GinkgetinCAS# 481-46-9 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 481-46-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5271805 | Appearance | Light yellow powder |
| Formula | C32H22O10 | M.Wt | 566.51 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Amentoflavone 4''',7''-dimethyl ether; 4''',7''-Dimethylamentoflavone; Ginkgotin | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 83.3 mg/mL (147.04 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
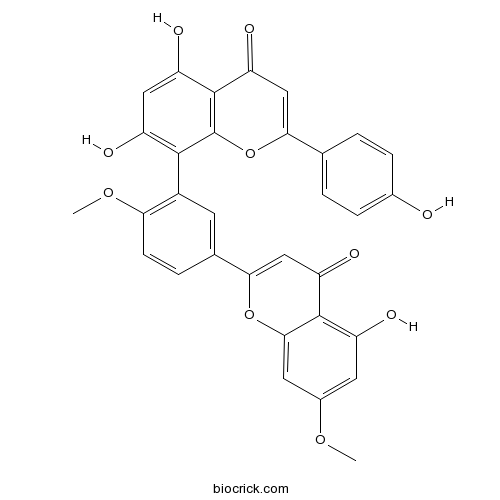
| Chemical Name | 5,7-dihydroxy-8-[5-(5-hydroxy-7-methoxy-4-oxochromen-2-yl)-2-methoxyphenyl]-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)chromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C=C(C=C1)C2=CC(=O)C3=C(C=C(C=C3O2)OC)O)C4=C(C=C(C5=C4OC(=CC5=O)C6=CC=C(C=C6)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | AIFCFBUSLAEIBR-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C32H22O10/c1-39-18-10-20(34)30-23(37)13-27(41-28(30)11-18)16-5-8-25(40-2)19(9-16)29-21(35)12-22(36)31-24(38)14-26(42-32(29)31)15-3-6-17(33)7-4-15/h3-14,33-36H,1-2H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Ginkgetin is a good STAT3 inhibitor , which has anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, anti-influenza virus and anti-fungal activities. Ginkgetin induces apoptosis in PC-3 cells via activation of caspase 3 and inhibition of survival genes as a potent chemotherapeutic agent for prostate cancer treatment. |
| Targets | Bcl-2/Bax | Caspase | STAT | COX | PGE | PRAP | Bcl-xL | Antifection |
| In vitro | Ginkgetin induces apoptosis via activation of caspase and inhibition of survival genes in PC-3 prostate cancer cells.[Pubmed: 23523142]Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013 May 1;23(9):2692-5.Ginkgetin is a natural biflavonoid isolated from leaves of Ginkgo biloba L. Though it was known to have anti-inflammatory, anti-influenza virus, anti-fungal activity, osteoblast differentiation stimulating activity and neuro-protective effects, the underlying antitumor mechanism of Ginkgetin still remains unclear. Thus, in the present study, anti-cancer mechanism of Ginkgetin was elucidated in human prostate cancer PC-3 cells.
|
| In vivo | Neuroprotective effects of ginkgetin against neuro-injury in Parkinson's disease model induced by MPTP via chelating iron.[Pubmed: 25968939]Free Radic Res. 2015 May 12:1-39.Disruption of neuronal iron homeostasis and oxidative stress are closely related to the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease (PD). Ginkgetin, a natural biflavonoid isolated from leaves of Ginkgo biloba L, has many known effects, including anti-inflammatory, anti-influenza virus, and anti-fungal activities, but its underlying mechanism of the neuroprotective effects in PD remains unclear.
|
| Kinase Assay | Effects of Ginkgetin from Ginkgo biloba Leaves on cyclooxygenases and in vivo skin inflammation.[Pubmed: 11988854]Ginkgetin inhibits the growth of DU-145 prostate cancer cells through inhibition of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 activity.[Pubmed: 25611086]Cancer Sci. 2015 Apr;106(4):413-20.Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) is constitutively activated in human cancers. Therefore, STAT3 is a therapeutic target of cancer drug discovery. We previously reported that natural products inhibited constitutively activated STAT3 in human prostate tumor cells.
Planta Med. 2002 Apr;68(4):316-21.Ginkgetin, a biflavone from Ginkgo biloba leaves, was previously reported to be a phospholipase A2 inhibitor and this compound showed the potent antiarthritic activity in rat adjuvant-induced arthritis as well as analgesic activity.
This investigation was carried out to find effects on cyclooxygenase (COX)-1 and -2 including an in vivo effect.
|

Ginkgetin Dilution Calculator

Ginkgetin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7652 mL | 8.826 mL | 17.6519 mL | 35.3039 mL | 44.1298 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.353 mL | 1.7652 mL | 3.5304 mL | 7.0608 mL | 8.826 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1765 mL | 0.8826 mL | 1.7652 mL | 3.5304 mL | 4.413 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0353 mL | 0.1765 mL | 0.353 mL | 0.7061 mL | 0.8826 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0177 mL | 0.0883 mL | 0.1765 mL | 0.353 mL | 0.4413 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Ginkgetin is a natural biflavonoid isolated from leaves of Ginkgo biloba L; effects of anti-inflammation and anticancer have been reported. IC50 value: Target: in vitro: Ginkgetin inhibits COX-2 dependent phases of prostaglandin D(2) (PGD(2)) generation in bone marrow-derived mast cells (BMMC) in a concentration-dependent manner with IC(50) values of 0.75 microM. Ginkgetin consistently inhibited the production of leukotriene C(4) (LTC(4)) in a dose dependent manner, with an IC(50) value of 0.33 microM. Ginkgetin also inhibited degranulation reaction in a dose dependent manner, with an IC(50) value of 6.52 microM [1]. Ginkgetin inhibited both inducible and constitutively activated STAT3 and blocked the nuclear translocation of p-STAT3 in DU-145 prostate cancer cells. Furthermore, ginkgetin selectively inhibited the growth of prostate tumor cells stimulated with activated STAT3. Ginkgetin induced STAT3 dephosphorylation at Try705 and inhibited its localization to the nucleus, leading to the inhibition of expression of STAT3 target genes such as cell survival-related genes (cyclin D1 and survivin) and anti-apoptotic proteins (Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL) [2]. Ginkgetin suppressed the viability of PC-3 cells in a concentration-dependent manner and also significantly increased the sub-G1 DNA contents of cell cycle in PC-3 cells. Ginkgetin activated caspase-3 and attenuated the expression of survival genes such as Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, survivin and Cyclin D1 at protein and mRNA levels [3]. Ginkgetin (1 - 10 microM) and the biflavonoid mixture (10 - 50 microg/ml), mainly a 1 : 1 mixture of ginkgetin and isoginkgetin, from G. biloba leaves, inhibited production of prostaglandin E2 from lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 264.7 cells [4]. in vivo: Ginkgetin inhibited tumor growth in xenografted nude mice and down-regulated p-STAT3Tyr705 and survivin in tumor tissues [2]. At total doses of 1,000 microg/site on the dorsal skin (15 mm x 15 mm), ginkgetin inhibited prostaglandin E2 production by 65.6 % along with a marked suppression of COX-2 induction. In addition, ginkgetin and the biflavonoid mixture (100 - 1,000 microg/ear) dose-dependently inhibited skin inflammation of croton oil induced ear edema in mice by topical application [4].
References:
[1]. Son JK, et al. Ginkgetin, a Biflavone from Ginko biloba leaves, inhibits cyclooxygenases-2 and 5-lipoxygenase in mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 2005 Dec;28(12):2181-4.
[2]. Jeon YJ, et al. Ginkgetin inhibits the growth of DU-145 prostate cancer cells through inhibition of STAT3 activity. Cancer Sci. 2015 Jan 22. doi: 10.1111/cas.12608.
[3]. You OH, et al. Ginkgetin induces apoptosis via activation of caspase and inhibition of survival genes in PC-3 prostate cancer cells. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013 May 1;23(9):2692-5.
[4]. Kwak WJ, et al. Effects of Ginkgetin from Ginkgo biloba Leaves on cyclooxygenases and in vivo skin inflammation. Planta Med. 2002 Apr;68(4):316-21.
- Plumbagin
Catalog No.:BCN2586
CAS No.:481-42-5
- Juglone
Catalog No.:BCN2639
CAS No.:481-39-0
- Ecgonine
Catalog No.:BCN1907
CAS No.:481-37-8
- Epiandrosterone
Catalog No.:BCC4481
CAS No.:481-29-8
- alpha-Spinasterol
Catalog No.:BCN5564
CAS No.:481-18-5
- Alpha-Santonin
Catalog No.:BCN7828
CAS No.:481-06-1
- Edoxaban tosylate
Catalog No.:BCC1544
CAS No.:480449-71-6
- Edoxaban
Catalog No.:BCC1543
CAS No.:480449-70-5
- Lucialdehyde B
Catalog No.:BCN2450
CAS No.:480439-84-7
- TFB-TBOA
Catalog No.:BCC5919
CAS No.:480439-73-4
- Carbenicillin, Disodium Salt
Catalog No.:BCC1200
CAS No.:4800-94-6
- Benzofuroxan
Catalog No.:BCC8852
CAS No.:480-96-6
- Cepharanthine
Catalog No.:BCN5393
CAS No.:481-49-2
- Tangeretin
Catalog No.:BCN2386
CAS No.:481-53-8
- Aloeemodin
Catalog No.:BCN5565
CAS No.:481-72-1
- Citreorosein
Catalog No.:BCN5566
CAS No.:481-73-2
- Chrysophanol
Catalog No.:BCN5567
CAS No.:481-74-3
- Estriol 3-sulfate
Catalog No.:BCN2236
CAS No.:481-95-8
- Homoferreirin
Catalog No.:BCN4765
CAS No.:482-01-9
- Byakangelicin 2'-O-Isovalerate
Catalog No.:BCC8899
CAS No.:108006-56-0
- Isopimpinellin
Catalog No.:BCN5568
CAS No.:482-27-9
- Isoquercitrin
Catalog No.:BCN5569
CAS No.:482-35-9
- Hyperoside
Catalog No.:BCN5570
CAS No.:482-36-0
- Kaempferitrin
Catalog No.:BCN5572
CAS No.:482-38-2
Ginkgetin induces apoptosis via activation of caspase and inhibition of survival genes in PC-3 prostate cancer cells.[Pubmed:23523142]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013 May 1;23(9):2692-5.
Ginkgetin is a natural biflavonoid isolated from leaves of Ginkgo biloba L. Though it was known to have anti-inflammatory, anti-influenza virus, anti-fungal activity, osteoblast differentiation stimulating activity and neuro-protective effects, the underlying antitumor mechanism of Ginkgetin still remains unclear. Thus, in the present study, anti-cancer mechanism of Ginkgetin was elucidated in human prostate cancer PC-3 cells. Ginkgetin suppressed the viability of PC-3 cells in a concentration-dependent manner and also significantly increased the sub-G1 DNA contents of cell cycle in PC-3 cells. Ginkgetin activated caspase-3 and attenuated the expression of survival genes such as Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, survivin and Cyclin D1 at protein and mRNA levels. Consistently, pan-caspase inhibitor Z-DEVD-fmk blocked sub G1 accumulation and cleavages of PRAP and caspase 3 induced by Ginkgetin in PC-3 cells. Overall, these findings suggest that Ginkgetin induces apoptosis in PC-3 cells via activation of caspase 3 and inhibition of survival genes as a potent chemotherapeutic agent for prostate cancer treatment.
Ginkgetin inhibits the growth of DU-145 prostate cancer cells through inhibition of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 activity.[Pubmed:25611086]
Cancer Sci. 2015 Apr;106(4):413-20.
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) is constitutively activated in human cancers. Therefore, STAT3 is a therapeutic target of cancer drug discovery. We previously reported that natural products inhibited constitutively activated STAT3 in human prostate tumor cells. We used a dual-luciferase assay to screen 200 natural products isolated from herbal medicines and we identified Ginkgetin obtained from the leaves of Ginkgo biloba L. as a STAT3 inhibitor. Ginkgetin inhibited both inducible and constitutively activated STAT3 and blocked the nuclear translocation of p-STAT3 in DU-145 prostate cancer cells. Furthermore, Ginkgetin selectively inhibited the growth of prostate tumor cells stimulated with activated STAT3. Ginkgetin induced STAT3 dephosphorylation at Try705 and inhibited its localization to the nucleus, leading to the inhibition of expression of STAT3 target genes such as cell survival-related genes (cyclin D1 and survivin) and anti-apoptotic proteins (Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL). Therefore, Ginkgetin inhibited the growth of STAT3-activated tumor cells. We also found that Ginkgetin inhibited tumor growth in xenografted nude mice and downregulated p-STAT3(Tyr705) and survivin in tumor tissues. This is the first report that Ginkgetin exerts antitumor activity by inhibiting STAT3. Therefore, Ginkgetin is a good STAT3 inhibitor and may be a useful lead molecule for development of a therapeutic STAT3 inhibitor.
Effects of Ginkgetin from Ginkgo biloba Leaves on cyclooxygenases and in vivo skin inflammation.[Pubmed:11988854]
Planta Med. 2002 Apr;68(4):316-21.
Ginkgetin, a biflavone from Ginkgo biloba leaves, was previously reported to be a phospholipase A2 inhibitor and this compound showed the potent antiarthritic activity in rat adjuvant-induced arthritis as well as analgesic activity. This investigation was carried out to find effects on cyclooxygenase (COX)-1 and -2 including an in vivo effect. Ginkgetin (1 - 10 microM) and the biflavonoid mixture (10 - 50 microg/ml), mainly a 1 : 1 mixture of Ginkgetin and isoGinkgetin, from G. biloba leaves, inhibited production of prostaglandin E2 from lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 264.7 cells. This inhibition was mediated, at least in part, by down-regulation of COX-2 expression, but not by direct inhibition of COX-1 or COX-2 activity. Down-regulation of COX-2 by Ginkgetin was also proved in the dorsal skin of ICR mouse treated by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate (TPA). At total doses of 1,000 microg/site on the dorsal skin (15 mm x 15 mm), Ginkgetin inhibited prostaglandin E2 production by 65.6 % along with a marked suppression of COX-2 induction. In addition, Ginkgetin and the biflavonoid mixture (100 - 1,000 microg/ear) dose-dependently inhibited skin inflammation of croton oil induced ear edema in mice by topical application. The present study suggests that Ginkgetin from G. biloba leaves down-regulates COX-2 induction in vivo and this down-regulating potential is associated with an anti-inflammatory activity against skin inflammatory responses.
Neuroprotective effects of ginkgetin against neuroinjury in Parkinson's disease model induced by MPTP via chelating iron.[Pubmed:25968939]
Free Radic Res. 2015;49(9):1069-80.
Disruption of neuronal iron homeostasis and oxidative stress are closely related to the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease (PD). Ginkgetin, a natural biflavonoid isolated from leaves of Ginkgo biloba L, has many known effects, including anti-inflammatory, anti-influenza virus, and anti-fungal activities, but its underlying mechanism of the neuroprotective effects in PD remains unclear. The present study utilized PD models induced by 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP(+)) and 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2, 3, 6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) to explore the neuroprotective ability of Ginkgetin in vivo and in vitro. Our results showed that Ginkgetin could provide significant protection from MPP(+)-induced cell damage in vitro by decreasing the levels of intracellular reactive oxygen species and maintaining mitochondrial membrane potential. Meanwhile, Ginkgetin dramatically inhibited cell apoptosis induced by MPP+ through the caspase-3 and Bcl2/Bax pathway. Moreover, Ginkgetin significantly improved sensorimotor coordination in a mouse PD model induced by MPTP by dramatically inhibiting the decrease of tyrosine hydroxylase expression in the substantia nigra and superoxide dismutase activity in the striatum. Interestingly, Ginkgetin could strongly chelate ferrous ion and thereby inhibit the increase of the intracellular labile iron pool through downregulating L-ferritin and upregulating transferrin receptor 1. These results indicate that the neuroprotective mechanism of Ginkgetin against neurological injury induced by MPTP occurs via regulating iron homeostasis. Therefore, Ginkgetin may provide neuroprotective therapy for PD and iron metabolism disorder related diseases.


