Epimedin CCAS# 110642-44-9 |
- Epimedin A
Catalog No.:BCN1038
CAS No.:110623-72-8
- Baohuoside VI
Catalog No.:BCC8129
CAS No.:119760-73-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 110642-44-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5748394 | Appearance | Yellow powder |
| Formula | C39H50O19 | M.Wt | 822.80 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Epimedin-C; Baohuoside-VI | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in methan | ||
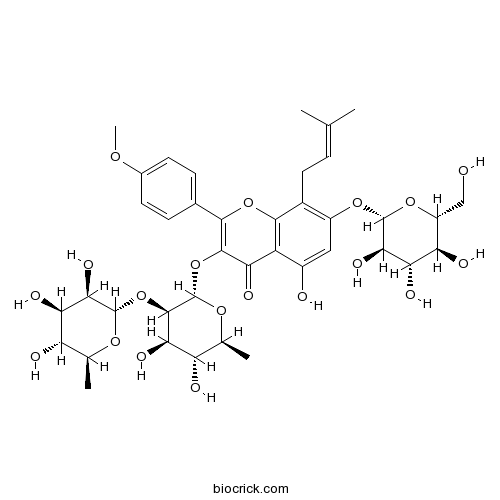
| Chemical Name | 3-[(2S,3R,4R,5R,6S)-4,5-dihydroxy-6-methyl-3-[(2S,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxyoxan-2-yl]oxy-5-hydroxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-8-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)-7-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxychromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1C(C(C(C(O1)OC2C(C(C(OC2OC3=C(OC4=C(C3=O)C(=CC(=C4CC=C(C)C)OC5C(C(C(C(O5)CO)O)O)O)O)C6=CC=C(C=C6)OC)C)O)O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ULZLIYVOYYQJRO-JIYCBSMMSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C39H50O19/c1-14(2)6-11-19-21(54-38-32(50)29(47)26(44)22(13-40)55-38)12-20(41)23-27(45)35(33(56-34(19)23)17-7-9-18(51-5)10-8-17)57-39-36(30(48)25(43)16(4)53-39)58-37-31(49)28(46)24(42)15(3)52-37/h6-10,12,15-16,22,24-26,28-32,36-44,46-50H,11,13H2,1-5H3/t15-,16-,22+,24-,25-,26+,28+,29-,30+,31+,32+,36+,37-,38+,39-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Epimedin C and diphylloside A have antiinflammation effect, can reduce the swelling of the rats foot induced by egg. The accumulation of epimedinsA, B, C, and icariin in a traditional medicinal plant could be suppressed by light stress. |
| Targets | Immunology & Inflammation related |
| In vitro | Light stress suppresses the accumulation of epimedins A, B, C, and icariin in Epimedium, a traditional medicinal plant.[Reference: WebLink]Acta Physiol Plant, 2013, 35(11):3271-5.Epimedium is well-known in China and East Asia due to high content of flavonoid derivatives, including icariin, Epimedin A, epimedin B, and Epimedin C, hereafter designated as bioactive components, which have been extensively utilized to cure many diseases. So far, the molecular mechanism of the bioactive components biosynthesis remains unclear.
|
| In vivo | Antiinflammatory Effect of Epimedin C and Diphylloside A of Epimedium Wushanense T.S.Ying.s.[Reference: WebLink]Chinese Journal of Modern Applied Pharmacy, 2012(3):198-201. To study the antiinflammatory effect of Epimedin C and diphylloside A of Epimedium wushanense T.S.Ying.s on rats. |
| Structure Identification | Biomed Chromatogr. 2014 Oct;28(10):1306-12.Metabolite profiles of epimedin C in rat plasma and bile by ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole-TOF-MS.[Pubmed: 24853580]Epimedin C is one of the major bioactive constituents of Herba Epimedii. In this study, the metabolite profiles of Epimedin C in rat plasma and bile were qualitatively investigated, and the possible metabolic pathways of Epimedin C were subsequently proposed.
|

Epimedin C Dilution Calculator

Epimedin C Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.2154 mL | 6.0768 mL | 12.1536 mL | 24.3072 mL | 30.3841 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.2431 mL | 1.2154 mL | 2.4307 mL | 4.8614 mL | 6.0768 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1215 mL | 0.6077 mL | 1.2154 mL | 2.4307 mL | 3.0384 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0243 mL | 0.1215 mL | 0.2431 mL | 0.4861 mL | 0.6077 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0122 mL | 0.0608 mL | 0.1215 mL | 0.2431 mL | 0.3038 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Epmedin C, a natural product, has estrogen-like effects for ovariectomized mice. IC50 value: Target: In vitro: In vivo: Anesthetized with 0.4%pentobarbital sodium, mice of the ovariectomized group were conducted with Bilateral oophorectomy, while fat beside ovaries were removed on mice of the sham-operation group. Compared with the sham-operation group, body weight of mice of model group were significantly increased, uterus weight and uterine factor and estradiol levels were significantly reduced, which suggested a significant difference. In comparison of the ovariectomized group, body weight of mice were relieved significantly and uterus weight and uterine factor and estradiol levels were increased significantly in all Epmedin C groups [1].
References:
[1]. WEN Yu, et al. Effect of Epmedin C on Estrogen in Ovariectomized Mice. Modern Chinese Medicine, 2012-05
- Epimedin B
Catalog No.:BCN1039
CAS No.:110623-73-9
- Epimedin A
Catalog No.:BCN1038
CAS No.:110623-72-8
- human Insulin expressed in yeast
Catalog No.:BCC7689
CAS No.:11061-68-0
- Laminin (925-933)
Catalog No.:BCC1015
CAS No.:110590-60-8
- Salermide
Catalog No.:BCC7867
CAS No.:1105698-15-4
- Albrassitriol
Catalog No.:BCN7274
CAS No.:110557-39-6
- Scutebarbatine F
Catalog No.:BCN5377
CAS No.:910099-78-4
- 6,11-Di-O-acetylalbrassitriol
Catalog No.:BCN7273
CAS No.:110538-20-0
- Crotastriatine
Catalog No.:BCN2101
CAS No.:11051-94-8
- BYK 204165
Catalog No.:BCC2449
CAS No.:1104546-89-5
- ML-7 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1770
CAS No.:110448-33-4
- Dolastatin 10
Catalog No.:BCC4056
CAS No.:110417-88-4
- beta-Escin
Catalog No.:BCC8172
CAS No.:11072-93-8
- Asebotin
Catalog No.:BCN7233
CAS No.:11075-15-3
- Garcinexanthone A
Catalog No.:BCN5993
CAS No.:1107620-67-6
- Cinobufotalin
Catalog No.:BCN2283
CAS No.:1108-68-5
- MCOPPB trihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4161
CAS No.:1108147-88-1
- Sparfloxacin
Catalog No.:BCC4848
CAS No.:110871-86-8
- Entrectinib
Catalog No.:BCC6410
CAS No.:1108743-60-7
- Wilforine
Catalog No.:BCN5994
CAS No.:11088-09-8
- [Sar9,Met(O2)11]-Substance P
Catalog No.:BCC6960
CAS No.:110880-55-2
- Tunicamycin
Catalog No.:BCC7699
CAS No.:11089-65-9
- PF-04620110
Catalog No.:BCC2335
CAS No.:1109276-89-2
- Squalene
Catalog No.:BCN5995
CAS No.:111-02-4
Metabolite profiles of epimedin C in rat plasma and bile by ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole-TOF-MS.[Pubmed:24853580]
Biomed Chromatogr. 2014 Oct;28(10):1306-12.
Epimedin C is one of the major bioactive constituents of Herba Epimedii. In this study, the metabolite profiles of Epimedin C in rat plasma and bile were qualitatively investigated, and the possible metabolic pathways of Epimedin C were subsequently proposed. After oral administration of Epimedin C at a single dose of 80 mg/kg, rat biological samples were collected and pretreated by protein precipitation. Then these pretreated samples were injected into an Acquity UPLC BEH C18 column and detected by ultra-performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. In all, 12 metabolites were identified in the biosamples. Of these, eight, two from plasma and six from bile, are, to our knowledge, reported here for the first time. The results indicated that Epimedin C was metabolized via desugarization, dehydrogenation, hydrogenation, dehydroxylation, hydroxylation, demethylation and glucuronidation pathways in vivo. Thus, this study revealed the possible metabolite profiles of Epimedin C in rat plasma and bile.


