CrebanineCAS# 25127-29-1 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 25127-29-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 159999 | Appearance | Cryst. |
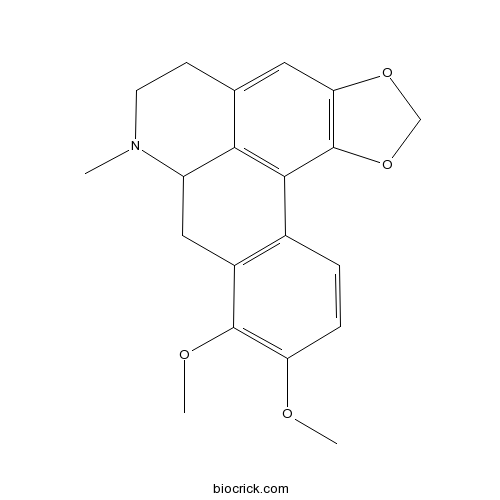
| Formula | C20H21NO4 | M.Wt | 339.4 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| SMILES | CN1CCC2=CC3=C(C4=C2C1CC5=C4C=CC(=C5OC)OC)OCO3 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | UVDQDNQWGQFIAO-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H21NO4/c1-21-7-6-11-8-16-20(25-10-24-16)18-12-4-5-15(22-2)19(23-3)13(12)9-14(21)17(11)18/h4-5,8,14H,6-7,9-10H2,1-3H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Crebanine has antiarrhythmic, anticancer, anti-inflammatory, and analgesic properties; it can significantly improve the cognitive deficits induced by scopolamine, via the alpha-7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, crebanine or its scaffold can be used as the starting point to develop a drug for Alzheimer's disease.Crebanine can reduce TNF-α-induced cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and survival by suppressing NF-κB activity and expression profile of its downstream genes. |
| Targets | TNF-α | NF-kB | Caspase | COX | VEGFR | NO | Sodium Channel | AChR | PARP | Bcl-2/Bax | MMP(e.g.TIMP) | Akt | MAPK | p38MAPK | AP-1 | p65 | IL Receptor |
| In vitro | Induction of G1 arrest and apoptosis in human cancer cells by crebanine, an alkaloid from Stephania venosa.[Pubmed: 22863844]Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2012;60(10):1283-9.In this study, we focused the effects of Crebanine, an alkaloid isolated from the tuber of Stephania venosa, on various human cancer cells. Anti-invasion effect of crebanine and O-methylbulbocapnine from Stephania venosa via down-regulated matrix metalloproteinases and urokinase plasminogen activator.[Pubmed: 23985774]Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2013;61(11):1156-65.
Antiinflammatory Activities of Crebanine by Inhibition of NF-κB and AP-1 Activation through Suppressing MAPKs and Akt Signaling in LPS-Induced RAW264.7 Macrophages.[Pubmed: 26499331 ]Biol Pharm Bull. 2016;39(1):54-61.Crebanine, an aporphine alkaloid, displays various biological activities such as anticancer and antimicrobial activities. |
| In vivo | The effect of crebanine on memory and cognition impairment via the alpha-7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor.[Pubmed: 22749860]Life Sci. 2012 Aug 21;91(3-4):107-14.The aims of the present study were to investigate the effect of Crebanine on memory and cognition impairment in mice and to elucidate the underlying molecular mechanisms. |
| Kinase Assay | Crebanine inhibits voltage-dependent Na+ current in guinea-pig ventricular myocytes.[Pubmed: 24484592]Crebanine, an aporphine alkaloid, sensitizes TNF-α-induced apoptosis and suppressed invasion of human lung adenocarcinoma cells A549 by blocking NF-κB-regulated gene products.[Pubmed: 24867094]Tumour Biol. 2014 Sep;35(9):8615-24.Crebanine is an alkaloid known to exhibit anticancer, but its mechanism is not well understood. Besides, the nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) transcription factor has been correlated with inflammation, carcinogenesis, tumor cell survival, invasion, and angiogenesis. Chin J Nat Med. 2014 Jan;12(1):20-3.To study the effects of Crebanine on voltage-gated Na(+) channels in cardiac tissues.
|
| Animal Research | Site of Analgesic Action and Its Mechanism of Crebanine.[Reference: WebLink]Natural Product Research & Development,2011,23(2):341.The main aim was to determine the site of analgesic action and the mechanism of Crebanine. |

Crebanine Dilution Calculator

Crebanine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9464 mL | 14.7319 mL | 29.4638 mL | 58.9275 mL | 73.6594 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5893 mL | 2.9464 mL | 5.8928 mL | 11.7855 mL | 14.7319 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2946 mL | 1.4732 mL | 2.9464 mL | 5.8928 mL | 7.3659 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0589 mL | 0.2946 mL | 0.5893 mL | 1.1786 mL | 1.4732 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0295 mL | 0.1473 mL | 0.2946 mL | 0.5893 mL | 0.7366 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- FRATide
Catalog No.:BCC5821
CAS No.:251087-38-4
- Antazoline HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4627
CAS No.:2508-72-7
- Salvisyrianone
Catalog No.:BCN4821
CAS No.:250691-57-7
- NNC 63-0532
Catalog No.:BCC7177
CAS No.:250685-44-0
- Pedunsaponin A
Catalog No.:BCN8192
CAS No.:250613-27-5
- Cyclo(RGDyK)
Catalog No.:BCC6512
CAS No.:250612-42-1
- (±)-Acetylcarnitine chloride
Catalog No.:BCC6617
CAS No.:2504-11-2
- Excavatin M
Catalog No.:BCN5116
CAS No.:250293-31-3
- PNU 177864 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7664
CAS No.:250266-51-4
- Boc-His(Dnp)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3401
CAS No.:25024-53-7
- Otophylloside F
Catalog No.:BCN6441
CAS No.:250217-73-3
- 1,2:4,5-Di-O-isopropylidene-beta-D-fructopyranose
Catalog No.:BCN1475
CAS No.:25018-67-1
- Urotensin II (human)
Catalog No.:BCC5796
CAS No.:251293-28-4
- SU 16f
Catalog No.:BCC7639
CAS No.:251356-45-3
- M344
Catalog No.:BCC2162
CAS No.:251456-60-7
- Tesaglitazar
Catalog No.:BCC7828
CAS No.:251565-85-2
- 5-Chloro-2-nitrobenzoic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8743
CAS No.:2516-95-2
- Acevaltrate
Catalog No.:BCN7127
CAS No.:25161-41-5
- Loline
Catalog No.:BCN2003
CAS No.:25161-91-5
- Isohomoarbutin
Catalog No.:BCN7612
CAS No.:25162-30-5
- Dynamin inhibitory peptide
Catalog No.:BCC1034
CAS No.:251634-21-6
- AM 1172
Catalog No.:BCC7675
CAS No.:251908-92-6
- SLV 320
Catalog No.:BCC7656
CAS No.:251945-92-3
- A 205804
Catalog No.:BCC3944
CAS No.:251992-66-2
Crebanine inhibits voltage-dependent Na+ current in guinea-pig ventricular myocytes.[Pubmed:24484592]
Chin J Nat Med. 2014 Jan;12(1):20-3.
AIM: To study the effects of Crebanine on voltage-gated Na(+) channels in cardiac tissues. METHODS: Single ventricular myocytes were enzymatically dissociated from adult guinea-pig heart. Voltage-dependent Na(+) current was recorded using the whole cell voltage-clamp technique. RESULTS: Crebanine reversibly inhibited Na(+) current with an IC50 value of 0.283 mmol.L(-1) (95% confidence range: 0.248-0.318 mmol.L(-1)). Crebanine at 0.262 mmol.L(-1) caused a negative shift (about 12 mV) in the voltage-dependence of steady-state inactivation of Na(+) current, and retarded its recovery from inactivation, but did not affect its activation curve. CONCLUSION: In addition to blocking other voltage-gated ion channels, Crebanine blocked Na(+) channels in guinea-pig ventricular myocytes. Crebanine acted as an inactivation stabilizer of Na(+) channels in cardiac tissues.
Antiinflammatory Activities of Crebanine by Inhibition of NF-kappaB and AP-1 Activation through Suppressing MAPKs and Akt Signaling in LPS-Induced RAW264.7 Macrophages.[Pubmed:26499331]
Biol Pharm Bull. 2016;39(1):54-61.
Crebanine, an aporphine alkaloid, displays various biological activities such as anticancer and antimicrobial activities. In this study, we further investigated the suppressive effect of Crebanine on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced expression of proinflammatory mediators and the molecular mechanisms underlying these activities in RAW264.7 macrophages. Crebanine inhibited the production of proinflammatory cytokines including interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells. Moreover, Crebanine suppressed LPS-induced inducible nitric oxide (iNO) and prostaglandin E2 and reduced the expression of iNO synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 in RAW264.7 cells. Crebanine suppressed LPS-induced phosphorylation of Akt and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), including extracellular signaling-regulated kinase 1/2, c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase, and p38 MAPK signaling. In addition, the specific inhibitor of MAPKs and Akt reduced the expression of IL-6 and NO production in LPS-induced macrophages. Furthermore, Crebanine inhibited LPS-induced nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB) activation by reducing the phosphorylation of p65 at Ser536 but not the p65 translocation to the nucleus and inhibitory factor kappa B alpha degradation. Crebanine also suppressed phosphorylation and nucleus translocation of activator protein-1 (AP-1). These observations suggest that the antiinflammatory properties of Crebanine may stem from the inhibition of proinflammatory mediators via suppression of the NF-kappaB, AP-1, MAPKs, and Akt signaling pathways.
Crebanine, an aporphine alkaloid, sensitizes TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis and suppressed invasion of human lung adenocarcinoma cells A549 by blocking NF-kappaB-regulated gene products.[Pubmed:24867094]
Tumour Biol. 2014 Sep;35(9):8615-24.
Crebanine is an alkaloid known to exhibit anticancer, but its mechanism is not well understood. Besides, the nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kappaB) transcription factor has been correlated with inflammation, carcinogenesis, tumor cell survival, invasion, and angiogenesis. In this study, we investigated the effects of Crebanine on tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha)-induced NF-kappaB activation and the expression of NF-kappaB-regulated gene products. We found that Crebanine reduced the cell proliferation of lung, ovarian, and breast cancer cells. Crebanine also potentiated TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis which correlated with the suppression of the gene products linked to cell survival, B cell lymphoma-extra large, and proliferation, cyclin D1. In addition, Crebanine affected TNF-alpha-induced activation of caspase-8, caspase-3, and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase cleavage, indicating that the apoptotic effects of TNF-alpha were enhanced by Crebanine. Moreover, Crebanine reduced TNF-alpha-induced A549 cell invasion and migration. Furthermore, Crebanine suppressed the TNF-alpha-mediated expression of proteins that involved cancer cell invasion (matrix metalloproteinase 9 urokinase-type plasminogen activator, urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor and intercellular adhesion molecule 1) and angiogenesis (COX-2 and VEGF), all of which are known to be regulated by NF-kappaB. We also demonstrated that TNF-alpha induced NF-kappaB DNA-binding activity, which was inhibited by Crebanine. Moreover, Crebanine suppressed the TNF-alpha-induced degradation of inhibitor of NF-kappaB alpha (IkappaBa), which led to reduced NF-kappaB translocation to the nucleus. Taken together, our results demonstrated that Crebanine reduced TNF-alpha-induced cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and survival by suppressing NF-kappaB activity and expression profile of its downstream genes.
The effect of crebanine on memory and cognition impairment via the alpha-7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor.[Pubmed:22749860]
Life Sci. 2012 Aug 21;91(3-4):107-14.
AIMS: The aims of the present study were to investigate the effect of Crebanine on memory and cognition impairment in mice and to elucidate the underlying molecular mechanisms. MAIN METHODS: The memory-enhancing effects of Crebanine were assessed with a water maze test using scopolamine-induced amnesic mice. The molecular mechanism was explored in silico by docking Crebanine against acetylcholine binding proteins (AChBPs) and in vitro with a radioligand competition assay using (+/-)-[(3)H]-epibatidine. The pharmacological behavior was assessed by observing changes to the functional activity of alpha7-nAChRs expressed in Xenopus oocytes and by fluorescent assays on recombinant ligand gated ion channel (LGIC) receptors expressed in mammalian cells. KEY FINDINGS: The administration of Crebanine significantly improved the cognitive deficits induced by scopolamine, as measured by the water maze test. The docking results demonstrated that Crebanine bound to the active binding site of the AChBP template with a good docking energy. Crebanine significantly inhibited the binding of (+/-)-[(3)H]-epibatidine to AChBPs with K(i) values of 179 nM and 538 nM for Ls and Ac, respectively. Further functional assays performed using two separate protocols indicated that Crebanine is an antagonist of the alpha7-nAChR with an IC(50) of 19.1muM. SIGNIFICANCE: The observed actions of Crebanine against amnesia and its effect on alpha7-nAChRs will be beneficial for target-based drug design; Crebanine or its scaffold can be used as the starting point to develop a drug for Alzheimer's disease. The cognition-enhancing effects of Crebanine and the underlying mechanism based on alpha7-nAChRs are consistent with its traditional use. These findings demonstrate the potential utility of Crebanine in the development of neurodegenerative therapy.
Anti-invasion effect of crebanine and O-methylbulbocapnine from Stephania venosa via down-regulated matrix metalloproteinases and urokinase plasminogen activator.[Pubmed:23985774]
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2013;61(11):1156-65. Epub 2013 Aug 28.
The alkaloids isolated from Stephania venosa (S. venosa) have been shown to inhibit the proliferation and to induce the apoptosis of cancer cells. However, the anti-metastatic effect of the alkaloids on cancer cell invasion is unknown. In this study, we investigated the anti-invasive properties of four alkaloids from S. venosa, Crebanine (CN), O-methylbulbocapnine (OMBC), tetrahydropalmatine (THP), and N-methyltetrahydropalmatine (NMTHP), in HT1080 human fibrosacroma cells. Treatment of the cells with 15 microg/mL of CN and OMBC reduced the chemo-invasion of HT1080 cells to 45 and 50%, respectively, whereas THP and NMTHP had a negative effect. On the other hand, CN and OMBC had no effect on cell migration. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA) are the extracellular matrix (ECM) degradation enzymes that play an important role in cancer cell metastasis. Results from zymography and western blot analysis showed that CN and OMBC comparatively reduced MMP-2, MMP-9, MT1-MMP and uPA expression in a dose-dependent manner. However, CN and OMBC had no effect on the activity of collagenase, MMP-2 and MMP-9. We also found that CN and OMBC reduced the nuclear translocation and DNA binding activity of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB), which is the expressed mediator of ECM degradation enzymes. These findings demonstrated that CN and OMBC mediated HT1080 cell invasion by the reduction of MMP-2, MMP-9, uPA and MT1-MMP expression, possibly by targeting of NF-kappaB signaling pathway in the HT1080 cells.
Induction of G1 arrest and apoptosis in human cancer cells by crebanine, an alkaloid from Stephania venosa.[Pubmed:22863844]
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2012;60(10):1283-9. Epub 2012 Aug 3.
In this study, we focused the effects of Crebanine, an alkaloid isolated from the tuber of Stephania venosa, on various human cancer cells. Crebanine treatment was found to significantly inhibit the proliferation of human leukemic cells (HL-60, U937 and K562), human fibrosarcoma cells (HT1080) and cervix cancer cell lines (KB-3-1 and KB-V1), of which HL-60 cells were the most sensitive to its treatment. In contrast, Crebanine caused much less toxicity in human normal fibroblast cells. Our results demonstrated that Crebanine mediated cell cycle arrest at G0/G1 phase and this was associated with down-regulation of cyclins A and D. In addition, Crebanine induced apoptosis, which was detected by observation of the membrane phospholipid exposure in flow cytometry. Its induction of apoptosis was accompanied by an increase in cleavage of caspase-3, -8, -9 and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP), and was attributable to the augmentation of Bax/Bcl proteins level. Crebanine also decreased mitochondrial membrane potential. Taken together, Crebanine exerts anti-proliferative effects on human cancer cells through the induction of cell cycle arrest at the G1 phases and apoptosis. Our results suggest that Crebanine is a promising new candidate as a chemotherapeutic agent for cancer therapy.


