HomoharringtonineInhibitor of protein synthesis. Antileukemic agent CAS# 26833-87-4 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 26833-87-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 72332 | Appearance | White powder |
| Formula | C29H39NO9 | M.Wt | 545.61 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Omacetaxine mepesuccinate; HHT | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 50 mg/mL (91.64 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
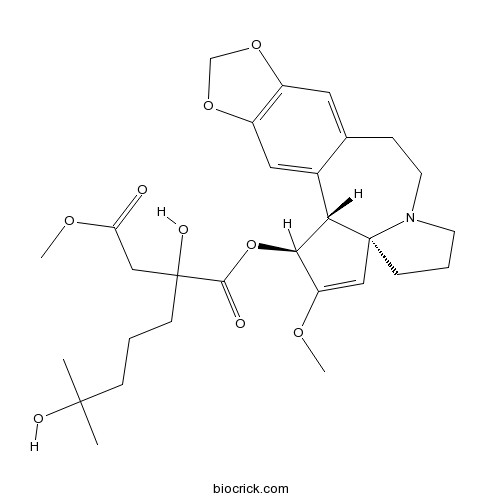
| SMILES | CC(C)(CCCC(CC(=O)OC)(C(=O)OC1C2C3=CC4=C(C=C3CCN5C2(CCC5)C=C1OC)OCO4)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | HYFHYPWGAURHIV-ZEDNPHJLSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C29H39NO9/c1-27(2,33)8-5-10-29(34,16-23(31)36-4)26(32)39-25-22(35-3)15-28-9-6-11-30(28)12-7-18-13-20-21(38-17-37-20)14-19(18)24(25)28/h13-15,24-25,33-34H,5-12,16-17H2,1-4H3/t24-,25+,28-,29?/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Homoharringtonine, a plant alkaloid with antitumor and antileukemic properties, inhibit protein translation by preventing the initial elongation step of protein synthesis via an interaction with the ribosomal A-site. Homoharringtonine might have clinical activity in some patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. |
| Targets | Caspase | PARP | Bcl-2/Bax | MEK | ERK |
| In vitro | Homoharringtonine mediates myeloid cell apoptosis via upregulation of pro-apoptotic bax and inducing caspase-3-mediated cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP).[Pubmed: 15224352 ]Am J Hematol. 2004 Jul;76(3):199-204.Homoharringtonine (HHT) is a plant alkaloid with antileukemia activity that is currently being used for treatment of acute, chronic leukemias and MDS. Homoharringtonine induces apoptosis and inhibits STAT3 via IL-6/JAK1/STAT3 signal pathway in Gefitinib-resistant lung cancer cells.[Pubmed: 26166037]Sci Rep. 2015 Jul 13;5:8477.Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are mostly used in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treatment. Unfortunately, treatment with Gefitinib for a period of time will result in drug resistance and cause treatment failure in clinic. |
| In vivo | Homoharringtonine-based induction regimens for patients with de-novo acute myeloid leukaemia: a multicentre, open-label, randomised, controlled phase 3 trial.[Pubmed: 23664707]Lancet Oncol. 2013 Jun;14(7):599-608.Homoharringtonine-based induction regimens have been widely used in China for patients with acute myeloid leukaemia. However, their efficacy has not been tested in a multicentre randomised controlled trial in a large population. We assessed the efficacy and safety of Homoharringtonine-based induction treatment for management of newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukaemia.
|
| Kinase Assay | Homoharringtonine contributes to imatinib sensitivity by blocking the EphB4/RhoA pathway in chronic myeloid leukemia cell lines.[Pubmed: 24415355 ]Homoharringtonine increases intestinal epithelial permeability by modulating specific claudin isoforms in Caco-2 cell monolayers.[Pubmed: 25513955]Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015 Jan;89:232-8.Homoharringtonine (HHT), a natural alkaloid produced by various Cephalotaxus species, has antileukemic activity in acute and chronic myelogenous leukemia. However, Homoharringtonine can also induce unanticipated effects in the gastrointestinal tract, such as diarrhea and nausea/vomiting, but the mechanism behind these adverse effects has not been clarified. Med Oncol. 2014 Feb;31(2):836.The purpose was to investigate the role of EphB4 in imatinib (IM) resistance and the mechanism responsible for Homoharringtonine (HHT) contributing to imatinib sensitivity for a chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) cell lines. |

Homoharringtonine Dilution Calculator

Homoharringtonine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8328 mL | 9.1641 mL | 18.3281 mL | 36.6562 mL | 45.8203 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3666 mL | 1.8328 mL | 3.6656 mL | 7.3312 mL | 9.1641 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1833 mL | 0.9164 mL | 1.8328 mL | 3.6656 mL | 4.582 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0367 mL | 0.1833 mL | 0.3666 mL | 0.7331 mL | 0.9164 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0183 mL | 0.0916 mL | 0.1833 mL | 0.3666 mL | 0.4582 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Homoharringtonine is a cytotoxic alkaloid, induces apoptosis and inhibits STAT3 via IL-6/JAK1/STAT3 signal pathway in Gefitinib-resistant lung cancer cells.
In Vitro:Homoharringtonine inhibits IL-6-induced STAT3 phosphorylation in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Homoharringtonine (HHT) inhibits cells growth, cell viability and colony formation, as well as induced cell apoptosis through mitochondria pathway. The cytotoxicity of Homoharringtonine on human NSCLC cell lines is investigated, A549 (wild type EGFR) and NCI-H1975 (H1975, mutant EGFR with L858R and T790M), Gefitinib is used as a control. By MTT assay, Homoharringtonine has moderate cytotoxicity to A549 with an IC50 of 3.7 μM and H1975 cells are more sensitive to Homoharringtonine with an IC50 of 0.7 μM. Homoharringtonine inhibits the cell proliferation and growth of A549 cells and H1975 cells in a time- and dose-dependent manner through MTT assay. By trypan blue exclusion assay, Homoharringtonine rapidly reduces viable A549 and H1975 cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Homoharringtonine significantly inhibits the clonogenic ability of A549 and H1975 cells[1].
In Vivo:Homoharringtonine (10 mg/kg) efficiently represses tumor growth compared to vehicle control or Gefitinib (P<0.05). Additionally, Homoharringtonine (HHT) treatment does not reduce the mice body weight, which suggests that Homoharringtonine has no apparent side effect. All the mice are euthanized, the tumors are isolated and imaged and the tumor sample cells are harvested to extract protein for determination if Homoharringtonine inhibits STAT3 phosphorylation via western blot. The level of STAT3 phosphorylation and MCL1 from Homoharringtonine treatment group is significantly decreased compared to vehicle control or Gefitinib treatment. Meanwhile, consistant with the results in the above, AKT1/2/3 and ERK1/2 phosphorylation is not inhibited with Homoharringtonine treatment. To further examine the STAT3 phosphorylation in the xenograft tumor samples with different treatments, the tumor samples are frozen and cutted into 10 μm sections for fluorescent immunohistochemistry. Homoharringtonine treatment inhibits STAT3 phosphorylation compared to vehicle control or Gefitinib treatment[1].
References:
[1]. Cao W, et al. Homoharringtonine induces apoptosis and inhibits STAT3 via IL-6/JAK1/STAT3 signal pathway in Gefitinib-resistant lung cancer cells. Sci Rep. 2015 Jul 13;5:8477
- Harringtonine
Catalog No.:BCN6794
CAS No.:26833-85-2
- Coronalolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5153
CAS No.:268214-52-4
- Coronalolide
Catalog No.:BCN5152
CAS No.:268214-51-3
- Coronalolide methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN5151
CAS No.:268214-50-2
- Udenafil
Catalog No.:BCC5213
CAS No.:268203-93-6
- Debilon
Catalog No.:BCN7696
CAS No.:26808-51-5
- Indapamide
Catalog No.:BCC4788
CAS No.:26807-65-8
- Dehydrodiisoeugenol
Catalog No.:BCN1240
CAS No.:2680-81-1
- Xanthatin
Catalog No.:BCN5150
CAS No.:26791-73-1
- Robtein
Catalog No.:BCN4658
CAS No.:2679-65-4
- Amoxicillin
Catalog No.:BCC4625
CAS No.:26787-78-0
- Alibendol
Catalog No.:BCC4758
CAS No.:26750-81-2
- Triptohypol F
Catalog No.:BCN5154
CAS No.:268541-26-0
- Penfluridol
Catalog No.:BCC4696
CAS No.:26864-56-2
- 1,3-Bis[2-(4-aminophenyl)-2-propyl]benzene
Catalog No.:BCC8419
CAS No.:2687-27-6
- Isomahanimbine
Catalog No.:BCN3175
CAS No.:26871-46-5
- 6-Hydroxybenzofuran-2(3H)-one
Catalog No.:BCN5155
CAS No.:2688-49-5
- Oxysophocarpine
Catalog No.:BCN5156
CAS No.:26904-64-3
- 2(-4-Chloro-3-hydroxy-1-butynyl)-5-1,(3-pentadiynyl)thiophene
Catalog No.:BCN1465
CAS No.:26905-70-4
- Etravirine (TMC125)
Catalog No.:BCC5027
CAS No.:269055-15-4
- Fmoc-Orn(Dde)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3534
CAS No.:269062-80-8
- H-D-Dab-OH.2HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3185
CAS No.:26908-94-1
- Timolol Maleate
Catalog No.:BCC4340
CAS No.:26921-17-5
- Aglaxiflorin D
Catalog No.:BCN6594
CAS No.:269739-78-8
Homoharringtonine contributes to imatinib sensitivity by blocking the EphB4/RhoA pathway in chronic myeloid leukemia cell lines.[Pubmed:24415355]
Med Oncol. 2014 Feb;31(2):836.
The purpose was to investigate the role of EphB4 in imatinib (IM) resistance and the mechanism responsible for Homoharringtonine (HHT) contributing to imatinib sensitivity for a chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) cell lines. We established cell lines from a patient with CML at the time of first diagnosis and relapsed phase and designated them as NPhA1 and NPhA2, respectively. Stable underexpressing EphB4 cells (NPhA2-sh) were obtained. The activated signal proteins in cells were tested by Western blot. The EphB4 was overexpressed in IM-resistant NPhA2 in comparison with the NPhA1 cell line, but the expression of EphB4 mRNA and protein significantly decreased in knockdown NPhA2-EphB4-sh cells compared with NPhA2 and NPhA1 (P < 0.001) cell lines. NPhA2-EphB4-sh cells were sensitive to IM (IC50 0.93 mg/L), and NPhA2 showed IM resistance (IC50 5.45 mg/L) (P < 0.001). Meanwhile, phospho-Rac1/cdc42 was significantly increased in NPhA2 cells compared to NPhA2-EphB4-sh (P < 0.001). The apoptosis rate reached 58.71 +/- 2.39 % with NPhA2 cells incubated with HHT + IM, which was higher than NPhA2 cells incubated with IM alone (P = 0.002). IC50 of NPhA2 cells incubated with IM was 5.45 mg/L. However, co-stimulation with HHT + IM decreased the IC50 of NPhA2 cells from 5.45 to 1.17 mg/L (P < 0.001). Furthermore, HHT blocked the expressions of EphB4/RhoA, but did not down-regulate the phospho-MEK/ERK in NPhA2 cells. The overexpression of EphB4 contributed to IM resistance in CML line cells. EphB4/RhoA may be a new marker of IM resistance. HHT + IM gained more treatment advantages than IM alone by blocking EphB4/RhoA pathways in CML cell lines.
Homoharringtonine mediates myeloid cell apoptosis via upregulation of pro-apoptotic bax and inducing caspase-3-mediated cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP).[Pubmed:15224352]
Am J Hematol. 2004 Jul;76(3):199-204.
Homoharringtonine (HHT) is a plant alkaloid with antileukemia activity that is currently being used for treatment of acute, chronic leukemias and MDS. In this study, we show that HHT can induce apoptosis in a variety of human myeloid leukemia cell lines (U937, HL-60, HEL, THP, and K562). U937 and HL60 cells undergo rapid apoptosis on treatment with HHT, as indicated by increased annexin V binding capacity, caspase-3 activation, and cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP). In addition, the expression of bax is upregulated during HHT-induced cell death, whereas the expression of bcl-2 is only slightly decreased. Importantly, treatment of primary leukemic cells, obtained from acute myeloid leukemia patients, resulted in rapid apoptosis. Thus, our data provide the mechanism of HHT and justify the use of HHT in the treatment of human myeloid leukemia.
Homoharringtonine increases intestinal epithelial permeability by modulating specific claudin isoforms in Caco-2 cell monolayers.[Pubmed:25513955]
Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015 Jan;89:232-8.
Homoharringtonine (HHT), a natural alkaloid produced by various Cephalotaxus species, has antileukemic activity in acute and chronic myelogenous leukemia. However, HHT can also induce unanticipated effects in the gastrointestinal tract, such as diarrhea and nausea/vomiting, but the mechanism behind these adverse effects has not been clarified. In the present study, we show that HHT affects the epithelial permeability of intestinal Caco-2 cell monolayers. HHT reduced the transepithelial electrical resistance (TER) of Caco-2 cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. The HHT effect was reversible and no cytotoxicity was observed at the concentrations used. HHT simultaneously increased the paracellular flux of the 4 kDa and 40 kDa FITC-dextrans associated with the TER reduction. Immunoblotting analysis revealed that HHT decreased the protein expression of TJ components such as claudin-3, -5, and -7. However, the transcription levels of these claudins were not repressed by HHT treatment. HHT also disturbed the cellular localization of claudin-1 and -4. These changes coincided with the reduced barrier function. Our findings suggest that HHT enhances the paracellular permeability of Caco-2 cell monolayers by modulating the protein expression and localization of claudin isoforms; these actions might be responsible for the gastrointestinal effects of HHT.
Homoharringtonine-based induction regimens for patients with de-novo acute myeloid leukaemia: a multicentre, open-label, randomised, controlled phase 3 trial.[Pubmed:23664707]
Lancet Oncol. 2013 Jun;14(7):599-608.
BACKGROUND: Homoharringtonine-based induction regimens have been widely used in China for patients with acute myeloid leukaemia. However, their efficacy has not been tested in a multicentre randomised controlled trial in a large population. We assessed the efficacy and safety of Homoharringtonine-based induction treatment for management of newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukaemia. METHODS: This open-label, randomised, controlled, phase 3 study was done in 17 institutions in China between September, 2007, and July, 2011. Untreated patients aged 14-59 years with acute myeloid leukaemia were randomly assigned (by a computer-generated allocation schedule without stratification) to receive one of three induction regimens in a 1:1:1 ratio: Homoharringtonine 2 mg/m(2) per day on days 1-7, cytarabine 100 mg/m(2) per day on days 1-7, and aclarubicin 20 mg/day on days 1-7 (HAA); Homoharringtonine 2 mg/m(2) per day on days 1-7, cytarabine 100 mg/m(2) per day on days 1-7, and daunorubicin 40 mg/m(2) per day on days 1-3 (HAD); or daunorubicin 40-45 mg/m(2) per day on days 1-3 and cytarabine 100 mg/m(2) per day on days 1-7 (DA). Patients in complete remission were offered two cycles of intermediate-dose cytarabine (2 g/m(2) every 12 h on days 1-3). The primary endpoints were the proportion of patients who achieved complete remission after two cycles of induction treatment and event-free survival in the intention-to-treat population. The trial is registered in the Chinese Clinical Trial Register, number ChiCTR-TRC-06000054. FINDINGS: We enrolled 620 patients, of whom 609 were included in the intention-to-treat analysis. 150 of 206 patients (73%) in the HAA group achieved complete remission versus 125 of 205 (61%) in the DA group (p=0.0108); 3-year event-free survival was 35.4% (95% CI 28.6-42.2) versus 23.1% (95% CI 17.4-29.3; p=0.0023). 133 of 198 patients (67%) in the HAD group had complete remission (vs DA, p=0.20) and 3-year event-free survival was 32.7% (95% CI 26.1-39.5; vs DA, p=0.08). Adverse events were much the same in all groups, except that more patients in the HAA (12 of 206 [5.8%]) and HAD (13 of 198 [6.6%]) groups died within 30 days than in the DA group (two of 205 [1%]; p=0.0067 vs HAA; p=0.0030 vs HAD). INTERPRETATION: A regimen of Homoharringtonine, cytarabine, and aclarubicin is a treatment option for young, newly diagnosed patients with acute myeloid leukaemia. FUNDING: Chinese National High Tech Programme, Key Special Research Foundation of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China, National Nature Science Foundation of China, National Clinical Key Specialty Construction Project.
Homoharringtonine induces apoptosis and inhibits STAT3 via IL-6/JAK1/STAT3 signal pathway in Gefitinib-resistant lung cancer cells.[Pubmed:26166037]
Sci Rep. 2015 Jul 13;5:8477.
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are mostly used in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treatment. Unfortunately, treatment with Gefitinib for a period of time will result in drug resistance and cause treatment failure in clinic. Therefore, exploring novel compounds to overcome this resistance is urgently required. Here we investigated the antitumor effect of Homoharringtonine (HHT), a natural compound extracted from Cephalotaxus harringtonia, on Gefitinib-resistant NSCLC cell lines in vitro and in vivo. NCI-H1975 cells with EGFR T790M mutation are more sensitive to HHT treatment compared with that of A549 cells with wild type EGFR. HHT inhibited cells growth, cell viability and colony formation, as well as induced cell apoptosis through mitochondria pathway. Furthermore, we explored the mechanism of HHT inhibition on NSCLC cells. Higher level of interleukin-6 (IL-6) existed in lung cancer patients and mutant EGFR and TGFbeta signal requires the upregulation of IL-6 through the gp130/JAK pathway to overactive STAT3, an oncogenic protein which has been considered as a potential target for cancer therapy. HHT reversiblely inhibited IL-6-induced STAT3 Tyrosine 705 phosphorylation and reduced anti-apoptotic proteins expression. Gefitinib-resistant NSCLC xenograft tests also confirmed the antitumor effect of HHT in vivo. Consequently, HHT has the potential in Gefitinib-resistant NSCLC treatment.
Apoptotic response to homoharringtonine in human wt p53 leukemic cells is independent of reactive oxygen species generation and implicates Bax translocation, mitochondrial cytochrome c release and caspase activation.[Pubmed:11368358]
Leukemia. 2001 Apr;15(4):567-74.
In the present study, we investigated the in vitro apoptotic response of leukemic cells to the cellular stress induced by Homoharringtonine (HHT), a plant alkaloid with antileukemic activity which is currently being tested for treatment of acute and chronic leukemias. A comparison of leukemic cell lines with different p53 gene status revealed a considerably higher sensitivity to HHT-induced apoptosis in the cells with a wt p53, and apoptotic events in wt p53 leukemia cells (MOLT-3 cell line) were studied in more detail. To this end, we examined components of apoptotic cascades including Bax expression and its intracellular localization, changes of mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels, cytochrome c release from mitochondria and activation of caspases. Bax protein levels did not increase despite an up-regulation of bax at mRNA level. However, Bax translocation from cytosol towards mitochondria was observed. In addition, we observed a release of cytochrome c from the mitochondria, and the localization changes of both Bax and cytochrome c were found already at the early, annexin V-negative stage of HHT-induced apoptosis. HHT-treated MOLT-3 cells revealed loss of MMP as well as activation of caspases demonstrated by DEVD-, IETD- and LEHD-tetrapeptide cleavage activity in the cell lysates. ROS levels only slightly increased in HHT-treated cells and antioxidants did not prevent apoptosis and MMP changes. Therefore, wt p53 leukemic cells respond to HHT-specific cellular stress by induction of ROS-independent apoptotic pathway characterized by translocation of Bax, mitochondrial cytochrome c release and activation of caspases.
Homoharringtonine: an effective new natural product in cancer chemotherapy.[Pubmed:8745664]
Bull Cancer. 1995 Dec;82(12):987-95.
Homoharringtonine (HHT) is a cytotoxic alkaloid isolated from the evergreen tree cephalotaxus harringtonia native to the southern provinces of China. The principal mechanism of action of HHT is the inhibition of protein synthesis in a dose- and time-dependent manner by acting on the ribosomes of cancer cells. It blocks the progression of cells from G1 phase into S phase and from G2 phase into M phase. It is synergestic or additive in vitro with AraC, amsacrine, actinomycin D and dexamethasone. Clinical studies have indicated that HHT is effective in treating acute myeloid leukemia (AML), chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), but not acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and solid tumors. The dose limiting toxicities are hypotention and myelosuppression. Homoharringtonine has relatively mild extramedullary toxicities and no anthracycline-like cardiac toxicity, which make it a suitable candidate for the treatment of aged patients. Pharmacological studies indicate that HHT belongs to the category of multidrug resistance (MDR)-related drugs. The cells resistant to HHT are cross-resistant to anthracycline, vinca alkaloids, mitoxantrone, but not cis-platine and AraC. Multiple mechanisms, including the sequential emergence of overexpression of multidrug resistance-associated protein (MRP) and MDR1 genes, are involved in the cross-resistance of tumor cells to HHT.
Inhibition of translation in eukaryotic systems by harringtonine.[Pubmed:319998]
Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jan;72(2):323-30.
The Cephalotaxus alkaloids harringtonine, Homoharringtonine and isoharringtonine inhibit protein synthesis in eukaryotic cells. The alkaloids do not inhibit, in model systems, any of the steps of the initiation process but block poly(U)-directed polyphenylalanine synthesis as well as peptide bond formation in the fragment reaction assay, the sparsomycin-induced binding of (C)U-A-C-C-A-[3H]Leu-Ac, and the enzymic and the non-enzymic binding of Phe-tRNA to ribosomes. These results suggest that the Cephalotaxus alkaloids inhibit the elongation phase of translation by preventing substrate binding to the acceptor site on the 60-S ribosome subunit and therefore block aminoacyl-tRNA binding and peptide bond formation. However, the Cephalotaxus alkaloids do not inhibit polypeptide synthesis and peptidyl[3H]puromycin formation in polysomes. Furthermore, these alkaloids strongly inhibit [14C]trichlodermin binding to free ribosomes but hardly affect the interaction of the antibiotic with yeast polysomot interact with polysomes and therefore only inhibit cycles of elongation. This explains the polysome run off that has been observed by some workers in the presence of harringtonine.


