DencichineCAS# 5302-45-4 |
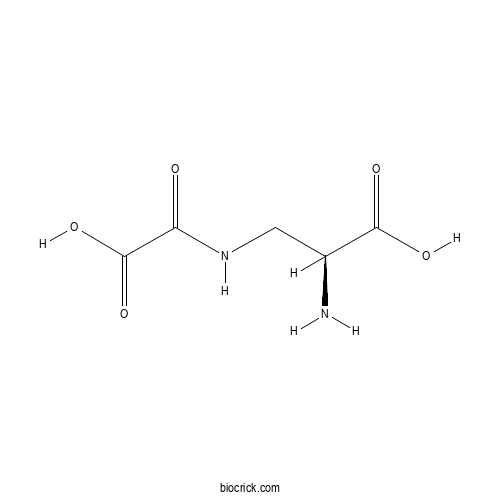
- Dencichin
Catalog No.:BCN2555
CAS No.:7554-90-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 5302-45-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 440259 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C5H8N2O5 | M.Wt | 176.13 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (2S)-2-amino-3-(oxaloamino)propanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | C(C(C(=O)O)N)NC(=O)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NEEQFPMRODQIKX-REOHCLBHSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C5H8N2O5/c6-2(4(9)10)1-7-3(8)5(11)12/h2H,1,6H2,(H,7,8)(H,9,10)(H,11,12)/t2-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Dencichine Dilution Calculator

Dencichine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.6776 mL | 28.3881 mL | 56.7762 mL | 113.5525 mL | 141.9406 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.1355 mL | 5.6776 mL | 11.3552 mL | 22.7105 mL | 28.3881 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5678 mL | 2.8388 mL | 5.6776 mL | 11.3552 mL | 14.1941 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1136 mL | 0.5678 mL | 1.1355 mL | 2.271 mL | 2.8388 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0568 mL | 0.2839 mL | 0.5678 mL | 1.1355 mL | 1.4194 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Schisandrathera D
Catalog No.:BCX0481
CAS No.:2694046-04-1
- Schisanhenol B
Catalog No.:BCX0480
CAS No.:102681-52-7
- Indole-3-acetic acid β-D-glucopyranosyl ester
Catalog No.:BCX0479
CAS No.:19817-95-9
- Gypenoside LXXV
Catalog No.:BCX0478
CAS No.:110261-98-8
- Sinapyl alcohol
Catalog No.:BCX0477
CAS No.:537-33-7
- Rankinidine
Catalog No.:BCX0476
CAS No.:106466-66-4
- Methyl indole-3-acetate
Catalog No.:BCX0475
CAS No.:1912-33-0
- Galanal B
Catalog No.:BCX0474
CAS No.:104113-52-2
- Labda-8(17),12E,14-trien-16,15-olide
Catalog No.:BCX0473
CAS No.:917078-10-5
- Mulberrofuran V
Catalog No.:BCX0472
CAS No.:174423-49-5
- 6'-O-p-Hydroxybenzoylgastrodin
Catalog No.:BCX0471
CAS No.:1551525-70-2
- 15-Hydroxylabda-8(17),12E-dien-16-al
Catalog No.:BCX0470
CAS No.:283614-59-5
- Deoxylimonin
Catalog No.:BCX0483
CAS No.:989-23-1
- 5-Methoxydadahol A
Catalog No.:BCX0484
CAS No.:2410566-84-4
- 4-(3-Hydroxydecyl)phenol
Catalog No.:BCX0485
CAS No.:1465124-36-0
- Oxyphyllone D
Catalog No.:BCX0486
CAS No.:1190094-25-7
- Rugulolide A
Catalog No.:BCX0487
CAS No.:3002032-70-1
- Rugulolide B
Catalog No.:BCX0488
CAS No.:3002032-71-2
- 2,4-Dihydroxybezaldehyde
Catalog No.:BCX0489
CAS No.:95-01-2
- Ethyl 2,4-dihydroxybenzoate
Catalog No.:BCX0490
CAS No.:4143-00-4
- 7-epi-α-Cyperone
Catalog No.:BCX0491
CAS No.:547-26-2
- 4-Hydroxy-4-methylcyclohex-2-en-1-one
Catalog No.:BCX0492
CAS No.:70150-56-0
- Sanggenon E
Catalog No.:BCX0493
CAS No.:81381-69-3
- Rugulolide D
Catalog No.:BCX0494
CAS No.:3002032-69-8
Guanosine-Based Multidrug Strategy Delivery for Synergistic Anti-Inflammation.[Pubmed:38335274]
ACS Macro Lett. 2024 Feb 9:260-265.
The development of codelivery approaches for combination therapy is of great significance, especially for natural products that need to be combined to achieve therapeutic effects. Targeted delivery of multiple drugs through a single carrier remains a challenge. Here, a multi-drug-loaded hydrogel, incorporating quercetin, demethyleneberberine, and Dencichine, based on a G(4)-quadruplex was designed and prepared. Catechol drugs were responsively released in a simulated inflammatory pathological environment by a borate ester linkage, while coagulating Dencichine encapsulated in the hydrogel was released along with the degradation of assemblies. The multi-drug-loaded codelivery system is expected to enhance the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease through the synergistic effect of the components. The preparation, characteristic, and physicochemical properties of the multi-drug-loaded assembly were depicted by NMR, CD, and TEM. Degradation assays in vitro proved the good biocompatibility and safety of the hydrogel and a potential pathway to injectable administration. The assays of typical inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-alpha and IL-6, indicated that these can be significantly suppressed by the treatment of the hydrogel. The current work provided a simple strategy to construct a multi-drug-loaded hydrogel carrier, which facilitated synergistic therapy for natural products by a codelivery approach.
Screening and verification of hemostatic effective components group of Panax Notoginseng based on spectrum-effect relationships.[Pubmed:38056541]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Mar 1;321:117539.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Panax Notoginseng (PN) can disperse blood stasis, hemostasis, and detumescence analgesic, which can be used for hemoptysis, hematemesis and another traumatic bleeding, and it is known as "A miracle hemostatic medicine". Studies show that the chemical composition of PN is relatively comprehensive, however, its hemostatic active ingredients have not been fully clarified. AIM OF STUDY: This study aimed to clarify the hemostatic effective components group (HECG) of PN, provide a foundation for the assessment of PN's quality and its comprehensive development, and for further studies on the pharmacodynamic material basis of other Traditional Chinese Medicines (TCMs). MATERIALS AND METHODS: UPLC-MS was used to establish the fingerprint and identify the common peaks in 44 batches of PN extracts (PNE). In addition, the plasma recalcification time and in vitro coagulation time were measured. For spectrum-effect analysis, bivariate correlation analysis (BCA) and partial least squares regression analysis (PLSR) were used to screen the hemostasis candidate active monomers of PN. The monomers were prepared by combining several preparative chromatography techniques. The efficacy was verified by plasma recalcification time, in vitro coagulation time, and a rat model of gastric hemorrhage. RESULTS: A total of 30 common peaks and hemostatic efficacy indexes of 44 batches of PNE were obtained. A total of 18 components were positively correlated with the comprehensive coagulation index by two statistical methods. Six and eleven monomers were obtained respectively by chromatographic preparation and procurement, and one monomer was eliminated due to preparation difficulty and other reasons. Seven active monomers with direct hemostatic effect and one active monomer with synergistic hemostatic effect were screened through plasma recalcification time, and their combinations were used as candidate HECG for hemostatic effect verification. The results of in vitro experiments showed that plasma recalcification time and in vitro coagulation time were significantly reduced (P < 0.05) in the HECG group, compared to the PNE group. The results of in vivo experiment also indicated that the hemostatic effect of HECG was comparable to that of PNE and PN powder. CONCLUSION: The composition and efficacy of the HECG of PN were screened and verified using the spectral correlation method and in vivo and in vitro efficacy verification; the HECG included Dencichine, Ginsenoside Rg(1), Ginsenoside Rd, Ginsenoside Rh(1), Ginsenoside F(1), Notoginsenoside R(1), Notoginsenoside Ft(1) and Notoginsenoside Fe. These results laid a foundation for the quality evaluation of PN and provided a reference for the basic research of pharmacodynamic material basis of other TCMs.
Research progress on the pharmacological effects and chemical constituents of Pien Tze Huang and its potential Q-markers.[Pubmed:37777316]
Chin J Nat Med. 2023 Sep;21(9):658-669.
Pien Tze Huang (PTH) was documented as an imperial prescription composed of Notoginseng Radix, Calculus Bovis, Snake Gallbladder, and Musk. It is famous in China and Asian countries due to its excellent effects in heat clearing, detoxifying, swelling reduction, and pain relieving. Modern pharmacological studies demonstrate that PTH shows excellent effects against various inflammatory diseases, liver diseases, and cancers. This review summaries the pharmacological effects, clinical applications, and mainchemical components of PTH. More importantly, its potential quality markers (Q-markers) were then analyzed based on the "five principles" of Q-markers under the guidance of Traditional Chinese Medicine theory, including transfer and traceability, specificity, efficacy, compatibility, and measurability. As a result, ginsenosides Rb1, ginsenoside Rg1, ginsenoside Rd, ginsenoside Re, notoginsenoside R1, Dencichine, bilirubin, biliverdin, taurocholic acid, and muscone are considered as the Q-markers of PTH. These findings will provide guidance and assistance for the construction of a quality control system for PTH.
Remodeling metabolism of Corynebacterium glutamicum for high-level dencichine production.[Pubmed:37748563]
Bioresour Technol. 2023 Nov;388:129800.
Dencichine, a sought-after compound in the medical industry, requires a more efficient and sustainable production method than the current plant extraction process. This study successfully remodeled the metabolic pathway of Corynebacterium glutamicum to produce Dencichine from the precursors of L-2,3-diaminopropionate (L-DAP) and oxalyl-coenzyme A. Firstly, a synthetic pathway for L-DAP was established by introducing exogenous enzymes ZmaU/ZmaV. This resulted in a production of 628 mg/L by overexpressing key genes and reducing the endogenous competitive pathway. Secondly, an oxalyl-CoA synthetic pathway was created through the enzymatic conversion of glyoxylate by introducing heterologous enzymes. Finally, with the integration of the exogenous enzyme BAHD, de novo synthesis of Dencichine in C. glutamicum was achieved, and production reached 31.75 mg/L within 48-hour fermentation. This achievement represents the first successful biosynthesis of Dencichine in C. glutamicum, offering a promising approach for natural product through microbial fermentation.
Determination of Dencichine in Panax notoginseng in the Forest and Field Using High Performance Liquid Chromatography.[Pubmed:37546611]
ACS Omega. 2023 Jul 18;8(30):27450-27457.
Dencichine is a nonprotein amino acid, an effective ingredient in Panax notoginseng with hemostatic and anti-inflammatory effects. There are few studies on the effects of regions and cultivation models on the accumulation of Dencichine. In the current study, the content of Dencichine in P. notoginseng collected from its global cultivation and trading center Yunnan, China, (>640 samples) was determined using an optimized high-performance liquid chromatography method coupled with a diode array detector but without derivatization. The recovery rate of this method was 80-110%, the relative standard deviation was <10%, and the limits of detection and quantification were 0.003% (w/w) and 0.01% (w/w), respectively. The content of Dencichine in each part of P. notoginseng was as follows: rootlets (39.59%) > main roots (29.91%) > leaves (16.21%) > stems (14.29%). For leaves, P. notoginseng in the forest (5.52 +/- 2.26 mg/g) was significantly higher than that in the field (3.93 +/- 1.72 mg/g) but opposite for main roots. The origins and altitudes made different contributions to the accumulation of Dencichine in P. notoginseng. This study provides an effective analytical method to determine Dencichines in various parts of P. notoginseng from different origins and altitudes and supports quality control and product development of P. notoginseng.
[Research summary of chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Panax notoginseng and predictive analysis on its Q-markers].[Pubmed:37282894]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023 Apr;48(8):2059-2067.
Panax notoginseng contains triterpene saponins, flavonoids, amino acids, polysaccharides, volatile oil and other active components, which have the effects of promoting blood circulation, stopping bleeding, removing blood stasis, etc. This study summarized the herbal research, chemical constituents and main pharmacological activities of P. notoginseng, and based on the theory of Q-markers of traditional Chinese medicine, predicted and analyzed the Q-markers of P. notoginseng from the aspects of plant kinship, efficacy, drug properties, measurability of chemical components, etc. It was found that ginsenosides Rg_1, Re, and Rb_1 with specific content ratio, ginsenosides Rb_2, Rb_3, Rc, Rd, Rh_2, and Rg_3, notoginseng R_1, Dencichine and quercetin could be used as potential Q-markers of P. notoginseng, which facilitated the formulation of quality standards reflecting the efficacy of P. notoginseng.
An instant beverage rich in nutrients and secondary metabolites manufactured from stems and leaves of Panax notoginseng.[Pubmed:36570153]
Front Nutr. 2022 Dec 7;9:1058639.
INTRODUCTION: Radix Notoginseng, one of the most famous Chinese traditional medicines, is the dried root of Panax notoginseng (Araliaceae). Stems and leaves of P. notoginseng (SLPN) are rich in secondary metabolites and nutrients, and authorized as a food resource, however, its utilization needs further research. METHODS: A SLPN-instant beverage was manufactured from SLPN through optimization by response surface design with 21-fold of 48.50% ethanol for 39 h, and this extraction was repeated twice; the extraction solution was concentrated to 1/3 volume using a vacuum rotatory evaporator at 45 degrees C, and then spray dried at 110 degrees C. Nutritional components including 14 amino acids, ten mineral elements, 15 vitamins were detected in the SLPN-instant beverage; forty-three triterpenoid saponins, e.g., ginsenoside La, ginsenoside Rb3, notoginsenoside R1, and two flavonoid glycosides, as well as Dencichine were identified by UPLC-MS. RESULTS: The extraction rate of SLPN-instant beverage was 37.89 +/- 0.02%. The majority nutrients were Gly (2.10 +/- 0.63 mg/g), His (1.23 +/- 0.07 mg/g), alpha-VE (18.89 +/- 1.87 mug/g), beta-VE (17.53 +/- 1.98 mug/g), potassium (49.26 +/- 2.70 mg/g), calcium (6.73 +/- 0.27 mg/g). The total saponin of the SLPN-instant beverage was 403.05 +/- 34.98 mg/g, majority was notoginsenoside Fd and with contents of 227 +/- 2.02 mg/g. In addition, catechin and gamma-aminobutyric acid were detected with levels of 24.57 +/- 0.21 mg/g and 7.50 +/- 1.85 mg/g, respectively. The SLPN-instant beverage showed good antioxidant activities with half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC(50)) for scavenging hydroxyl (OH(-)) radicals, superoxide anion (O(2-)) radicals, 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radicals and 2,2'-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonate) (ABTS+) radicals were 0.1954, 0.2314, 0.4083, and 0.3874 mg/mL, respectively. CONCLUSION: We optimized an analytical method for in depth analysis of the newly authorized food resource SLPN. Together, an instant beverage with antioxidant activity, rich in nutrients and secondary metabolites, was manufactured from SLPN, which may improve the utilization of SLPN.
Biosynthesis of plant hemostatic dencichine in Escherichia coli.[Pubmed:36123371]
Nat Commun. 2022 Sep 19;13(1):5492.
Dencichine is a plant-derived nature product that has found various pharmacological applications. Currently, its natural biosynthetic pathway is still elusive, posing challenge to its heterologous biosynthesis. In this work, we design artificial pathways through retro-biosynthesis approaches and achieve de novo production of Dencichine. First, biosynthesis of the two direct precursors L-2, 3-diaminopropionate and oxalyl-CoA is achieved by screening and integrating microbial enzymes. Second, the solubility of Dencichine synthase, which is the last and only plant-derived pathway enzyme, is significantly improved by introducing 28 synonymous rare codons into the codon-optimized gene to slow down its translation rate. Last, the metabolic network is systematically engineered to direct the carbon flux to Dencichine production, and the final titer reaches 1.29 g L(-1) with a yield of 0.28 g g(-1) glycerol. This work lays the foundation for sustainable production of Dencichine and represents an example of how synthetic biology can be harnessed to generate unnatural pathways to produce a desired molecule.
Preparation of Rosin-Based Composite Membranes and Study of Their Dencichine Adsorption Properties.[Pubmed:35683833]
Polymers (Basel). 2022 May 26;14(11):2161.
In this work, rosin-based composite membranes (RCMs) were developed as selective sorbents for the preparation of Dencichine for the first time. The rosin-based polymer microspheres (RPMs) were synthesized using 4-ethylpyridine as a functional monomer and ethylene glycol maleic rosinate acrylate as a crosslinking. RCMs were prepared by spinning the RPMs onto the membranes by electrostatic spinning technology. The optimization of various parameters that affect RCMs was carried out, such as the ratio concentration and voltage intensity of electrospinning membrane. The RCMs were characterized by SEM, TGA and FT-IR. The performances of RCMs were assessed, which included adsorption isotherms, selective recognition and adsorption kinetics. The adsorption of Dencichine on RCMs followed pseudo-second-order and adapted Langmuir-Freundlich isotherm model. As for the RCMs, the fast adsorption stage appeared within the first 45 min, and the experimental maximum adsorption capacity was 1.056 mg/g, which is much higher than the previous Dencichine adsorbents reported in the literature. The initial decomposition temperature of RCMs is 297 degrees C, the tensile strength is 2.15 MPa and the elongation at break is 215.1%. The RCMs have good thermal stability and mechanical properties. These results indicated that RCMs are a tremendously promising adsorbent for enriching and purifying Dencichine from the notoginseng extracts.


