Ethyl gallateCAS# 831-61-8 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 831-61-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 13250 | Appearance | White powder |
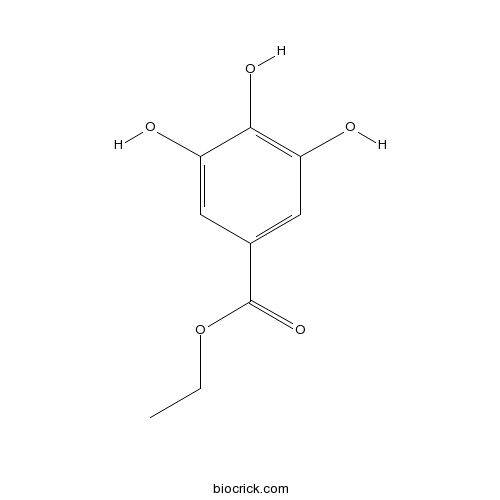
| Formula | C9H10O5 | M.Wt | 198.2 |
| Type of Compound | Phenols | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Ethyl 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoate; Gallic acid ethyl ester; 3,4,5-Trihydroxybenzoic acid ethyl ester | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 150 mg/mL (756.93 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
| Chemical Name | ethyl 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoate | ||
| SMILES | CCOC(=O)C1=CC(=C(C(=C1)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | VFPFQHQNJCMNBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C9H10O5/c1-2-14-9(13)5-3-6(10)8(12)7(11)4-5/h3-4,10-12H,2H2,1H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Ethyl gallate has anti-cancer, antioxidant activities, it may be an alternative class of vasopressors for use in septic shock. Ethyl gallate can treat acute lung injury (ALI) mainly by reducing the total cells and infiltration of activated polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs). Ethyl gallate inhibits Akt , NF-κB p-65, Bcl-2/Bax, and mRNA levels of MMP-2 and MMP-9. |
| Targets | NF-kB | p65 | Bcl-2/Bax | PI3K | Akt | MMP(e.g.TIMP) |
| In vitro | Ethyl gallate suppresses proliferation and invasion in human breast cancer cells via Akt-NF-κB signaling.[Pubmed: 25522911]Oncol Rep. 2015 Mar;33(3):1284-90.Euphorbia fischeriana Steud is a traditional Chinese Medicine that is known to possess a variety of anticarcinogenic properties. However, the bioactive constituents in Euphorbia fischeriana Steud and molecular mechanisms underlying this action in cancer treatment remain poorly understood. The present study investigated the chemotherapy activity and molecular targets of Ethyl gallate, which is identified as the major constituent extracted from the roots of Euphorbia fischeriana Steud in breast cancer cell lines in vitro.
|
| In vivo | In vitro protection of biological macromolecules against oxidative stress and in vivo toxicity evaluation of Acacia nilotica (L.) and ethyl gallate in rats.[Pubmed: 25043389]BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Jul 21;14:257.Recently, enormous research has been focused on natural bioactive compounds possessing potential antioxidant and anticancer properties using cell lines and animal models. Acacia nilotica (L.) is widely distributed in Asia, Africa, Australia and Kenya. The plant is traditionally used to treat mouth, ear and bone cancer. However, reports on Acacia nilotica (L.) Wild. Ex. Delile subsp. indica (Benth.) Brenan regarding its toxicity profile is limited. Hence in this study, we investigated the antioxidant capacity and acute toxicity of Ethyl gallate, a phenolic antioxidant present in the A. nilotica (L.) leaf extract.
Bioactive Components from Qingwen Baidu Decoction against LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Rats.[Pubmed: 28445422 ]Molecules. 2017 Apr 26;22(5). pii: E692.Qingwen Baidu Decoction (QBD) is an extraordinarily "cold" formula. It was traditionally used to cure epidemic hemorrhagic fever, intestinal typhoid fever, influenza, sepsis and so on. The purpose of this study was to discover relationships between the change of the constituents in different extracts of QBD and the pharmacological effect in a rat model of acute lung injury (ALI) induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS).
|
| Kinase Assay | Effect of ethyl gallate on invasion abilities and its mechanism of breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells.[Pubmed: 25924474]Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2015 Jan;50(1):45-9.This study is to investigate the effect of Ethyl gallate on invasion capabilities and its mechanism of breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells.
|
| Cell Research | In vitro evaluation of antiproliferative effect of ethyl gallate against human oral squamous carcinoma cell line KB.[Pubmed: 25104086 ]Nat Prod Res. 2015;29(4):366-9.Although some polyphenols are known to possess anticancer activity against different cancer cell lines through induction of apoptosis, the mode of antiproliferative effect of Ethyl gallate against human oral squamous carcinoma cell line KB was not studied until now. Therefore, the antiproliferative effect of Ethyl gallate was evaluated by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay in comparison with the reference drug paclitaxel.
|
| Animal Research | Benefits of ethyl gallate versus norepinephrine in the treatment of cardiovascular collapse in Pseudomonas aeruginosa septic shock in dogs.[Pubmed: 22020237]Crit Care Med. 2012 Feb;40(2):560-72.Vasopressor therapy is required in septic shock to maintain tissue perfusion in the face of hypotension. Unfortunately, there are significant side effects of current vasopressors, and newer agents need to be developed. We recently discovered that Ethyl gallate, a nonflavonoid phenolic antioxidant found in food substances, could reverse low mean arterial pressure found in an experimental model of septic shock due to inhibition of hydrogen peroxide signaling. In the present study, we compared the hemodynamic and biochemical effects of Ethyl gallate vs. those of the commonly used vasopressor, norepinephrine, in a bacteremic canine model of Pseudomonas aeruginosa sepsis in two protocols.
|

Ethyl gallate Dilution Calculator

Ethyl gallate Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.0454 mL | 25.227 mL | 50.4541 mL | 100.9082 mL | 126.1352 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.0091 mL | 5.0454 mL | 10.0908 mL | 20.1816 mL | 25.227 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5045 mL | 2.5227 mL | 5.0454 mL | 10.0908 mL | 12.6135 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1009 mL | 0.5045 mL | 1.0091 mL | 2.0182 mL | 2.5227 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0505 mL | 0.2523 mL | 0.5045 mL | 1.0091 mL | 1.2614 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Phlogacanthoside A
Catalog No.:BCN7540
CAS No.:830347-18-7
- Phlogacantholide B
Catalog No.:BCN7487
CAS No.:830347-16-5
- 1,6-Dioxaspiro[4.5]decan-2-methanol
Catalog No.:BCN4371
CAS No.:83015-88-7
- Methyl 3-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxybenzoate
Catalog No.:BCN1337
CAS No.:83011-43-2
- 4-Methoxycinnamic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5037
CAS No.:830-09-1
- Skimmianin
Catalog No.:BCN3468
CAS No.:83-95-4
- Tabernanthine
Catalog No.:BCN6957
CAS No.:83-94-3
- Riboflavine
Catalog No.:BCN2224
CAS No.:83-88-5
- Phytic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1282
CAS No.:83-86-3
- Rotenone
Catalog No.:BCN5412
CAS No.:83-79-4
- Ibogaine
Catalog No.:BCN4378
CAS No.:83-74-9
- 2-Hydroxy-1,4-naphoquinone
Catalog No.:BCN8398
CAS No.:83-72-7
- (-)-Epicatechin-3-(3''-O-methyl) gallate
Catalog No.:BCN3062
CAS No.:83104-86-3
- (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-(3''-O-methyl) gallate
Catalog No.:BCN1336
CAS No.:83104-87-4
- 5-Hydroxymethyl-7-methoxybenzofuran
Catalog No.:BCN4372
CAS No.:831222-78-7
- 4',5-Dihydroxy-3',5',6,7-tetramethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN1335
CAS No.:83133-17-9
- 3-Hydroxymethylenetanshinquinone
Catalog No.:BCN2492
CAS No.:83145-47-5
- (+)-Sophoridine
Catalog No.:BCC8360
CAS No.:83148-91-8
- Octreotide acetate
Catalog No.:BCC5643
CAS No.:83150-76-9
- Carpalasionin
Catalog No.:BCN7644
CAS No.:83150-97-4
- Angelol B
Catalog No.:BCN8037
CAS No.:83156-04-1
- Bonducellin
Catalog No.:BCN6823
CAS No.:83162-84-9
- Kaempferol 3-O-rhamninoside
Catalog No.:BCN6845
CAS No.:83170-31-4
- 8alpha-Tigloyloxyhirsutinolide 13-O-acetate
Catalog No.:BCN7108
CAS No.:83182-58-5
Benefits of ethyl gallate versus norepinephrine in the treatment of cardiovascular collapse in Pseudomonas aeruginosa septic shock in dogs.[Pubmed:22020237]
Crit Care Med. 2012 Feb;40(2):560-72.
INTERVENTIONS: Vasopressor therapy is required in septic shock to maintain tissue perfusion in the face of hypotension. Unfortunately, there are significant side effects of current vasopressors, and newer agents need to be developed. We recently discovered that Ethyl gallate, a nonflavonoid phenolic antioxidant found in food substances, could reverse low mean arterial pressure found in an experimental model of septic shock due to inhibition of hydrogen peroxide signaling. In the present study, we compared the hemodynamic and biochemical effects of Ethyl gallate vs. those of the commonly used vasopressor, norepinephrine, in a bacteremic canine model of Pseudomonas aeruginosa sepsis in two protocols. MEASUREMENTS AND MAIN RESULTS: We performed these studies in anesthetized and mechanically ventilated dogs. In the early treatment protocol, we infused P. aeruginosa until mean arterial pressure first decreased to approximately 60 mm Hg (about 2-3 hrs), after which we stopped the infusion and randomly administered Ethyl gallate or norepinephrine in respective groups. In the late treatment protocol, we administered Ethyl gallate or norepinephrine after a sustained approximately 5-hr decrease in mean arterial pressure to 60 mm Hg and continued the infusion for the duration of the experiment. We followed parameters for over 10 hrs after the initiation of P. aeruginosa in both groups. We measured stroke work, urine output, serum creatinine, among other parameters, and used serum troponin T as an index of myocardial injury. We found that in both protocols, Ethyl gallate and norepinephrine improved mean arterial pressure and stroke work to similar extents over the duration of the study. Particularly in the late treatment protocol, Ethyl gallate resulted in a lower heart rate, a lower troponin T, and a greater urine output as compared with norepinephrine (p < .05). CONCLUSIONS: These results suggest that phenolic antioxidants, such as Ethyl gallate, that inhibit hydrogen peroxide signaling, may represent an alternative class of vasopressors for use in septic shock.
In vitro evaluation of antiproliferative effect of ethyl gallate against human oral squamous carcinoma cell line KB.[Pubmed:25104086]
Nat Prod Res. 2015;29(4):366-9.
Although some polyphenols are known to possess anticancer activity against different cancer cell lines through induction of apoptosis, the mode of antiproliferative effect of Ethyl gallate against human oral squamous carcinoma cell line KB was not studied until now. Therefore, the antiproliferative effect of Ethyl gallate was evaluated by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay in comparison with the reference drug paclitaxel. Generation of reactive oxygen species, mitochondrial membrane potential loss, DNA damage and apoptosis were determined using 2,7-diacetyldichlorofluorescein fluorescence, uptake of rhodamine-123 by mitochondria, comet assay and acridine orange/ethidium bromide dual-dye staining method. Both Ethyl gallate and paclitaxel exhibited cytotoxicity in a dose-dependent manner. The 50% inhibitory concentration for Ethyl gallate was 30 and 20 mug/mL for paclitaxel. A volume of 50 mug/mL of Ethyl gallate was found to be significantly effective (P < 0.05) in controlling the cancer cell proliferation leading to acute apoptosis.
In vitro protection of biological macromolecules against oxidative stress and in vivo toxicity evaluation of Acacia nilotica (L.) and ethyl gallate in rats.[Pubmed:25043389]
BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Jul 21;14:257.
BACKGROUND: Recently, enormous research has been focused on natural bioactive compounds possessing potential antioxidant and anticancer properties using cell lines and animal models. Acacia nilotica (L.) is widely distributed in Asia, Africa, Australia and Kenya. The plant is traditionally used to treat mouth, ear and bone cancer. However, reports on Acacia nilotica (L.) Wild. Ex. Delile subsp. indica (Benth.) Brenan regarding its toxicity profile is limited. Hence in this study, we investigated the antioxidant capacity and acute toxicity of Ethyl gallate, a phenolic antioxidant present in the A. nilotica (L.) leaf extract. METHODS: The antioxidant activity of Ethyl gallate against Fenton's system (Fe3+/H2O2/ascorbic acid) generated oxidative damage to pBR322 DNA and BSA was investigated. We also studied the interaction of Ethyl gallate to CT-DNA by wave scan and FTIR analysis. The amount of Ethyl gallate present in the A. nilotica (L.) leaf extract was calculated using HPLC and represented in gram equivalence of Ethyl gallate. The acute toxicity profile of Ethyl gallate in the A. nilotica (L.) leaf extract was analyzed in albino Wistar rats. Measurement of liver and kidney function markers, total proteins and glucose were determined in the serum. Statistical analysis was done using statistical package for social sciences (SPSS) tool version 16.0. RESULTS: Ethyl gallate was found to be effective at 100 mug/mL concentration by inhibiting the free radical mediated damage to BSA and pBR322 DNA. We also found that the interaction of Ethyl gallate and A. nilotica (L.) leaf extract to CT-DNA occurs through intercalation. One gram of A. nilotica (L.) leaf extract was found to be equivalent to 20 mg of Ethyl gallate through HPLC analysis. Based on the acute toxicity results, A. nilotica (L.) leaf extract and Ethyl gallate as well was found to be non-toxic and safe. CONCLUSIONS: Results revealed no mortality or abnormal biochemical changes in vivo and the protective effect of A. nilotica (L.) leaf extract and Ethyl gallate on DNA and protein against oxidative stress in vitro. Hence, A. nilotica (L.) leaf extract or Ethyl gallate could be used as potential antioxidants with safe therapeutic application in cancer chemotherapy.
Ethyl gallate suppresses proliferation and invasion in human breast cancer cells via Akt-NF-kappaB signaling.[Pubmed:25522911]
Oncol Rep. 2015 Mar;33(3):1284-90.
Euphorbia fischeriana Steud is a traditional Chinese Medicine that is known to possess a variety of anticarcinogenic properties. However, the bioactive constituents in Euphorbia fischeriana Steud and molecular mechanisms underlying this action in cancer treatment remain poorly understood. The present study investigated the chemotherapy activity and molecular targets of Ethyl gallate, which is identified as the major constituent extracted from the roots of Euphorbia fischeriana Steud in breast cancer cell lines in vitro. The results showed Ethyl gallate obviously decreased cell proliferation in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Highly invasive MDA-MB-231 cells were found to be highly sensitive to treatment. Furthermore, significantly decreased metastatic potential of highly metastatic MDA-MB231 cells by Ethyl gallate was identified via the inhibition of cell motility using invasion and migration through a polyethylene terephthalate membrane. Ethyl gallate treatment decreased the activity of matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and MMP-9 by the downregulation of mRNA levels using RT-PCR, enzymes that are critical to tumor invasion. Treatment with Ethyl gallate decreased phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt and nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) activation in MDA-MB-231 cells. These results indicate that Ethyl gallate suppresses proliferation and invasion in human breast cancer cells by modulating the PI3K/Akt pathway, which may contribute to inhibiting their downstream targets such as NF-kappaB p-65, Bcl-2/Bax, and mRNA levels of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in breast cancer cells. Thus, the present study shed new light on Ethyl gallate, an important bioactive constituent of Euphorbia fischeriana Steud, in human breast cancer treatment. The findings may provide basal theories for wide therapeutic application in human breast cancer.
[Effect of ethyl gallate on invasion abilities and its mechanism of breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells].[Pubmed:25924474]
Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2015 Jan;50(1):45-9.
This study is to investigate the effect of Ethyl gallate on invasion capabilities and its mechanism of breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells. Using cell adhesion and transwell assay, separately, the effects of Ethyl gallate on the invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells were measured. The Akt-NF-kappaB signal pathway protein expressions were analyzed with Western blot. Also, the mRNA levels of MMP-9 and MMP-2 were analyzed by RT-PCR. Ethyl gallate inhibited the abilities of motility, adhesion and invasion of breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells in vitro (P<0.05), inhibited the mRNA levels of MMP-9, MMP-2, phosphorylation of AKt and protein expression of NF-kappaB. It is concluded that Ethyl gallate can inhibit the abilities of invasion of breast cancer in vitro by inhibiting the mRNA levels of MMP-9/MMP-2, phosphorylation of Akt and protein expression of NF-kappaB.


