FIPIPhospholipase D inhibitor CAS# 939055-18-2 |
- BAF312 (Siponimod)
Catalog No.:BCC5114
CAS No.:1230487-00-9
- PF-543
Catalog No.:BCC1854
CAS No.:1415562-82-1
- SKI II
Catalog No.:BCC5029
CAS No.:312636-16-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 939055-18-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 16739265 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C23H24FN5O2 | M.Wt | 421.5 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | 5-Fluoro-2-indolyl deschlorohalopemide | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 14.67 mg/mL (34.81 mM; Need ultrasonic and warming) | ||
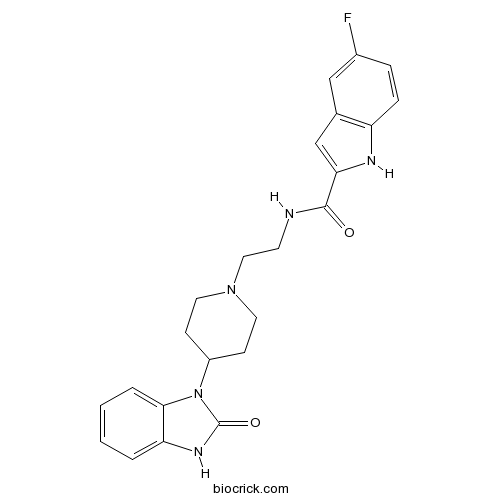
| Chemical Name | 5-fluoro-N-[2-[4-(2-oxo-3H-benzimidazol-1-yl)piperidin-1-yl]ethyl]-1H-indole-2-carboxamide | ||
| SMILES | C1CN(CCC1N2C3=CC=CC=C3NC2=O)CCNC(=O)C4=CC5=C(N4)C=CC(=C5)F | ||
| Standard InChIKey | LHABRXRGDLASIH-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C23H24FN5O2/c24-16-5-6-18-15(13-16)14-20(26-18)22(30)25-9-12-28-10-7-17(8-11-28)29-21-4-2-1-3-19(21)27-23(29)31/h1-6,13-14,17,26H,7-12H2,(H,25,30)(H,27,31) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent phosholipase D (PLD) inhibitor (IC50 values are 20 and 25 nM for PLD2 and PLD1 respectively). Ameliorates PLD2-driven suppression of membrane ruffling and cell spreading. Orally available. |

FIPI Dilution Calculator

FIPI Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3725 mL | 11.8624 mL | 23.7248 mL | 47.4496 mL | 59.312 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4745 mL | 2.3725 mL | 4.745 mL | 9.4899 mL | 11.8624 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2372 mL | 1.1862 mL | 2.3725 mL | 4.745 mL | 5.9312 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0474 mL | 0.2372 mL | 0.4745 mL | 0.949 mL | 1.1862 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0237 mL | 0.1186 mL | 0.2372 mL | 0.4745 mL | 0.5931 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
FIPI is a derivative of halopemide which potently inhibits both PLD1 and PLD2 with IC50s of 25 nM and 20 nM, respectively.
In Vitro:Despite the high clearance of greater than 2 L/h/kg, FIPI shows a half-life of greater than 5 h, a Cmax of greater than 10-fold the 50 versus PLD2, and moderate bioavailability of 18%[1]. FIPI inhibits both PLD1 and PLD2 in a dose-dependent manner, with 50% loss of activity observed at approximately 25 nM. FIPI is not an irreversible suicide inhibitor but neither is it rapidly and completely reverses upon removal of the drug. IPI does not alter PLD subcellular localization, access to PIP2, actin stress fibers, or upstream signaling events. FIPI rescues PLD2-suppressed membrane ruffling and cell spreading[2]. FIPI attenuats the thimerosal-induced PLD activation, and the Hg-induced PLD activation in MAECs in a dose-dependent manner, and the agonist- and oxidant-induced PLD activation in a dose-dependent manner in MAECs[3].
References:
[1]. Monovich L, et al. Optimization of halopemide for phospholipase D2 inhibition. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007 Apr 15;17(8):2310-1.
[2]. Su W, et al. 5-Fluoro-2-indolyl des-chlorohalopemide (FIPI), a phospholipase D pharmacological inhibitor that alters cell spreading and inhibits chemotaxis. Mol Pharmacol. 2009 Mar;75(3):437-46.
[3]. Secor JD, et al. Novel lipid-soluble thiol-redox antioxidant and heavy metal chelator, N,N'-bis(2-mercaptoethyl)isophthalamide (NBMI) and phospholipase D-specific inhibitor, 5-fluoro-2-indolyl des-chlorohalopemide (FIPI) attenuate mercury-induced lipid si
- 9-Oxo-2,7-bisaboladien-15-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4484
CAS No.:93888-59-6
- Isochamaejasmine
Catalog No.:BCN3128
CAS No.:93859-63-3
- KU-0063794
Catalog No.:BCC2484
CAS No.:938440-64-3
- ATPγS tetralithium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7855
CAS No.:93839-89-5
- 22-beta-Acetoxyglycyrrhizin
Catalog No.:BCN7904
CAS No.:938042-17-2
- 3-Prenyl-2,4,6-trihydroxybenzophenone
Catalog No.:BCN1303
CAS No.:93796-20-4
- Roxatidine Acetate HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4534
CAS No.:93793-83-0
- gamma-Secretase Modulators
Catalog No.:BCC1586
CAS No.:937812-80-1
- Neurodazine
Catalog No.:BCC7738
CAS No.:937807-66-4
- Neogambogic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2321
CAS No.:93772-31-7
- Jangomolide
Catalog No.:BCN4483
CAS No.:93767-25-0
- GRP (human)
Catalog No.:BCC5810
CAS No.:93755-85-2
- Hirsutanonol 5-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN4485
CAS No.:93915-36-7
- Toonaciliatin M
Catalog No.:BCN7881
CAS No.:93930-04-2
- Fluvastatin
Catalog No.:BCC1579
CAS No.:93957-54-1
- Fluvastatin Sodium
Catalog No.:BCC2317
CAS No.:93957-55-2
- [Ac-Tyr1,D-Phe2]GRF 1-29, amide (human)
Catalog No.:BCC5719
CAS No.:93965-89-0
- PF-00562271
Catalog No.:BCC3684
CAS No.:939791-38-5
- ACTB-1003
Catalog No.:BCC5587
CAS No.:939805-30-8
- BI 6015
Catalog No.:BCC6249
CAS No.:93987-29-2
- p53 and MDM2 proteins-interaction-inhibitor chiral
Catalog No.:BCC1830
CAS No.:939981-37-0
- RG7112
Catalog No.:BCC1894
CAS No.:939981-39-2
- p53 and MDM2 proteins-interaction-inhibitor racemic
Catalog No.:BCC1831
CAS No.:939983-14-9
- Synephrine
Catalog No.:BCN6308
CAS No.:94-07-5
5-Fluoro-2-indolyl des-chlorohalopemide (FIPI), a phospholipase D pharmacological inhibitor that alters cell spreading and inhibits chemotaxis.[Pubmed:19064628]
Mol Pharmacol. 2009 Mar;75(3):437-46.
The signaling enzyme phospholipase D (PLD) and the lipid second messenger it generates, phosphatidic acid (PA), are implicated in many cell biological processes, including Ras activation, cell spreading, stress fiber formation, chemotaxis, and membrane vesicle trafficking. PLD production of PA is inhibited by the primary alcohol 1-butanol, which has thus been widely employed to identify PLD/PA-driven processes. However, 1-butanol does not always effectively reduce PA accumulation, and its use may result in PLD-independent deleterious effects. Consequently, identification of potent specific small-molecule PLD inhibitors would be an important advance for the field. We examine one such here, 5-fluoro-2-indolyl des-chlorohalopemide (FIPI), which was identified recently in an in vitro chemical screen for PLD2 inhibitors, and show that it rapidly blocks in vivo PA production with subnanomolar potency. We were surprised to find that several biological processes blocked by 1-butanol are not affected by FIPI, suggesting the need for re-evaluation of proposed roles for PLD. However, FIPI does inhibit PLD regulation of F-actin cytoskeleton reorganization, cell spreading, and chemotaxis, indicating potential utility for it as a therapeutic for autoimmunity and cancer metastasis.
Novel lipid-soluble thiol-redox antioxidant and heavy metal chelator, N,N'-bis(2-mercaptoethyl)isophthalamide (NBMI) and phospholipase D-specific inhibitor, 5-fluoro-2-indolyl des-chlorohalopemide (FIPI) attenuate mercury-induced lipid signaling leading to protection against cytotoxicity in aortic endothelial cells.[Pubmed:21994240]
Int J Toxicol. 2011 Dec;30(6):619-38.
Here, we investigated thiol-redox-mediated phospholipase D (PLD) signaling as a mechanism of mercury cytotoxicity in mouse aortic endothelial cell (MAEC) in vitro model utilizing the novel lipid-soluble thiol-redox antioxidant and heavy metal chelator, N,N'-bis(2-mercaptoethyl)isophthalamide (NBMI) and the novel PLD-specific inhibitor, 5-fluoro-2-indolyl des-chlorohalopemide (FIPI). Our results demonstrated (i) mercury in the form of mercury(II) chloride, methylmercury, and thimerosal induced PLD activation in a dose- and time-dependent manner; (ii) NBMI and FIPI completely attenuated mercury- and oxidant-induced PLD activation; (iii) mercury induced upstream phosphorylation of extracellular-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) leading to downstream threonine phosphorylation of PLD(1) which was attenuated by NBMI; (iv) mercury caused loss of intracellular glutathione which was restored by NBMI; and (v) NBMI and FIPI attenuated mercury- and oxidant-induced cytotoxicity in MAECs. For the first time, this study demonstrated that redox-dependent and PLD-mediated bioactive lipid signaling was involved in mercury-induced vascular EC cytotoxicity which was protected by NBMI and FIPI.
Optimization of halopemide for phospholipase D2 inhibition.[Pubmed:17317170]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007 Apr 15;17(8):2310-1.
Halopemide, which was identified by HTS to inhibit phospholipase D2 (PLD2), provided the basis for an exploratory effort to identify potent inhibitors of PLD2 for use as inflammatory mediators. Parallel synthesis and purification were utilized to rapidly identify orally available amide analogs derived from indole 2-carboxylic acids with superior potency versus PLD2.


