Indole-3-acrylic acid methyl esterCAS# 19626-92-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 19626-92-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 12572409 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C12H11NO2 | M.Wt | 201.2 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
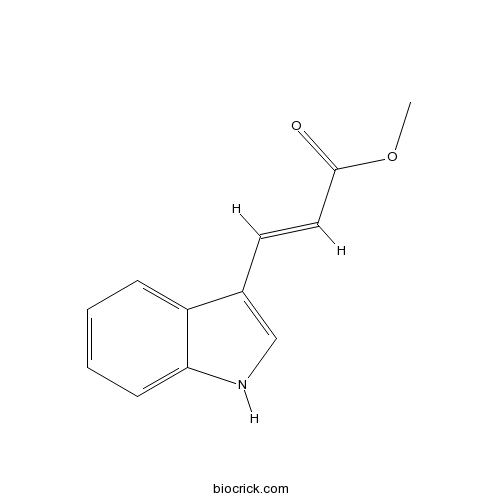
| Chemical Name | methyl (E)-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)prop-2-enoate | ||
| SMILES | COC(=O)C=CC1=CNC2=CC=CC=C21 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | JKVXFZPEUCTHQO-VOTSOKGWSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C12H11NO2/c1-15-12(14)7-6-9-8-13-11-5-3-2-4-10(9)11/h2-8,13H,1H3/b7-6+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Indole-3-acrylic acid methyl ester Dilution Calculator

Indole-3-acrylic acid methyl ester Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.9702 mL | 24.8509 mL | 49.7018 mL | 99.4036 mL | 124.2545 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.994 mL | 4.9702 mL | 9.9404 mL | 19.8807 mL | 24.8509 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.497 mL | 2.4851 mL | 4.9702 mL | 9.9404 mL | 12.4254 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0994 mL | 0.497 mL | 0.994 mL | 1.9881 mL | 2.4851 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0497 mL | 0.2485 mL | 0.497 mL | 0.994 mL | 1.2425 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Angelol A
Catalog No.:BCN8036
CAS No.:19625-17-3
- 17 alpha-propionate
Catalog No.:BCC1296
CAS No.:19608-29-8
- 25S-Inokosterone
Catalog No.:BCN3873
CAS No.:19595-18-7
- (R)-Nepicastat HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4315
CAS No.:195881-94-8
- HTMT dimaleate
Catalog No.:BCC6736
CAS No.:195867-54-0
- 2,6,16-Kauranetriol 2-O-beta-D-allopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN1509
CAS No.:195735-16-1
- Atrasentan hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1380
CAS No.:195733-43-8
- (+-)-Byakangelicin
Catalog No.:BCN5000
CAS No.:19573-01-4
- 2,16,19-Kauranetriol 2-O-beta-D-allopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN1510
CAS No.:195723-38-7
- Methyl 4-O-feruloylquinate
Catalog No.:BCC9041
CAS No.:195723-10-5
- Piromidic Acid
Catalog No.:BCC3840
CAS No.:19562-30-2
- AP1903
Catalog No.:BCC5361
CAS No.:195514-63-7
- 4-Methoxycinnamaldehyde
Catalog No.:BCN2700
CAS No.:1963-36-6
- Bay 11-7085
Catalog No.:BCC5105
CAS No.:196309-76-9
- Axillarine
Catalog No.:BCN2059
CAS No.:19637-66-2
- Prosaptide TX14(A)
Catalog No.:BCC8020
CAS No.:196391-82-9
- Siegesmethyethericacid
Catalog No.:BCC9248
CAS No.:196399-16-3
- (4S,5R)-3-tert-butoxycarbony-2-(4-anisy)-4-phenyl-5-oxazolidinecarboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCN8365
CAS No.:196404-55-4
- (RS)-3,5-DHPG
Catalog No.:BCC6613
CAS No.:19641-83-9
- 2S-Amino-3R-octadecanol
Catalog No.:BCN1775
CAS No.:196497-48-0
- 4-Acetyl Ramelteon
Catalog No.:BCC1107
CAS No.:1346598-94-4
- BIBX 1382
Catalog No.:BCC1418
CAS No.:196612-93-8
- Oseltamivir
Catalog No.:BCC1825
CAS No.:196618-13-0
- Giffonin R
Catalog No.:BCN8116
CAS No.:1966183-72-1
Synthesis and evaluation of anti-oxidant and cytotoxic activities of novel 10-undecenoic acid methyl ester based lipoconjugates of phenolic acids.[Pubmed:28179945]
Beilstein J Org Chem. 2017 Jan 4;13:26-32.
The synthesis of five novel methyl 10-undecenoate-based lipoconjugates of phenolic acids from undecenoic acid was carried out. Undecenoic acid was methylated to methyl 10-undecenoate which was subjected to a thiol-ene reaction with cysteamine hydrochloride. Further amidation of the amine was carried out with different phenolic acids such as caffeic, ferulic, sinapic, coumaric and cinnamic acid. All synthesized compounds were fully characterized and their structures were con fi rmed by spectral data. The anti-oxidant activity of the synthesized lipoconjugates of phenolic acids was studied by the 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical scavenging assay and also by the inhibition of linoleic acid oxidation in micellar medium by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). The prepared compounds were also screened for their cytotoxic activity against five cell lines. It was observed that the lipoconjugates of caffeic acid, sinapic acid, ferulic acid, and coumaric acid displayed anticancer and anti-oxidant properties. The anticancer properties of these derivatives have been assessed by their IC50 inhibitory values in the proliferation of MDA-MB231, SKOV3, MCF7, DU 145 and HepG2 cancer cell lines.
Gibbs energy additivity approaches to QSRR in generating gas chromatographic retention time for identification of fatty acid methyl ester.[Pubmed:28168549]
Anal Bioanal Chem. 2017 Apr;409(11):2777-2789.
The Gibbs energy additivity method was used to correlate the retention time (t R) of common fatty acid methyl esters (FAMEs) to their chemical structures. The t R of 20 standard FAMEs eluted from three capillary columns of different polarities (ZB-WAXplus, BPX70, and SLB-IL111) under both isothermal gas chromatography and temperature-programmed gas chromatography (TPGC) conditions were accurately predicted. Also, the predicted t R of FAMEs prepared from flowering pak choi seed oil obtained by multistep TPGC with the BPX70 column were within 1.0% of the experimental t R. The predicted t R or mathematical t R (t R(math)) values could possibly be used as references in identification of common FAMEs. Hence, FAMEs prepared from horse mussel and fish oil capsules were chromatographed on the BPX70 and ZB-WAXplus columns in single-step and multistep TPGC. Identification was done by comparison of t R with the t R of standard FAMEs and with t R(math). Both showed correct identifications. The proposed model has six numeric constants. Five of six could be directly transferred to other columns of the same stationary phase. The first numeric constant (a), which contained the column phase ratio, could also be transferred with the adjustment of the column phase ratio to the actual phase ratio of the transferred column. Additionally, the numeric constants could be transferred across laboratories, with similar correction of the first numeric constant. The TPGC t R predicted with the transferred column constants were in good agreement with the reported experimental t R of FAMEs. Moreover, hexane was used in place of the conventional t M marker in the calculation. Hence, the experimental methods were much simplified and practically feasible. The proposed method for using t R(math) as the references would provide an alternative to the uses of real FAMEs as the references. It is simple and rapid and with good accuracy compared with the use of experimental t R as references.
Protocatechuic acid methyl ester ameliorates fluoride toxicity in A549 cells.[Pubmed:28012895]
Food Chem Toxicol. 2017 Nov;109(Pt 2):941-950.
The present study is aimed to determine the potential benefits of protocatechuic acid methyl ester (PCAME) against fluoride (F(-)) induced lung toxicity using A549 cells. The cells were treated with sodium fluoride (NaF) alone and in combination with PCAME for different time points (0-24 h) and evaluated for intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, F(-) content, oxidative stress markers, apoptosis and mRNA expression of redox signaling and inflammatory genes. The results shown that PCAME alleviates the toxic effects of F(-)via modulating its bioavailability, intracellular calcium level, mitochondrial membrane integrity and redox signaling in A549 cells. F(-) induced changes in ROS generation, oxidative stress markers, TUNEL positive cells and mRNA levels of inflammatory genes were further normalized by PCAME. Taken together, these findings revealed that PCAME effectively attenuated the F(-) induced changes in oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis markers by reducing its cellular content, ROS generation and biochemical and molecular changes. Thus PCAME can be used as a nutraceutical agent for F(-) toxicity.
Gallic acid attenuates hypertension, cardiac remodeling, and fibrosis in mice with NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester-induced hypertension via regulation of histone deacetylase 1 or histone deacetylase 2.[Pubmed:28234674]
J Hypertens. 2017 Jul;35(7):1502-1512.
OBJECTIVE: Gallic acid, a natural chemical found in plants, has been reported to show antioxidant, anticancer, and anti-inflammatory effects. We investigated the efficacy of a short-term or long-term treatment with gallic acid in N-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME)-induced hypertensive mice and the underlying regulatory mechanism. METHODS: Hypertension was sufficiently induced after 2 weeks of L-NAME administration. Cardiac remodeling was assessed by echocardiography. Hypertrophic markers, transcription factors, and fibrosis-related gene expression were evaluated by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction and western blotting. RESULTS: Gallic acid effectively lowered SBP, regardless of the administration route (intraperitoneal or oral). L-NAME increased the left ventricular (LV) thickness without an increase in the total heart weight. Weekly echocardiography demonstrated that gallic acid significantly reduced LV posterior wall and septum thickness in chronic L-NAME mice from 3 to 7 weeks. The administration of gallic acid to mice showed a dual preventive and therapeutic effect on the L-NAME-induced LV remodeling. The effect was associated with the suppression of the gene expression of hypertrophy markers and the GATA-binding factor 6 (GATA6) transcription factor. Short-term or long-term treatment with gallic acid attenuated cardiac fibrosis and reduced the expression of histone deacetylase 1 and 2 in H9c2 cells and in rat primary cardiac fibroblasts, as well as in vivo. Small interfering RNA knockdown confirmed the association of these enzymes with L-NAME-induced cardiac remodeling and fibrosis. CONCLUSION: These results suggested that gallic acid may be a potential therapeutic agent for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases with hypertension and cardiac fibrosis.


