Diosbulbin BCAS# 20086-06-0 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 20086-06-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 177107 | Appearance | Powder |
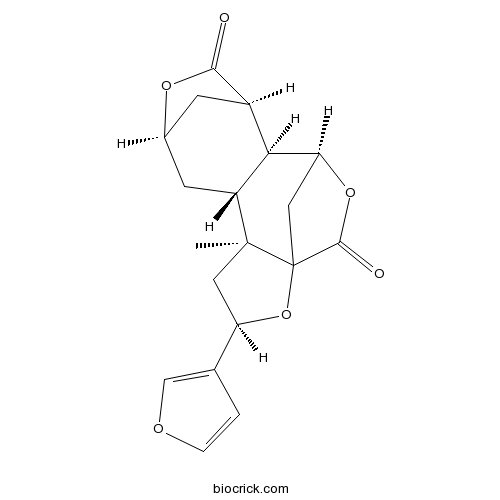
| Formula | C19H20O6 | M.Wt | 344.4 |
| Type of Compound | Diterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 16 mg/mL (46.46 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
| SMILES | CC12CC(OC13CC(C4C2CC5CC4C(=O)O5)OC3=O)C6=COC=C6 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QEANLIISUSNNDX-XBHMPIGQSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C19H20O6/c1-18-6-13(9-2-3-22-8-9)25-19(18)7-14(24-17(19)21)15-11-4-10(5-12(15)18)23-16(11)20/h2-3,8,10-15H,4-7H2,1H3/t10-,11+,12+,13+,14-,15+,18-,19?/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Diosbulbin B has potential anti-tumor effects which may be related to influencing the immune system for the first time, it also exhibits potential hepatotoxicity. |
| Targets | P450 (e.g. CYP17) |
| In vivo | Ferulic acid prevents liver injury and increases the anti-tumor effect of diosbulbin B in vivo.[Pubmed: 24903991]J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2014 Jun;15(6):540-7.
Diosbulbin B-induced liver injury in mice and its mechanism.[Pubmed: 24107456]Hum Exp Toxicol. 2014 Jul;33(7):729-36.Dioscorea bulbifera L., a commonly used medicinal plant in China, is reported to induce hepatotoxicity.
The present study is undertaken to investigate the hepatotoxicity induced by Diosbulbin B (DB), a diterpene lactone isolated from D. bulbifera L., and to further explore its underlying mechanism.
|
| Kinase Assay | Cytochrome p450-mediated metabolic activation of diosbulbin B.[Pubmed: 25024403]Metabolism of diosbulbin B in vitro and in vivo in rats: formation of reactive metabolites and human enzymes involved.[Pubmed: 25053620]Drug Metab Dispos. 2014 Oct;42(10):1737-50.Diosbulbin B (DB), a major constituent of the furano-norditerpenes in Dioscorea bulbifera Linn, exhibits potential antineoplasmic activity and hepatotoxicity. The metabolism and reactive metabolites of Diosbulbin B in vitro (with human and animal liver microsomes) and in vivo in rats were investigated.
Drug Metab Dispos. 2014 Oct;42(10):1727-36.Diosbulbin B (DIOB), a furan-containing diterpenoid lactone, is the most abundant component of Dioscorea bulbifera L. (DB), a traditional Chinese medicine herb. Administration of purified Diosbulbin B or DB extracts has been reported to cause liver injury in animals. The mechanisms of Diosbulbin B-induced hepatotoxicity remain unknown. The major objective of this study was to identify reactive metabolites of Diosbulbin B.
|

Diosbulbin B Dilution Calculator

Diosbulbin B Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9036 mL | 14.518 mL | 29.036 mL | 58.072 mL | 72.59 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5807 mL | 2.9036 mL | 5.8072 mL | 11.6144 mL | 14.518 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2904 mL | 1.4518 mL | 2.9036 mL | 5.8072 mL | 7.259 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0581 mL | 0.2904 mL | 0.5807 mL | 1.1614 mL | 1.4518 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.029 mL | 0.1452 mL | 0.2904 mL | 0.5807 mL | 0.7259 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Epicurzerenone
Catalog No.:BCN3521
CAS No.:20085-85-2
- Pseudoneolinderane
Catalog No.:BCN8034
CAS No.:20082-45-5
- 16-Nor-15-oxodehydroabietic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3943
CAS No.:200813-31-6
- 7-Hydroxy-PIPAT maleate
Catalog No.:BCC6760
CAS No.:200722-46-9
- (-)-Phyllocladene
Catalog No.:BCN7661
CAS No.:20070-61-5
- Piplartine
Catalog No.:BCN4037
CAS No.:20069-09-4
- Hennadiol
Catalog No.:BCN4679
CAS No.:20065-99-0
- Fmoc-D-Gln(Trt)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3488
CAS No.:200623-62-7
- Fmoc-D-Gln-OPfp
Catalog No.:BCC3487
CAS No.:200622-33-9
- Fmoc-N-Me-Glu(OtBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3213
CAS No.:200616-40-6
- Fmoc-D-Glu(OtBu)-OPfp
Catalog No.:BCC3497
CAS No.:200616-21-3
- Hotrienol
Catalog No.:BCN6340
CAS No.:20053-88-7
- Diosbulbin C
Catalog No.:BCN4880
CAS No.:20086-07-1
- Epinodosin
Catalog No.:BCN3282
CAS No.:20086-60-6
- Xanthotoxol
Catalog No.:BCN4881
CAS No.:2009-24-7
- (D)-(+)-Neopterin
Catalog No.:BCC7960
CAS No.:2009-64-5
- m-3M3FBS
Catalog No.:BCC7209
CAS No.:200933-14-8
- SB 243213 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6035
CAS No.:200940-23-4
- Ac-RYYRWK-NH2
Catalog No.:BCC5755
CAS No.:200959-47-3
- Ac-RYYRIK-NH2
Catalog No.:BCC5736
CAS No.:200959-48-4
- Fmoc-Lys(Me)3-OH Chloride
Catalog No.:BCC3267
CAS No.:201004-29-7
- SB-269970
Catalog No.:BCC1927
CAS No.:201038-74-6
- Ravenine
Catalog No.:BCN6666
CAS No.:20105-22-0
- cis-Methylkhellactone
Catalog No.:BCN7690
CAS No.:20107-13-5
Cytochrome p450-mediated metabolic activation of diosbulbin B.[Pubmed:25024403]
Drug Metab Dispos. 2014 Oct;42(10):1727-36.
Diosbulbin B (DIOB), a furan-containing diterpenoid lactone, is the most abundant component of Dioscorea bulbifera L. (DB), a traditional Chinese medicine herb. Administration of purified DIOB or DB extracts has been reported to cause liver injury in animals. The mechanisms of DIOB-induced hepatotoxicity remain unknown. The major objective of this study was to identify reactive metabolites of DIOB. A DIOB-derived cis-enedial was trapped by N-acetyl lysine (NAL) and glutathione (GSH) or N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) in rat and human liver microsomal incubation systems after exposure to DIOB. Four metabolites (M1-M4) associated with GSH were detected by liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. Apparently, M1 was derived from both NAL and GSH. M2 and M3 resulted from the reaction of GSH without the involvement of NAL. Two molecules of GSH participated in the formation of M4. M2 and M3 were also detected in bile and urine of rats given DIOB. M5, a DIOB-derived NAC/NAL conjugate, was detected in microsomal incubations with DIOB fortified with NAC and NAL as trapping agents. Biomimetic M1-M5 were prepared by oxidation of DIOB with Oxone for metabolite identification. Microsomal incubation study demonstrated that ketoconazole inhibited the production of the enedial in a concentration-dependent manner, and CYP3A4 was found to be the enzyme responsible for the metabolic activation of DIOB. The metabolism study facilitates the understanding of the role of bioactivation of DIOB in its hepatotoxicity.
Metabolism of diosbulbin B in vitro and in vivo in rats: formation of reactive metabolites and human enzymes involved.[Pubmed:25053620]
Drug Metab Dispos. 2014 Oct;42(10):1737-50.
Diosbulbin B (DB), a major constituent of the furano-norditerpenes in Dioscorea bulbifera Linn, exhibits potential antineoplasmic activity and hepatotoxicity. The metabolism and reactive metabolites of DB in vitro (with human and animal liver microsomes) and in vivo in rats were investigated. The human enzymes involved in DB metabolism were identified. DB was first catalyzed into reactive metabolites of 2-butene-1,4-dial derivatives dependent on NADPH and then trapped by Tris base or oxidized to hemiacetal lactones (M12 and M13) in microsomal incubations. Tris base was used as buffer constituent and as a trapping agent for aldehyde. Methoxylamine and glutathione (GSH) were also used as trapping agents. DB metabolism in vivo in rats after oral administration was consistent with that in vitro. The structures of M12 and M13, as well as mono-GSH conjugates of DB (M31), were confirmed by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the chemically synthesized products. The bioactivation enzymes of DB were identified as CYP3A4/5, 2C9, and 2C19. CYP3A4 was found to be the primary enzyme using human recombinant cytochrome P450 enzymes, specific inhibitory studies, and a relative activity factor approach for pooled human liver microsomes. Michaelis-Menten constants K(m) and V(max) were determined by the formation of M31. The reactive metabolites may be related to the hepatotoxicity of DB. The gender difference in CYP3A expression in mice and rats contributed to the gender-related liver injury and pharmacokinetics in mice and rats, respectively.
Ferulic acid prevents liver injury and increases the anti-tumor effect of diosbulbin B in vivo.[Pubmed:24903991]
J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2014 Jun;15(6):540-7.
The present study is designed to investigate the protection by ferulic acid against the hepatotoxicity induced by Diosbulbin B and its possible mechanism, and further observe whether ferulic acid augments Diosbulbin B-induced anti-tumor activity. The results show that ferulic acid decreases Diosbulbin B-increased serum alanine transaminase/aspartate transaminase (ALT/AST) levels. Ferulic acid also decreases lipid peroxide (LPO) levels which are elevated in Diosbulbin B-treated mice. Histological evaluation of the liver demonstrates hydropic degeneration in Diosbulbin B-treated mice, while ferulic acid reverses this injury. Moreover, the activities of copper- and zinc-containing superoxide dismutase (CuZn-SOD) and catalase (CAT) are decreased in the livers of Diosbulbin B-treated mice, while ferulic acid reverses these decreases. Further results demonstrate that the mRNA expressions of CuZn-SOD and CAT in Diosbulbin B-treated mouse liver are significantly decreased, while ferulic acid prevents this decrease. In addition, ferulic acid also augments Diosbulbin B-induced tumor growth inhibition compared with Diosbulbin B alone. Taken together, the present study shows that ferulic acid prevents Diosbulbin B-induced liver injury via ameliorating Diosbulbin B-induced liver oxidative stress injury and augments Diosbulbin B-induced anti-tumor activity.
Diosbulbin B-induced liver injury in mice and its mechanism.[Pubmed:24107456]
Hum Exp Toxicol. 2014 Jul;33(7):729-36.
Dioscorea bulbifera L., a commonly used medicinal plant in China, is reported to induce hepatotoxicity. The present study is undertaken to investigate the hepatotoxicity induced by Diosbulbin B (DB), a diterpene lactone isolated from D. bulbifera L., and to further explore its underlying mechanism. DB was administered to mice at the doses of 0, 16, 32, and 64 mg/kg once daily for 12 consecutive days. Liver injury induced by DB was evidenced by the increased activity of serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and alkaline phosphatase (ALP). Liver histological evaluation showed that the mice treated with DB exhibited liver damage with the swelling of hepatocytes. Further results showed that the amount of malondialdehyde (MDA) in the liver was increased in mice treated with DB, while the glutathione amount and the enzymatic activity of glutathione peroxidase (GPx), glutathione-S-transferase (GST), copper/zinc-superoxide dismutase (CuZn-SOD), manganese-SOD (Mn-SOD), and catalase (CAT) were all decreased. DB also decreased the gene expression of CuZn-SOD and CAT. Taken together, our results indicate that oral administration of DB for 12 consecutive days can lead to the oxidative stress liver injury in mice.


