FlavidinCAS# 83924-98-5 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 83924-98-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 158594 | Appearance | Powder |
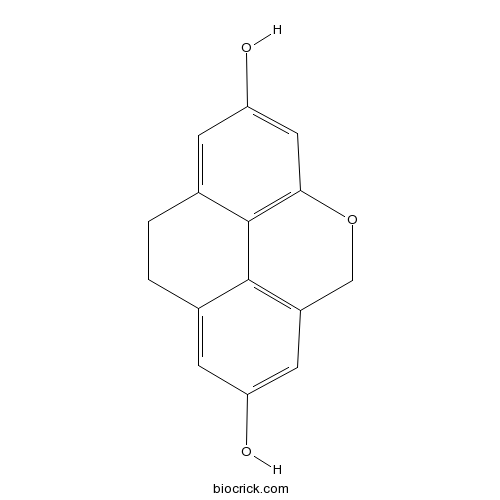
| Formula | C15H12O3 | M.Wt | 240.25 |
| Type of Compound | Phenols | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| SMILES | C1CC2=CC(=CC3=C2C4=C(CO3)C=C(C=C41)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QMOLHJKSZMURCV-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H12O3/c16-11-3-8-1-2-9-4-12(17)6-13-15(9)14(8)10(5-11)7-18-13/h3-6,16-17H,1-2,7H2 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Flavidin shows very good antioxidant capacity. 2. Flavidin can enhance fluorescent imaging, allowing more sensitive and specific cell labeling in tissues, it should have wide application in molecular detection, providing a general insight into how to optimize simultaneously the behavior of the biomolecule and the chemical probe. |
| Targets | PGE | COX |

Flavidin Dilution Calculator

Flavidin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.1623 mL | 20.8117 mL | 41.6233 mL | 83.2466 mL | 104.0583 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8325 mL | 4.1623 mL | 8.3247 mL | 16.6493 mL | 20.8117 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4162 mL | 2.0812 mL | 4.1623 mL | 8.3247 mL | 10.4058 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0832 mL | 0.4162 mL | 0.8325 mL | 1.6649 mL | 2.0812 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0416 mL | 0.2081 mL | 0.4162 mL | 0.8325 mL | 1.0406 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Mometasone furoate
Catalog No.:BCC4801
CAS No.:83919-23-7
- Isogomisin O
Catalog No.:BCN4381
CAS No.:83916-76-1
- 13-Hydroxylabda-8(17),14-dien-18-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1332
CAS No.:83915-59-7
- 12-Acetoxyabietic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4380
CAS No.:83905-81-1
- Gramodendrine
Catalog No.:BCN2155
CAS No.:83905-67-3
- Azithromycin
Catalog No.:BCC4385
CAS No.:83905-01-5
- TCS 2312
Catalog No.:BCC7541
CAS No.:838823-31-7
- WIKI4
Catalog No.:BCC2455
CAS No.:838818-26-1
- Cetirizine DiHCl
Catalog No.:BCC4517
CAS No.:83881-52-1
- Cetirizine
Catalog No.:BCC1469
CAS No.:83881-51-0
- Obovatol
Catalog No.:BCN8265
CAS No.:83864-78-2
- Angeloylisogomisin O
Catalog No.:BCN4379
CAS No.:83864-70-4
- Flavidinin
Catalog No.:BCN3599
CAS No.:83925-00-2
- 4-Epicommunic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4382
CAS No.:83945-57-7
- GNF-7
Catalog No.:BCC6529
CAS No.:839706-07-9
- Pluripotin
Catalog No.:BCC6178
CAS No.:839707-37-8
- 2,7-Dimethyl-1,4-dihydroxynaphthalene 1-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN7611
CAS No.:839711-70-5
- Cariprazine
Catalog No.:BCC1453
CAS No.:839712-12-8
- Hexestrol
Catalog No.:BCC4484
CAS No.:84-16-2
- Rutaecarpine
Catalog No.:BCN4385
CAS No.:84-26-4
- Ophiohayatone C
Catalog No.:BCN3608
CAS No.:84-33-3
- Syrosingopine
Catalog No.:BCN5365
CAS No.:84-36-6
- Stylopine
Catalog No.:BCN3715
CAS No.:84-39-9
- Tectoquinone
Catalog No.:BCN3481
CAS No.:84-54-8
Antioxidant biomarkers from Vanda coerulea stems reduce irradiated HaCaT PGE-2 production as a result of COX-2 inhibition.[Pubmed:21060890]
PLoS One. 2010 Oct 28;5(10):e13713.
BACKGROUND: In our investigations towards the isolation of potentially biologically active constituents from Orchidaceae, we carried out phytochemical and biological analyses of Vanda species. A preliminary biological screening revealed that Vanda coerulea (Griff. ex. Lindl) crude hydro-alcoholic stem extract displayed the best DPPH /(*)OH radical scavenging activity and in vitro inhibition of type 2 prostaglandin (PGE-2) release from UV(B) (60 mJ/cm(2)) irradiated HaCaT keratinocytes. PRINCIPAL FINDINGS: Bio-guided fractionation and phytochemical analysis led to the isolation of five stilbenoids: imbricatin (1) methoxycoelonin (2) gigantol (3) Flavidin (4) and coelonin (5). Stilbenoids (1-3) were the most concentrated in crude hydro-alcoholic stem extract and were considered as Vanda coerulea stem biomarkers. Dihydro-phenanthropyran (1) and dihydro-phenanthrene (2) displayed the best DPPH/(*)OH radical scavenging activities as well as HaCaT intracellular antioxidant properties (using DCFH-DA probe: IC(50) 8.8 microM and 9.4 microM, respectively) compared to bibenzyle (3) (IC(50) 20.6 microM). In turn, the latter showed a constant inhibition of PGE-2 production, stronger than stilbenoids (1) and (2) (IC(50) 12.2 microM and 19.3 microM, respectively). Western blot analysis revealed that stilbenoids (1-3) inhibited COX-2 expression at 23 microM. Interestingly, stilbenoids (1) and (2) but not (3) were able to inhibit human recombinant COX-2 activity. CONCLUSIONS: Major antioxidant stilbenoids (1-3) from Vanda coerulea stems displayed an inhibition of UV(B)-induced COX-2 expression. Imbricatin (1) and methoxycoelonin (2) were also able to inhibit COX-2 activity in a concentration-dependent manner thereby reducing PGE-2 production from irradiated HaCaT cells. Our studies suggest that stilbenoids (1-3) could be potentially used for skin protection against the damage caused by UV(B) exposure.
Amine Landscaping to Maximize Protein-Dye Fluorescence and Ultrastable Protein-Ligand Interaction.[Pubmed:28757182]
Cell Chem Biol. 2017 Aug 17;24(8):1040-1047.e4.
Chemical modification of proteins provides great opportunities to control and visualize living systems. The most common way to modify proteins is reaction of their abundant amines with N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) esters. Here we explore the impact of amine number and positioning on protein-conjugate behavior using streptavidin-biotin, a central research tool. Dye-NHS modification of streptavidin severely damaged ligand binding, necessitating development of a new streptavidin-retaining ultrastable binding after labeling. Exploring the ideal level of dye modification, we engineered a panel bearing 1-6 amines per subunit: "amine landscaping." Surprisingly, brightness increased as amine number decreased, revealing extensive quenching following conventional labeling. We ultimately selected Flavidin (fluorophore-friendly streptavidin), combining ultrastable ligand binding with increased brightness after conjugation. Flavidin enhanced fluorescent imaging, allowing more sensitive and specific cell labeling in tissues. Flavidin should have wide application in molecular detection, providing a general insight into how to optimize simultaneously the behavior of the biomolecule and the chemical probe.
Antioxidant activities of flavidin in different in vitro model systems.[Pubmed:15351397]
Bioorg Med Chem. 2004 Oct 1;12(19):5141-6.
Flavidin was isolated from Orchidaceae species and purified by silica gel column chromatography. The structure was identified using physical and spectral ((1)H, (13)C NMR, and mass) data. Antioxidant potency of Flavidin was investigated employing various established in vitro model systems viz., beta-carotene-linoleate, 1,1-diphenyl-2-picryl hydrazyl (DPPH), phosphomolybdenum method, and scavenging of hydrogen peroxide methods. Flavidin showed very good antioxidant activity (90.2%) and almost equivalent to that of BHA at 50ppm level by beta-carotene-linoleate method. Radical scavenging activity of Flavidin was compared with BHA at 5, 10, 20, and 40ppm concentration and Flavidin showed more radical scavenging activity than BHA at all the tested concentrations. Furthermore, Flavidin showed very good antioxidant capacity by the formation of phosphomolybdenum complex method. Besides this, Flavidin showed effective hydrogen peroxide scavenging activity. The data obtained in the in vitro models clearly establish the antioxidant potency of Flavidin. However, comprehensive studies need to be conducted to ascertain the in vivo safety of Flavidin in experimental animal models. This is the first report on antioxidant activity of 9,10-dihydro-5H-phenanthro-(4,5 bcd)-pyrans/Flavidin type of compounds.


