CorydalineCAS# 518-69-4 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 518-69-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 101301 | Appearance | White-beige powder |
| Formula | C22H27NO4 | M.Wt | 369.44 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | (+)-Corydaline; Corydalin | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 33.33 mg/mL (90.22 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
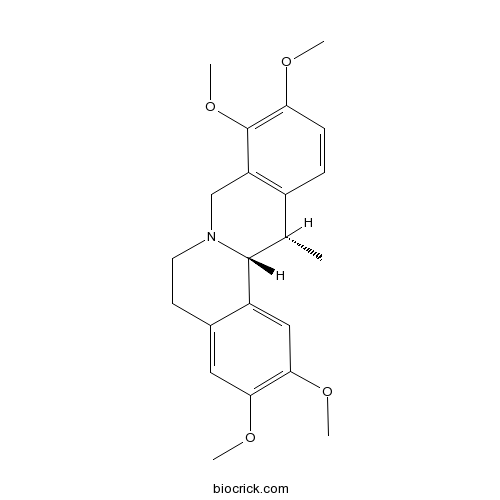
| Chemical Name | (13S,13aR)-2,3,9,10-tetramethoxy-13-methyl-6,8,13,13a-tetrahydro-5H-isoquinolino[2,1-b]isoquinoline | ||
| SMILES | CC1C2C3=CC(=C(C=C3CCN2CC4=C1C=CC(=C4OC)OC)OC)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | VRSRXLJTYQVOHC-YEJXKQKISA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C22H27NO4/c1-13-15-6-7-18(24-2)22(27-5)17(15)12-23-9-8-14-10-19(25-3)20(26-4)11-16(14)21(13)23/h6-7,10-11,13,21H,8-9,12H2,1-5H3/t13-,21+/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Corydaline is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, is also an inhibitor of CYP2C19 and CYP2C9. Corydaline has antiallergic, and antinociceptive activities. Corydaline promotes gastric emptying and small intestinal transit and facilitates gastric accommodation. |
| Targets | P450 (e.g. CYP17) | NADPH-oxidase |
| In vitro | In vitro metabolism of corydaline in human liver microsomes and hepatocytes using liquid chromatography-ion trap mass spectrometry.[Pubmed: 22689485]J Sep Sci. 2012 May;35(9):1102-9.Corydaline is a pharmacologically active isoquinoline alkaloid isolated from Corydalis tubers. It exhibits the antiacetylcholinesterase, antiallergic, antinociceptive, and gastric emptying activities. The purposes of this study were to establish in vitro metabolic pathways of Corydaline in human liver microsomes and hepatocytes by identification of their metabolites using liquid chromatography-ion trap mass spectrometry.
|
| In vivo | Gender differences in corydaline pharmacokinetics in rats.[Pubmed: 25430796]Xenobiotica. 2014 Nov 28:1-8.
1. Corydaline, an isoquinoline alkaloid, is one of the major active constituents in a new prokinetic botanical agent, DA-9701. It has been recommended that preclinical pharmacokinetic studies of natural medicines include both genders. Therefore, in this study, the pharmacokinetics of Corydaline in male and female rats was evaluated following intravenous and oral administration of pure Corydaline or DA-9701. Effects of corydaline from Corydalis tuber on gastric motor function in an animal model.[Pubmed: 20522959]Biol Pharm Bull. 2010;33(6):958-62.The aim of this study was to evaluate the prokinetic and gastric-relaxing effects of the isoquinoline alkaloid Corydaline, which was extracted from Corydalis tubers (CT).
Corydaline is a marker compound used for quality control of DA-9701, a prokinetic agent formulated from extracts of Pharbitidis semen and Corydalis tuber that is currently in clinical trials in Korea for the treatment of functional dyspepsia (FD). DA-9701 was previously reported to be a potential therapeutic agent for the treatment of abnormalities in gastrointestinal motor function in FD patients; however, the therapeutic effects of Corydaline on FD have yet to be demonstrated in an in vivo study.
|
| Kinase Assay | Corydaline inhibits multiple cytochrome P450 and UDP-glucuronosyltransferase enzyme activities in human liver microsomes.[Pubmed: 21826053]Molecules. 2011 Aug 5;16(8):6591-602.Corydaline is a bioactive alkaloid with various antiacetylcholinesterase, antiallergic, and antinociceptive activities found in the medicinal herb Corydalis Tubers.
|
| Animal Research | Pharmacokinetics of chlorogenic acid and corydaline in DA-9701, a new botanical gastroprokinetic agent, in rats.[Pubmed: 24417753]Xenobiotica. 2014 Jul;44(7):635-43.1.Few studies describing the pharmacokinetic properties of chlorogenic acid (CA) and Corydaline (CRD) which are marker compounds of a new prokinetic botanical agent, DA-9701, have been reported.
|

Corydaline Dilution Calculator

Corydaline Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7068 mL | 13.534 mL | 27.068 mL | 54.136 mL | 67.67 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5414 mL | 2.7068 mL | 5.4136 mL | 10.8272 mL | 13.534 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2707 mL | 1.3534 mL | 2.7068 mL | 5.4136 mL | 6.767 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0541 mL | 0.2707 mL | 0.5414 mL | 1.0827 mL | 1.3534 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0271 mL | 0.1353 mL | 0.2707 mL | 0.5414 mL | 0.6767 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Corydaline is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor isolated from Corydalis yanhusuo.
References:
[1]. Xiao HT, et al. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors from Corydalis yanhusuo. Nat Prod Res. 2011 Sep;25(15):1418-22.
- Tetrandrine
Catalog No.:BCN5955
CAS No.:518-34-3
- (-)-beta-Peltatin
Catalog No.:BCN3606
CAS No.:518-29-6
- Podophyllotoxin
Catalog No.:BCN5957
CAS No.:518-28-5
- Evodiamine
Catalog No.:BCN1092
CAS No.:518-17-2
- Dehydroglyasperin D
Catalog No.:BCN6829
CAS No.:517885-72-2
- Rengynic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5644
CAS No.:517883-38-4
- Carteolol HCl
Catalog No.:BCC6466
CAS No.:51781-21-6
- Mefloquine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1737
CAS No.:51773-92-3
- Valechlorine
Catalog No.:BCN2763
CAS No.:51771-49-4
- Estra-4,9-diene-3,17-dione
Catalog No.:BCC8959
CAS No.:5173-46-6
- Uncarine E
Catalog No.:BCC8263
CAS No.:5171-37-9
- Shikonine
Catalog No.:BCN3530
CAS No.:517-89-5
- Emodin
Catalog No.:BCN5649
CAS No.:518-82-1
- Xanthopurpurin
Catalog No.:BCN6723
CAS No.:518-83-2
- Cycleanine
Catalog No.:BCN8445
CAS No.:518-94-5
- Isomaculosidine
Catalog No.:BCN7069
CAS No.:518-96-7
- 3,3'-Di-O-methylellagic acid 4'-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN1431
CAS No.:51803-68-0
- Nimesulide
Catalog No.:BCC4435
CAS No.:51803-78-2
- Oxoepistephamiersine
Catalog No.:BCN5645
CAS No.:51804-68-3
- Dihydrooxoepistephamiersine
Catalog No.:BCN5646
CAS No.:51804-69-4
- Raltegravir (MK-0518)
Catalog No.:BCC2137
CAS No.:518048-05-0
- KX1-004
Catalog No.:BCC5440
CAS No.:518058-84-9
- 2',4'-Dihydroxychalcone
Catalog No.:BCN5647
CAS No.:1776-30-3
- UMI-77
Catalog No.:BCC5567
CAS No.:518303-20-3
Gender differences in corydaline pharmacokinetics in rats.[Pubmed:25430796]
Xenobiotica. 2015 May;45(5):456-63.
1. Corydaline, an isoquinoline alkaloid, is one of the major active constituents in a new prokinetic botanical agent, DA-9701. It has been recommended that preclinical pharmacokinetic studies of natural medicines include both genders. Therefore, in this study, the pharmacokinetics of Corydaline in male and female rats was evaluated following intravenous and oral administration of pure Corydaline or DA-9701. 2. After intravenous administration of Corydaline, the area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) was significantly greater (by 46.4%) in female rats compared to male rats due to a 29.3% reduction in non-renal clearance in female rats. The gender difference in Corydaline hepatic metabolic clearance was supported by a significantly slower metabolism of Corydaline in hepatic microsomes of female rats mediated via male-specific (CYP2C11 and CYP3A2) or male-dominant (CYP3A1) CYP isozymes. 3. Following oral administration of pure Corydaline or DA-9701, the AUC and Cmax values of Corydaline in female rats were significantly greater (by 793% and 466% increase for Corydaline administration or by 501% and 143% increase for DA-9701 administration) than in male rats. Greater F values of Corydaline in female rats could be due to smaller hepatic first-pass extraction as a result of slower hepatic metabolism of Corydaline. 4. However, we observed a comparable disappearance of Corydaline in male and female human liver microsomes, consistent with little gender difference in CYP2C9 and CYP3A activities in humans compared to that in rats. Thus, gender differences in Corydaline metabolism are not expected to occur in humans.
Effects of corydaline from Corydalis tuber on gastric motor function in an animal model.[Pubmed:20522959]
Biol Pharm Bull. 2010;33(6):958-62.
The aim of this study was to evaluate the prokinetic and gastric-relaxing effects of the isoquinoline alkaloid Corydaline, which was extracted from Corydalis tubers (CT). Corydaline is a marker compound used for quality control of DA-9701, a prokinetic agent formulated from extracts of Pharbitidis semen and Corydalis tuber that is currently in clinical trials in Korea for the treatment of functional dyspepsia (FD). DA-9701 was previously reported to be a potential therapeutic agent for the treatment of abnormalities in gastrointestinal motor function in FD patients; however, the therapeutic effects of Corydaline on FD have yet to be demonstrated in an in vivo study. In the current study, oral administration of Corydaline not only significantly accelerated gastric emptying in normal rats but also improved delayed gastric emptying to near normal levels. Furthermore, Corydaline induced significant gastric relaxation, shifting the pressure-volume curve towards higher volumes compared to controls. These results suggest that Corydaline promotes gastric emptying and small intestinal transit and facilitates gastric accommodation.
Pharmacokinetics of chlorogenic acid and corydaline in DA-9701, a new botanical gastroprokinetic agent, in rats.[Pubmed:24417753]
Xenobiotica. 2014 Jul;44(7):635-43.
1.Few studies describing the pharmacokinetic properties of chlorogenic acid (CA) and Corydaline (CRD) which are marker compounds of a new prokinetic botanical agent, DA-9701, have been reported. The aim of the present study is to evaluate the pharmacokinetic properties CA and CRD following intravenous and oral administration of pure CA (1-8 mg/kg) or CRD (1.1-4.5 mg/kg) and their equivalent dose of DA-9701 to rats. 2. Dose-proportional AUC and dose-independent clearance (10.3-12.1 ml/min/kg) of CA were observed following its administration. Oral administration of CA as DA-9701 did not influence the oral pharmacokinetic parameters of CA. Incomplete absorption of CA, its decomposition in the gastrointestinal tract, and/or pre-systemic metabolism resulted in extremely low oral bioavailability (F) of CA (0.478-0.899%). 3. CRD showed greater dose-normalized AUC in the higher dose group than that in lower dose group(s) after its administration due to saturation of its metabolism via decreased non-renal clearance (by 51.3%) and first-pass extraction. As a result, the F of CRD following 4.5 mg/kg oral CRD (21.1%) was considerably greater than those of the lower dose groups (9.10 and 13.8%). However, oral administration of CRD as DA-9701 showed linear pharmacokinetics as a result of increased AUC and F in lower-dose groups (by 182% and 78.5%, respectively) compared to those of pure CRD. The greater oral AUC of CRD for DA-9701 than for pure CRD could be due to decreased hepatic and/or GI first-pass extraction of CRD by other components in DA-9701.
In vitro metabolism of corydaline in human liver microsomes and hepatocytes using liquid chromatography-ion trap mass spectrometry.[Pubmed:22689485]
J Sep Sci. 2012 May;35(9):1102-9.
Corydaline is a pharmacologically active isoquinoline alkaloid isolated from Corydalis tubers. It exhibits the antiacetylcholinesterase, antiallergic, antinociceptive, and gastric emptying activities. The purposes of this study were to establish in vitro metabolic pathways of Corydaline in human liver microsomes and hepatocytes by identification of their metabolites using liquid chromatography-ion trap mass spectrometry. Human liver microsomal incubation of Corydaline in the presence of an NADPH-generating system resulted in the formation of nine metabolites, namely, four O-desmethylCorydaline [M1 (yuanhunine), M2 (9-O-desmethylCorydaline), M3 (isocorybulbine), and M4 (corybulbine)], three di-O-desmethylCorydaline [M5 (9,10-di-O-desmethylCorydaline), M6 (2,10-di-O-desmethylCorydaline), and M7 (3,10-di-O-desmethylCorydaline)], M8 (hydroxyyuanhunine), and M9 (hydroxyCorydaline). Incubation of Corydaline in human hepatocytes produced four metabolites including M1, M5, M6, and M9. O-Demethylation and hydroxylation were the major metabolic pathways for the metabolism of Corydaline in human liver microsomes and hepatocytes.
Corydaline inhibits multiple cytochrome P450 and UDP-glucuronosyltransferase enzyme activities in human liver microsomes.[Pubmed:21826053]
Molecules. 2011 Aug 5;16(8):6591-602.
Corydaline is a bioactive alkaloid with various antiacetylcholinesterase, antiallergic, and antinociceptive activities found in the medicinal herb Corydalis Tubers. The inhibitory potential of Corydaline on the activities of seven major human cytochrome P450 and four UDP-glucuronosyltransferase enzymes in human liver microsomes was investigated using LC-tandem MS. Corydaline was found to inhibit CYP2C19-catalyzed S-mephenytoin-4'-hydroxylatoin and CYP2C9-catalyzed diclofenac 4-hydroxylation, with K(i) values of 1.7 and 7.0 mM, respectively. Corydaline also demonstrated moderate inhibition of UGT1A1-mediated 17b-estradiol 3-glucuronidation and UGT1A9-mediated propofol glucuronidation with K(i) values of 57.6 and 37.3 mM, respectively. In the presence of Corydaline, CYP3A-mediated midazolam hydroxylation showed a decrease with increasing preincubation time in a dose-dependent manner with K(i) values of 30.0 mM. These in vitro results suggest that Corydaline should be evaluated for potential pharmacokinetic drug interactions in vivo due to potent inhibition of CYP2C19 and CYP2C9.


