acid derivatives.[Pubmed:24702857]
Bioorg Med Chem. 2014 May 1;22(9):2707-13.
Previously, we described the discovery of potent ferulic acid-based histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACIs) with halogeno-acetanilide as novel surface recognition moiety (SRM). In order to improve the affinity and activity of these HDACIs, twenty seven Isoferulic acid derivatives were described herein. The majority of title compounds displayed potent HDAC inhibitory activity. In particular, IF5 and IF6 exhibited significant enzymatic inhibitory activities, with IC50 values of 0.73 +/- 0.08 and 0.57 +/- 0.16 muM, respectively. Furthermore, these compounds showed moderate antiproliferative activity against human cancer cells. Especially, IF6 displayed promising profile as an antitumor candidate with IC50 value of 3.91 +/- 0.97 muM against HeLa cells. The results indicated that these Isoferulic acid derivatives could serve as promising lead compounds for further optimization.
Isoferulic acid, a new anti-glycation agent, inhibits fructose- and glucose-mediated protein glycation in vitro.[Pubmed:23722732]
Molecules. 2013 May 30;18(6):6439-54.
The inhibitory activity of Isoferulic acid (IFA) on fructose- and glucose-mediated protein glycation and oxidation of bovine serum albumin (BSA) was investigated. Our data showed that IFA (1.25-5 mM) inhibited the formation of fluorescent advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and non-fluorescent AGE [Nepsilon-(carboxymethyl) lysine: CML], as well as the level of fructosamine. IFA also prevented protein oxidation of BSA indicated by decreasing protein carbonyl formation and protein thiol modification. Furthermore, IFA suppressed the formation of beta-cross amyloid structures of BSA. Therefore, IFA might be a new promising anti-glycation agent for the prevention of diabetic complications via inhibition of AGEs formation and oxidation-dependent protein damage.
Evaluation of antioxidant activity of isoferulic acid in vitro.[Pubmed:21941899]
Nat Prod Commun. 2011 Sep;6(9):1285-8.
Isoferulic acid (3-hydroxy-4-methoxycinnamic acid, IFA), the isomer of ferulic acid (4-hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamic acid), is a rare phenolic acid occurring in Rhizoma Cimicifugae. Unlike ferulic acid, which has been well investigated, the antioxidant activity of IFA has not been measured. In this study, IFA was systematically evaluated for its in vitro antioxidant activity for the first time. IC50 values were calculated of 7.30 +/- 0.57, 4.58 +/- 0.17, 1.08 +/- 0.01, 8.84 +/- 0.43, 7.69 +/- 0.39, 1.57 +/- 0.2, 13.33 +/- 0.49 microg/mL, respectively, for lipid peroxidation, DPPH (1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl radical) and ABTS (3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulfonic acid diammonium salt) radical scavenging, reducing power on Fe3+ and CU2+ ions, and hydroxyl and superoxide anion radical scavenging. Comparison with the IC50 values with those of the positive controls, Trolox and butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA), it can be concluded that Isoferulic acid is an effective natural antioxidant in both lipid and aqueous media.
Kinetics of inhibitory effect of isoferulic acid on mushroom tyrosinase.[Pubmed:23931087]
J Cosmet Sci. 2013 Jul-Aug;64(4):235-41.
A study on the kinetics of inhibitory effect of Isoferulic acid on the monophenolase and diphenolase activity of mushroom tyrosinase was carried out using enzymological kinetic analysis method in a Na2HPO4-NaH2PO4 buffer solution (pH = 6.8) at 30 degrees C. It was found that Isoferulic acid efficiently inhibits both monophenolase and diphenolase activities of mushroom tyrosinase under experimental conditions. Concentrations of Isoferulic acid leading to 50% rate inhibition (IC50) on monophenolase and diphenolase activity were calculated to be 0.13 mmol/L and 0.39 mmol/L, respectively, which are much lower than that of arbutin (IC50 = 5.3 mmol/L for diphenolase activity). The presence of Isoferulic acid also prolongs the lag period in the oxidation process of l-tyrosine via tyrosinase-a 4.3-min lagging was observed with the presence of 0.20 mmol/L Isoferulic acid-compared to a 1.1-min lagging in the absence of Isoferulic acid. The Lineweaver-Burk plot demonstrates a competitive behavior of Isoferulic acid in the tyrosinase oxidation of l-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine, with maximum reaction rate (vm) and inhibition constant (KI) at 64.5 microM/min and 0.11 mmol/L, respectively.


