KB-R7943 mesylateInhibitor of the reverse mode of the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger CAS# 182004-65-5 |
- SEA0400
Catalog No.:BCC1941
CAS No.:223104-29-8
- Chlorthalidone
Catalog No.:BCC4649
CAS No.:77-36-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 182004-65-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 9823846 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C17H21N3O6S2 | M.Wt | 427.5 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 27 mg/mL (63.16 mM) H2O : 4.3 mg/mL (10.06 mM; Need warming) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
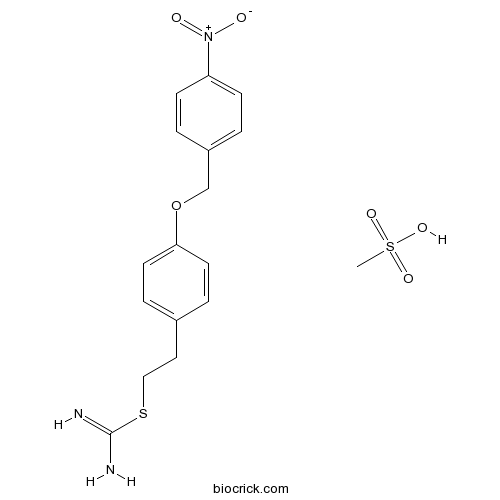
| Chemical Name | methanesulfonic acid;2-[4-[(4-nitrophenyl)methoxy]phenyl]ethyl carbamimidothioate | ||
| SMILES | CS(=O)(=O)O.C1=CC(=CC=C1CCSC(=N)N)OCC2=CC=C(C=C2)[N+](=O)[O-] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | WGIKEBHIKKWJLG-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C16H17N3O3S.CH4O3S/c17-16(18)23-10-9-12-3-7-15(8-4-12)22-11-13-1-5-14(6-2-13)19(20)21;1-5(2,3)4/h1-8H,9-11H2,(H3,17,18);1H3,(H,2,3,4) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent, selective inhibitor of the reverse mode of the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (IC50 = 0.7 μM). Also inhibits the mitochondrial Ca2+ uniporter (MCU; IC50 = 5.5 μM). Does not affect Na+-dependent transport systems or ionotropic glutamate receptors. |

KB-R7943 mesylate Dilution Calculator

KB-R7943 mesylate Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3392 mL | 11.6959 mL | 23.3918 mL | 46.7836 mL | 58.4795 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4678 mL | 2.3392 mL | 4.6784 mL | 9.3567 mL | 11.6959 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2339 mL | 1.1696 mL | 2.3392 mL | 4.6784 mL | 5.848 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0468 mL | 0.2339 mL | 0.4678 mL | 0.9357 mL | 1.1696 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0234 mL | 0.117 mL | 0.2339 mL | 0.4678 mL | 0.5848 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
KB-R7943 mesylate is a potent and selective inhibitor of Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (NCE) with IC50 value of 0.7 μM.
NCE is an antiporter membrane protein that exchanges 3 Na+ for 1 Ca2+ and can function to cause Ca2+ accumulation (reverse mode) or Ca2+ extrusion (forward mode) depending on the concentrations of each ion on either side of the membrane and on the membrane potential [1].
In transfected Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells expressing NCE, KB-R7943 (10 μM) inhibited NCX activity at high (140mM) but not at low (10mM) cytosolic Na+ concentrations [2].
In cultured rat forebrain neurons loaded with glutamate- (3 μM), N-methyl-D-aspartate- (30 μM), kainate- (100 μM) or KCl- (50 mM) induced [Ca2+] transients, KBR7943 inhibited these transients with IC50 values of 6.6, 8.2, 5.2 and 2.9 μM, respectively. While, KB-R7943 didn’t inhibit glutamate-induced neuronal injury [1]. In mice with ischemic acute renal failure (ARF), KB-R7943 significantly decreased endothelin-1 (ET-1) in the kidney and relieved the ARF-induced renal dysfunction [3].
References:
[1]. Hoyt KR, Arden SR, Aizenman E, et al. Reverse Na+/Ca2+ exchange contributes to glutamate-induced intracellular Ca2+ concentration increases in cultured rat forebrain neurons. Mol Pharmacol, 1998, 53(4): 742-749.
[2]. Condrescu M, Reeves JP. Inhibition of sodium-calcium exchange by KB-R7943: Dodecylamine and sphingosine in transfected Chinese hamster ovary cells. Cell Calcium, 2010, 47(5): 404-411.
[3]. Yamashita J, Ogata M, Takaoka M, et al. KB-R7943, a selective Na+/Ca2+ exchange inhibitor, protects against ischemic acute renal failure in mice by inhibiting renal endothelin-1 overproduction. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol, 2001, 37(3): 271-279.
- Meliasendanin D
Catalog No.:BCN7610
CAS No.:1820034-05-6
- BL 1249
Catalog No.:BCC7777
CAS No.:18200-13-0
- Ethyl beta-D-fructofuranoside
Catalog No.:BCN1145
CAS No.:1820-84-4
- Angenomalin
Catalog No.:BCN8246
CAS No.:18199-64-9
- Naringenin-4',7-diacetate
Catalog No.:BCN1144
CAS No.:18196-13-9
- Fmoc-Dap-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3187
CAS No.:181954-34-7
- Sequirin C
Catalog No.:BCN4688
CAS No.:18194-29-1
- DLPC
Catalog No.:BCC7929
CAS No.:18194-25-7
- KC 12291 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7618
CAS No.:181936-98-1
- Crotonoside
Catalog No.:BCN6281
CAS No.:1818-71-9
- 25-Anhydrocimigenol 3-O-beta-D-xyloside
Catalog No.:BCN3436
CAS No.:181765-11-7
- (-)-beta-Pinene
Catalog No.:BCN3857
CAS No.:18172-67-3
- 6-Angeloyloxyditropan-3-yl itaconate
Catalog No.:BCN1867
CAS No.:182015-05-0
- Nitrosostromelin
Catalog No.:BCN1745
CAS No.:182064-61-5
- Quinovic acid 3-O-(3',4'-O-isopropylidene)-beta-D-fucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN1519
CAS No.:182132-59-8
- Nyssoside
Catalog No.:BCN1146
CAS No.:182138-70-1
- 3,4-seco-Olean-12-en-4-ol-3,28-dioic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7151
CAS No.:182249-69-0
- Clausine I
Catalog No.:BCN4687
CAS No.:182261-94-5
- Lirioprolioside B
Catalog No.:BCN2740
CAS No.:182284-68-0
- Synthalin sulfate
Catalog No.:BCC6730
CAS No.:182285-12-7
- Antibiotic ZG 1494alpha
Catalog No.:BCN1850
CAS No.:182320-33-8
- Antibiotic 2158
Catalog No.:BCN1825
CAS No.:182320-34-9
- Baldrinal
Catalog No.:BCN2667
CAS No.:18234-46-3
- Rupatadine Fumarate
Catalog No.:BCC4535
CAS No.:182349-12-8
Mechanical strain injury increases intracellular sodium and reverses Na+/Ca2+ exchange in cortical astrocytes.[Pubmed:15779085]
Glia. 2005 Jul;51(1):35-46.
Traditionally, astrocytes have been considered less susceptible to injury than neurons. Yet, we have recently shown that astrocyte death precedes neuronal death in a rat model of traumatic brain injury (TBI) (Zhao et al.: Glia 44:140-152, 2003). A main mechanism hypothesized to contribute to cellular injury and death after TBI is elevated intracellular calcium ([Ca2+]i). Since calcium regulation is also influenced by regulation of intracellular sodium ([Na+]i), we used an in vitro model of strain-induced traumatic injury and live-cell fluorescent digital imaging to investigate alterations in [Na+]i in cortical astrocytes after injury. Changes in [Na+]i, or [Ca2+]i were monitored after mechanical injury or L-glutamate exposure by ratiometric imaging of sodium-binding benzofuran isophthalate (SBFI-AM), or Fura-2-AM, respectively. Mechanical strain injury or exogenous glutamate application produced increases in [Na+]i that were dependent on the severity of injury or concentration. Injury-induced increases in [Na+]i were significantly reduced, but not completely eliminated, by inhibition of glutamate uptake by DL-threo-beta-benzyloxyaspartate (TBOA). Blockade of sodium-dependent calcium influx through the sodium-calcium exchanger with 2-[2-[4-(4-Nitrobenzyloxy)phenyl]ethyl]isothiourea mesylate (KB-R7943) reduced [Ca2+]i after injury. KB-R7943 also reduced astrocyte death after injury. These findings suggest that in astrocytes subjected to mechanical injury or glutamate excitotoxicity, increases in intracellular Na+ may be a critical component in the injury cascade and a therapeutic target for reduction of lasting deficits after traumatic brain injury.
Na-K-Cl cotransporter-mediated intracellular Na+ accumulation affects Ca2+ signaling in astrocytes in an in vitro ischemic model.[Pubmed:15509746]
J Neurosci. 2004 Oct 27;24(43):9585-97.
Na-K-Cl cotransporter isoform 1 (NKCC1) plays an important role in maintenance of intracellular Na+, K+, and Cl- levels in astrocytes. We propose that NKCC1 may contribute to perturbations of ionic homeostasis in astrocytes under ischemic conditions. After 3-8 hr of oxygen and glucose deprivation (OGD), NKCC1-mediated 86Rb influx was significantly increased in astrocytes from NKCC1 wild-type (NKCC1+/+) and heterozygous mutant (NKCC1+/-) mice. Phosphorylated NKCC1 protein was increased in NKCC1+/+ astrocytes at 2 hr of OGD. Two hours of OGD and 1 hr of reoxygenation (OGD/REOX) triggered an 3.6-fold increase in intracellular Na+ concentration ([Na+]i) in NKCC1+/+ astrocytes. Inhibition of NKCC1 activity by bumetanide or ablation of the NKCC1 gene significantly attenuated the rise in [Na+]i. Moreover, NKCC1+/+ astrocytes swelled by 10-30% during 20-60 min of OGD. Either genetic ablation of NKCC1 or inhibition of NKCC1 by bumetanide-attenuated OGD-mediated swelling. An NKCC1-mediated increase in [Na+]i may subsequently affect Ca2+ signaling through the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (NCX). A rise in [Ca2+]i was detected after OGD/REOX in the presence of a sarcoplasmic-endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Ca2+-ATPase inhibitor thapsigargin. Moreover, OGD/REOX led to a significant increase in Ca2+ release from ER Ca2+ stores. Furthermore, KB-R7943 (2-[2-[4(4-nitrobenzyloxy)phenyl]ethyl]isothiourea mesylate), an inhibitor of reverse-mode operation of NCX, abolished the OGD/REOX-induced enhancement in filling of ER Ca2+ stores. OGD/REOX-mediated Ca2+ accumulation in ER Ca2+ stores was absent when NKCC1 activity was ablated or pharmacologically inhibited. These findings imply that stimulation of NKCC1 activity leads to Na+ accumulation after OGD/REOX and that subsequent reverse-mode operation of NCX contributes to increased Ca2+ accumulation by intracellular Ca2+ stores.
Sodium hydrogen exchange 1 (NHE-1) regulates connexin 43 expression in cardiomyocytes via reverse mode sodium calcium exchange and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase-dependent pathways.[Pubmed:18650245]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008 Oct;327(1):105-13.
Connexin 43, the major connexin isoform in gap junctions of cardiac ventricular myocytes, undergoes changes in distribution and expression in cardiac diseases. The Na(+)-H(+) exchanger (NHE-1), a key mediator of hypertrophy and heart failure, has been shown to be localized in the cardiomyocyte gap junctional regions; however, whether NHE-1 regulates gap junction proteins in the hypertrophied cardiomyocyte is not known. To address this question, neonatal rat ventricular myocytes were treated with phenylephrine (PE) for 24 h to induce hypertrophy. Increased Cx43 expression observed with PE treatment (132.4 +/- 6.3% compared to control; P < 0.05) was further significantly augmented by the specific NHE-1 inhibitor EMD87580 [N-[2-methyl-4,5-bis(methylsulfonyl)-benzoyl]-guanidine hydrochloride] (173.2 +/- 8.7% increase compared to control; P < 0.05 versus PE), an effect that was mimicked by another NHE-1 inhibitor cariporide [4-isopropyl-3-(methylsulfonyl)benzoyl-guanidine methanesulfonate]. PE-induced hypertrophy was associated with mitogen-activated protein kinase c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase (JNK) 1/2 activation, whereas inhibition of JNK1/2 with either SP600125 [anthra(1,9-cd)pyrazol-6(2H)-one 1,9-pyrazoloanthrone] or small interfering RNA significantly increased PE-induced up-regulation of Cx43 protein levels. Inhibition of reverse mode Na(+)-Ca(2+) exchange (NCX) with KB-R7943 [2-[2-[4-(4-nitrobenzyloxy)phenyl]ethyl]isothiourea mesylate] partially reversed JNK1/2 activation (195.2 +/- 21.4 versus 143.7 +/- 14.4% with KB-R7943; P < 0.05) and augmented up-regulation of Cx43 protein (121.1 +/- 8.3 versus 215.9 +/- 25.6% with KB-R7943; P < 0.05) in the presence of PE. Our results demonstrate that NHE-1 negatively regulates Cx43 protein expression in PE-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy via a JNK1/2-dependent pathway, which is probably activated by reverse mode NCX activity.
Fowl (Gallus domesticus) sperm motility depends upon mitochondrial calcium cycling driven by extracellular sodium.[Pubmed:15355879]
Biol Reprod. 2005 Jan;72(1):97-101.
A relationship between extracellular Ca(+2), fowl sperm phospholipase A2 activity, long-chain acylcarnitine content, and motility was demonstrated in previous work. Sperm motility appeared to depend upon Na+-dependent Ca(+2) cycling when sperm were incubated at body temperature without glucose. In the present work, motility decreased as a function of time when sperm were incubated in 2 mM Ca(+2) prepared with either buffered isotonic sucrose or LiCl. However, this effect was less pronounced in the case of LiCl. The sparing effect of Li+ was attributed to the mitochondrial Na+/Ca(+2) exchanger. Motile concentration decreased exponentially in response to micromolar concentrations of CGP 37157, a specific inhibitor of the mitochondrial Na+/Ca(+2) exchanger. KB-R7943 mesylate, an inhibitor of the reverse mode of the Na+/Ca(+2) exchanger, prevented re-initiation of motility when exogenous Ca(+2) was added to sperm rendered immotile by incubation with 1,2-bis-(o-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid, a high-affinity Ca(+2) chelator. The presence of voltage-gated Ca(+2) channels was confirmed by the effect of nifedipine on motile concentration. Neither motile concentration nor straight line velocity was affected by either ouabain or orthovanadate, which inhibit Na+-K+ ATPase and Ca(+2)-ATPase, respectively. In summary, we infer that 1) fowl sperm motility is dependent upon extracellular Ca(+2) cycling through mitochondria; 2) such cycling is dependent upon extracellular Na+; and 3) fowl sperm conserve ATP by moving neither Na+ nor Ca(+2) by active transport. Understanding the relationship between mitochondrial Ca(+2) cycling and ATP production may be applicable to long-term semen storage.
Chronic nicotine exposure selectively activates a carrier-mediated release of endogenous glutamate and aspartate from rat hippocampal synaptosomes.[Pubmed:22417725]
Neurochem Int. 2012 May;60(6):622-30.
The effect of chronic nicotine treatment on the release of endogenous glutamate (GLU), aspartate (ASP) and GABA evoked in vitro by KCl, 4-aminopyridine (4AP) and nicotinic agonists in synaptosomes of rat hippocampus was investigated. Rats were chronically administered with nicotine bitartrate or saline vehicle each for 14 days using osmotic mini-pumps. Hippocampal synaptosomes were stimulated with KCl, 4AP, nicotine or with choline (Ch) and 5-iodo-A-85380 dihydrochloride (5IA85380). The GLU and ASP overflow evoked by Ch, nicotine, KCl and 4AP were increased in treated animals while the nicotine-evoked GABA overflow was reduced and that evoked by Ch, KCl and 4AP was unaffected. The 5IA85380-evoked overflow of the three aminoacids (AAs) was always reduced. The increase of ASP and GLU overflow evoked by KCl, 4AP or Ch was blocked by dl-threo-beta-benzyloxyaspartic acid (dl-TBOA), a carrier transporter inhibitor, and by inhibitors of the Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchangers 2-[[4-[(4-nitrophenyl)methoxy]phenyl]methyl]-4-thiazolidinecarboxylic acid ethyl ester (SN-6) and 2-[2-[4-(4-nitrobenzyloxy)phenyl]ethyl]isothiourea mesylate (KB-R7943). In conclusion long-term nicotine treatment may selectively increase GLU and ASP overflow elicited by KCl, 4AP and Ch through the activation of a carrier-mediated release mechanism and completely abolished the stimulatory effects of alpha4beta2 nAChRs which modulate the release of all the three AA.


