Helicianeoide BCAS# 496066-89-8 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 496066-89-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 91758417 | Appearance | Yellow powder |
| Formula | C32H38O20 | M.Wt | 742.63 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
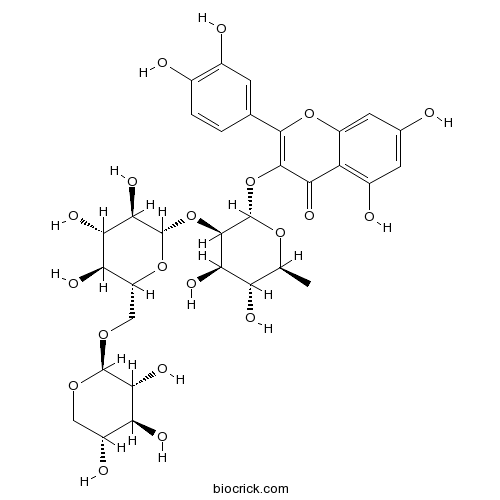
| Chemical Name | 3-[(2S,3R,4R,5R,6S)-4,5-dihydroxy-6-methyl-3-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-[[(2S,3R,4S,5R)-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxan-2-yl]oxymethyl]oxan-2-yl]oxyoxan-2-yl]oxy-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxychromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1C(C(C(C(O1)OC2=C(OC3=CC(=CC(=C3C2=O)O)O)C4=CC(=C(C=C4)O)O)OC5C(C(C(C(O5)COC6C(C(C(CO6)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GBLIGVGNDPHVIN-LOPYEWRSSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C32H38O20/c1-9-19(38)24(43)29(52-31-26(45)23(42)21(40)17(50-31)8-47-30-25(44)20(39)15(37)7-46-30)32(48-9)51-28-22(41)18-14(36)5-11(33)6-16(18)49-27(28)10-2-3-12(34)13(35)4-10/h2-6,9,15,17,19-21,23-26,29-40,42-45H,7-8H2,1H3/t9-,15+,17+,19-,20-,21+,23-,24+,25+,26+,29+,30-,31-,32-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Helicianeoide B Dilution Calculator

Helicianeoide B Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.3466 mL | 6.7328 mL | 13.4657 mL | 26.9313 mL | 33.6641 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.2693 mL | 1.3466 mL | 2.6931 mL | 5.3863 mL | 6.7328 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1347 mL | 0.6733 mL | 1.3466 mL | 2.6931 mL | 3.3664 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0269 mL | 0.1347 mL | 0.2693 mL | 0.5386 mL | 0.6733 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0135 mL | 0.0673 mL | 0.1347 mL | 0.2693 mL | 0.3366 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Helicianeoide A
Catalog No.:BCN2486
CAS No.:496066-82-1
- Pyromeconic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7177
CAS No.:496-63-9
- Benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8851
CAS No.:496-41-3
- Fenofibrate
Catalog No.:BCC4781
CAS No.:49562-28-9
- Estradiol heptanoate
Catalog No.:BCC8961
CAS No.:4956-37-0
- 11alpha,12alpha-Oxidotaraxerol palmitate
Catalog No.:BCN7129
CAS No.:495389-95-2
- Org 25543 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6288
CAS No.:495076-64-7
- (+)-Methysticin
Catalog No.:BCN8429
CAS No.:495-85-2
- Tigloyltropeine
Catalog No.:BCN1944
CAS No.:495-83-0
- Valtropine
Catalog No.:BCN1926
CAS No.:495-82-9
- Tropine isobutyrate
Catalog No.:BCN1923
CAS No.:495-80-7
- Desoxypeganine
Catalog No.:BCN8032
CAS No.:495-59-0
- Tetraethylenepentamine 5HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3867
CAS No.:4961-41-5
- Robustaflavone
Catalog No.:BCN8285
CAS No.:49620-13-5
- Angelicain
Catalog No.:BCN5605
CAS No.:49624-66-0
- Isomitraphylline
Catalog No.:BCN7800
CAS No.:4963-01-3
- Simiarenol acetate
Catalog No.:BCN5606
CAS No.:4965-99-5
- ZLN005
Catalog No.:BCC4882
CAS No.:49671-76-3
- Eltrombopag
Catalog No.:BCC4968
CAS No.:496775-61-2
- Eltrombopag Olamine
Catalog No.:BCC1549
CAS No.:496775-62-3
- Crobarbatine
Catalog No.:BCN2069
CAS No.:49679-23-4
- AR-C155858
Catalog No.:BCC1367
CAS No.:496791-37-8
- HhAntag
Catalog No.:BCC1617
CAS No.:496794-70-8
- Drupacine
Catalog No.:BCN7065
CAS No.:49686-57-9
A comparison of pectoralis versus lumbar skeletal muscle indices for defining sarcopenia in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma - two are better than one.[Pubmed:28388585]
Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 18;8(29):47007-47019.
BACKGROUNDS: Sarcopenia is known to be associated with poor clinical outcome in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). There is no consensus concerning the optimal method to define sarcopenia in DLBCL. METHODS: We retrospectively reviewed 193 DLBCL patients treated with rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP) therapy. Sarcopenia was classified by the region where the pretreatment skeletal muscle index (SMI) was measured. RESULTS: Both the sarcopenia-L3 and sarcopenia-pectoralis muscle (PM) groups had increased incidences of severe treatment-related toxicities and treatment discontinuation compared with the non-sarcopenia-L3 and non-sarcopenia-PM groups, respectively. The sarcopenia-L3 and non-sarcopenia-L3 groups had 5-year overall survival (OS) rates of 40.5% and 67.8% (p < 0.001), respectively. The sarcopenia-PM and non-sarcopenia-PM groups had 5-year OS rates of 35.9% and 69.0% (p < 0.001), respectively. When the sarcopenia-L3 alone and sarcopenia-PM alone groups were compared, there were no differences in baseline characteristics, treatment toxicity, or survival. In multivariate analysis, when compared with the non-sarcopenia-both group, OS was significantly worse in the sarcopenia-both group (HR, 2.480; 95% CI, 1.284 - 4.792; p = 0.007), but not in patients with either sarcopenia-L3 alone or sarcopenia-PM alone (p = 0.151). CONCLUSIONS: L3- and PM-SMIs are equally useful to define sarcopenia, which is related to intolerance to R-CHOP therapy and to worse survival in patients with DLBCL. More prognostic information can be obtained when these two SMIs are combined to define sarcopenia.
Publisher's Note: Measurement of the CP Asymmetry in B_{s}^{0}-B[over ]_{s}^{0} Mixing [Phys. Rev. Lett. 117, 061803 (2016)].[Pubmed:28388175]
Phys Rev Lett. 2017 Mar 24;118(12):129903.
This corrects the article DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.117.061803.
Prognostic significance of the red blood cell distribution width in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients.[Pubmed:28388534]
Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 20;8(25):40724-40731.
This study examined the prognostic value of the baseline red blood cell distribution width (RDW) in diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) patients. The associations between RDW and clinical characteristics were assessed in 161 DLBCL patients from 2005 to 2016. The log-rank test, univariate analysis, and Cox regression analysis were used to evaluate the relationship between RDW and survival. A RDW of 14.1% was considered to be the optimal cut-off value for predicting prognosis. A high RDW was associated with more frequent B symptoms (P=0.001), a higher International Prognostic Index score (P=0.032), more extranodal sites of disease (P=0.035), and significantly lower Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status (P=0.031). The log-rank test demonstrated that patients with a high RDW had a shorter overall survival (OS) (2-year OS rate, 53.6% vs. 83.6%, P<0.001) and progression-free survival (PFS) (2-year PFS rate, 44.7% vs. 81.8%, P<0.001). The multivariate analysis demonstrated that RDW >/=14.1% was an independent predictor of OS (odds ratio [OR] = 0.345, P<0.001) and PFS (OR = 0.393, P=0.001). We demonstrated that a high RDW predicted an unfavorable prognosis in patients with DLBCL.
Immune balance in Hepatitis B Infection: Present and Future Therapies.[Pubmed:28387980]
Scand J Immunol. 2017 Jul;86(1):4-14.
Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection affects millions of people worldwide and about half a million people die every year. India represents the second largest pool of chronic HBV infections with an estimated 40 million chronically infected patients. Persistence or clearance of HBV infection mainly depends upon host immune responses. Chronically infected individuals remain in immune tolerant phase unless HBV flares and leads to the development of chronic active hepatitis or acute-on-chronic liver failure. Strategies based on inhibition of viral replication (nucleoside analogues) or immune modulation (interferons) as monotherapy, or in combination in sequential therapies, are currently being used globally for reducing HBV viral load and mediating HBsAg clearance. However, the immune status and current therapies for promoting sustained virological responses in HBV-infected patients remain suboptimal. Elimination of cccDNA is major challenge for future therapies, and new molecules such as NTCP, Toll-like receptor (TLR)7 agonist (GS9620) and cyclophilin have emerged as potential targets for preventing HBV entry and replication. Other than these, HBV cccDNA elimination is the major target for future therapies.


