(-)-JQ1BET bromodomain inhibitor CAS# 1268524-71-5 |
- RVX-208
Catalog No.:BCC4475
CAS No.:1044870-39-4
- GSK 525768A
Catalog No.:BCC1603
CAS No.:1260530-25-3
- I-BET151 (GSK1210151A)
Catalog No.:BCC4476
CAS No.:1300031-49-5
- GSK1324726A
Catalog No.:BCC4038
CAS No.:1300031-52-0
- PFI-1 (PF-6405761)
Catalog No.:BCC2225
CAS No.:1403764-72-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1268524-71-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 49871818 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C23H25ClN4O2S | M.Wt | 456.99 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (218.82 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
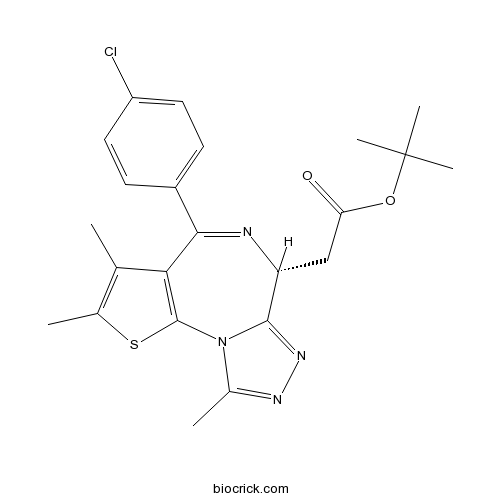
| SMILES | CC1=C(SC2=C1C(=NC(C3=NN=C(N32)C)CC(=O)OC(C)(C)C)C4=CC=C(C=C4)Cl)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DNVXATUJJDPFDM-QGZVFWFLSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C23H25ClN4O2S/c1-12-13(2)31-22-19(12)20(15-7-9-16(24)10-8-15)25-17(11-18(29)30-23(4,5)6)21-27-26-14(3)28(21)22/h7-10,17H,11H2,1-6H3/t17-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Inactive control for (+)-JQ1. Exhibits no significant interaction with BRD1-4 or a panel of other bromodomains. |

(-)-JQ1 Dilution Calculator

(-)-JQ1 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1882 mL | 10.9412 mL | 21.8823 mL | 43.7646 mL | 54.7058 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4376 mL | 2.1882 mL | 4.3765 mL | 8.7529 mL | 10.9412 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2188 mL | 1.0941 mL | 2.1882 mL | 4.3765 mL | 5.4706 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0438 mL | 0.2188 mL | 0.4376 mL | 0.8753 mL | 1.0941 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0219 mL | 0.1094 mL | 0.2188 mL | 0.4376 mL | 0.5471 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
(-)-JQ1 is the stereoisomer of JQ1, a cell-permeable small-molecule inhibitor of BET bromodomain that competitively binds to acetyl-lysine recognition motifs. JQ1 is a novel thieno-triazolo-1,4-diazepine with an appended and bulky t-butyl ester functional group at C6 position in its chemical structure, which allows for additional pendant group diversity and mitigates binding to the central benzodiazepine receptor. JQ1 competitively binds to the bromodomain displacing the BRD4 fusion oncoprotein from chromatin, which induces squamous differentiation and specific anti-proliferative effect in BRD4-dependent cell lines and patient-derived xenograft models. However, study results have shown that (-)-JQ1 fails to significantly interact with any bromodomain tested and exhibits inhibition against BRD4(1) with 50% inhibition concentration IC50 value of 10,000 nM.
Reference
Filippakopoulos P, Qi J, Picaud S, Shen Y, Smith WB, Fedorov O, Morse EM, Keates T, Hickman TT, Felletar I, Philpott M, Munro S, McKeown MR, Wang Y, Christie AL, West N, Cameron MJ, Schwartz B, Heightman TD, La Thangue N, French CA, Wiest O, Kung AL, Knapp S, Bradner JE. Selective inhibition of BET bromodomains. Nature. 2010 Dec 23;468(7327):1067-73. doi: 10.1038/nature09504. Epub 2010 Sep 24.
- Bromodomain Inhibitor, (+)-JQ1
Catalog No.:BCC1132
CAS No.:1268524-70-4
- 8alpha-Acetoxyarglabin
Catalog No.:BCN7315
CAS No.:126829-70-7
- 13-Acetoxy-3beta-hydroxygermacra-1(10)E,4E,7(11)-trien-12,6alpha-olide
Catalog No.:BCN7314
CAS No.:126829-66-1
- 5,7,3'-Trihydroxy-4'-methoxy-8-prenylflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN1590
CAS No.:1268140-15-3
- Ulipristal acetate
Catalog No.:BCC4068
CAS No.:126784-99-4
- Sventenic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3923
CAS No.:126778-79-8
- GR 89696 fumarate
Catalog No.:BCC7083
CAS No.:126766-32-3
- Sarafotoxin S6a
Catalog No.:BCC5834
CAS No.:126738-34-9
- Acetylsventenic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4849
CAS No.:126737-42-6
- Tilifodiolide
Catalog No.:BCN6145
CAS No.:126724-95-6
- Gancaonin I
Catalog No.:BCN7144
CAS No.:126716-36-7
- Gancaonin G
Catalog No.:BCN6837
CAS No.:126716-34-5
- MC 1046
Catalog No.:BCC1733
CAS No.:126860-83-1
- Ssioriside
Catalog No.:BCN6146
CAS No.:126882-53-9
- 3-Methoxy-5-heneicosylphenol
Catalog No.:BCN6147
CAS No.:126882-76-6
- MK 1903
Catalog No.:BCC6242
CAS No.:1268882-43-4
- LGX818
Catalog No.:BCC4184
CAS No.:1269440-17-6
- Sar-[D-Phe8]-des-Arg9-Bradykinin
Catalog No.:BCC5996
CAS No.:126959-88-4
- Methylenedihydrotanshinquinone
Catalog No.:BCN3221
CAS No.:126979-81-5
- Tetrahydro tanshinone I
Catalog No.:BCN2602
CAS No.:126979-84-8
- CDK inhibitor II
Catalog No.:BCC1464
CAS No.:1269815-17-9
- 5-Hydroxy-1,7-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)heptan-3-yl acetate
Catalog No.:BCN6586
CAS No.:1269839-24-8
- 1-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-7-(4-hydroxyphenyl)heptane-3,5-diyl diacetate
Catalog No.:BCN6572
CAS No.:1269839-26-0
- Locustatachykinin I
Catalog No.:BCC5926
CAS No.:126985-97-5
The BET bromodomain inhibitor JQ1 radiosensitizes non-small cell lung cancer cells by upregulating p21.[Pubmed:28143717]
Cancer Lett. 2017 Apr 10;391:141-151.
Radiotherapy is an important treatment modality in the management of locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, radioresistance markedly impairs its efficacy in clinic. Bromodomain and extra-terminal (BET) bromodomain inhibitors have demonstrated dramatic antitumor activity in several preclinical human cancer models. In this study, we investigated for the first time the effect of JQ1, a novel BET bromodomain inhibitor, on tumor cell radiosensitivity of NSCLC in vitro and in vivo. Our results demonstrated that JQ1 significantly enhanced the effect of irradiation in NSCLC cell lines through a c-myc-independent mechanism. The notable findings in response to this combined treatment were prolonged delay in IR-induced DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair, induced robust G2/M checkpoint arrest and increased cell apoptosis. Additional investigations revealed that induction of p21 played an important role in its radiosensitizing effects. In conclusion, these results suggested that BET bromodomain inhibition might offer a potential strategy for enhancing the effects of radiotherapy and reducing radioresistance.
Bromodomain inhibitors, JQ1 and I-BET 762, as potential therapies for pancreatic cancer.[Pubmed:28254412]
Cancer Lett. 2017 May 28;394:76-87.
Bromodomain inhibitors (JQ1 and I-BET 762) are a new generation of selective, small molecule inhibitors that target BET (bromodomain and extra terminal) proteins. By impairing their ability to bind to acetylated lysines on histones, bromodomain inhibitors interfere with transcriptional initiation and elongation. BET proteins regulate several genes responsible for cell cycle, apoptosis and inflammation. In this study, JQ1 and I-BET 762 decreased c-Myc and p-Erk 1/2 protein levels and inhibited proliferation in pancreatic cancer cells. The tumor microenvironment is known to play an important role in pancreatic cancer, and these drugs suppressed the production of nitric oxide and a variety of inflammatory cytokines, including IL-6, CCL2, and GM-CSF, in both immune and pancreatic cancer cells in vitro. Notably, the bromodomain inhibitors also reduced protein levels of p-Erk 1/2 and p-STAT3 in mouse models of pancreatic cancer. All of these proteins are essential for tumor promotion, progression and metastasis. In conclusion, the bromodomain inhibitors JQ1 and I-BET 762 targeted and suppressed multiple pathways in pancreatic cancer. I-BET 762 and a number of other bromodomain inhibitors are currently being tested in several clinical trials, making them potentially promising drugs for the treatment of pancreatic cancer, an often-fatal disease.
Gene expression profiling of patient-derived pancreatic cancer xenografts predicts sensitivity to the BET bromodomain inhibitor JQ1: implications for individualized medicine efforts.[Pubmed:28275007]
EMBO Mol Med. 2017 Apr;9(4):482-497.
c-MYC controls more than 15% of genes responsible for proliferation, differentiation, and cellular metabolism in pancreatic as well as other cancers making this transcription factor a prime target for treating patients. The transcriptome of 55 patient-derived xenografts show that 30% of them share an exacerbated expression profile of MYC transcriptional targets (MYC-high). This cohort is characterized by a high level of Ki67 staining, a lower differentiation state, and a shorter survival time compared to the MYC-low subgroup. To define classifier expression signature, we selected a group of 10 MYC target transcripts which expression is increased in the MYC-high group and six transcripts increased in the MYC-low group. We validated the ability of these markers panel to identify MYC-high patient-derived xenografts from both: discovery and validation cohorts as well as primary cell cultures from the same patients. We then showed that cells from MYC-high patients are more sensitive to JQ1 treatment compared to MYC-low cells, in monolayer, 3D cultured spheroids and in vivo xenografted tumors, due to cell cycle arrest followed by apoptosis. Therefore, these results provide new markers and potentially novel therapeutic modalities for distinct subgroups of pancreatic tumors and may find application to the future management of these patients within the setting of individualized medicine clinics.
PD-L1 Is a Therapeutic Target of the Bromodomain Inhibitor JQ1 and, Combined with HLA Class I, a Promising Prognostic Biomarker in Neuroblastoma.[Pubmed:28270499]
Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Aug 1;23(15):4462-4472.
Purpose: This study sought to evaluate the expression of programmed cell death-ligand-1 (PD-L1) and HLA class I on neuroblastoma cells and programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) and lymphocyte activation gene 3 (LAG3) on tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes to better define patient risk stratification and understand whether this tumor may benefit from therapies targeting immune checkpoint molecules.Experimental Design:In situ IHC staining for PD-L1, HLA class I, PD-1, and LAG3 was assessed in 77 neuroblastoma specimens, previously characterized for tumor-infiltrating T-cell density and correlated with clinical outcome. Surface expression of PD-L1 was evaluated by flow cytometry and IHC in neuroblastoma cell lines and tumors genetically and/or pharmacologically inhibited for MYC and MYCN. A dataset of 477 human primary neuroblastomas from GEO and ArrayExpress databases was explored for PD-L1, MYC, and MYCN correlation.Results: Multivariate Cox regression analysis demonstrated that the combination of PD-L1 and HLA class I tumor cell density is a prognostic biomarker for predicting overall survival in neuroblastoma patients (P = 0.0448). MYC and MYCN control the expression of PD-L1 in neuroblastoma cells both in vitro and in vivo Consistently, abundance of PD-L1 transcript correlates with MYC expression in primary neuroblastoma.Conclusions: The combination of PD-L1 and HLA class I represents a novel prognostic biomarker for neuroblastoma. Pharmacologic inhibition of MYCN and MYC may be exploited to target PD-L1 and restore an efficient antitumor immunity in high-risk neuroblastoma. Clin Cancer Res; 23(15); 4462-72. (c)2017 AACR.
Selective inhibition of BET bromodomains.[Pubmed:20871596]
Nature. 2010 Dec 23;468(7327):1067-73.
Epigenetic proteins are intently pursued targets in ligand discovery. So far, successful efforts have been limited to chromatin modifying enzymes, or so-called epigenetic 'writers' and 'erasers'. Potent inhibitors of histone binding modules have not yet been described. Here we report a cell-permeable small molecule (JQ1) that binds competitively to acetyl-lysine recognition motifs, or bromodomains. High potency and specificity towards a subset of human bromodomains is explained by co-crystal structures with bromodomain and extra-terminal (BET) family member BRD4, revealing excellent shape complementarity with the acetyl-lysine binding cavity. Recurrent translocation of BRD4 is observed in a genetically-defined, incurable subtype of human squamous carcinoma. Competitive binding by JQ1 displaces the BRD4 fusion oncoprotein from chromatin, prompting squamous differentiation and specific antiproliferative effects in BRD4-dependent cell lines and patient-derived xenograft models. These data establish proof-of-concept for targeting protein-protein interactions of epigenetic 'readers', and provide a versatile chemical scaffold for the development of chemical probes more broadly throughout the bromodomain family.


