(-)-Catechin gallate(CG)CAS# 130405-40-2 |
- (-)-Epicatechin gallate
Catalog No.:BCN6327
CAS No.:1257-08-5
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

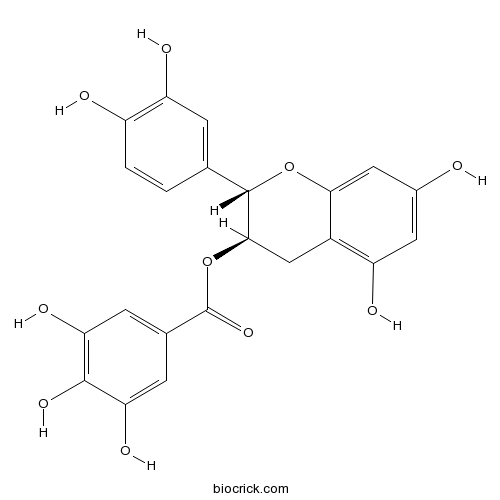
Chemical structure

3D structure
| Cas No. | 130405-40-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6419835 | Appearance | White-beige powder |
| Formula | C22H18O10 | M.Wt | 442.37 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | (-)-Catechin 3-gallate; (-)-Catechin 3-O-gallate | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 100 mg/mL (226.06 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
| Chemical Name | [(2S,3R)-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromen-3-yl] 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoate | ||
| SMILES | C1C(C(OC2=CC(=CC(=C21)O)O)C3=CC(=C(C=C3)O)O)OC(=O)C4=CC(=C(C(=C4)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | LSHVYAFMTMFKBA-CTNGQTDRSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C22H18O10/c23-11-6-14(25)12-8-19(32-22(30)10-4-16(27)20(29)17(28)5-10)21(31-18(12)7-11)9-1-2-13(24)15(26)3-9/h1-7,19,21,23-29H,8H2/t19-,21+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | (-)-Catechin gallate is a minor constituent in green tea catechins, it inhibits the activity of COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes. Catechin gallate (IC50=53 microM) shows cytotoxicity against the colorectal adenocarcinoma cell line HCT116, it also exhibits strong anti-proliferative and anti-inflammatory activities on pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cells. Catechin 3-gallate is a good inhibitor of maltase, with IC50 values of 62 uM, it inhibits both α-glucosidases and rabbit glycogen phosphorylase (GP) in vitro and in cell culture, would contribute to the protection or improvement of type 2 diabetes. |
| Targets | Caspase | IL Receptor | CDK | TNF-α | NF-kB |
| In vitro | In vitro cytotoxicity of (-)-catechin gallate, a minor polyphenol in green tea.[Pubmed: 17606338]Toxicol Lett. 2007 Jul 10;171(3):171-80.The cytotoxicity of (-)-Catechin gallate(CG), a minor polyphenolic constituent in green tea, towards cells derived from tissues of the human oral cavity was studied.
In vitro inhibition of α-glucosidases and glycogen phosphorylase by catechin gallates in green tea.[Reference: WebLink]Food Chem.,2010,122(4):1061-6.We investigated in vitro inhibition of mammalian carbohydrate-degrading enzymes by green tea extract and the component catechins, and further evaluated their inhibitory activities in cell cultures.
|
| Cell Research | Epicatechin gallate and catechin gallate are superior to epigallocatechin gallate in growth suppression and anti-inflammatory activities in pancreatic tumor cells.[Pubmed: 21241417 ]Cancer Sci. 2011 Apr;102(4):728-34.Green tea catechins are considered as possible cancer preventive agents for several cancer types but little is known regarding their effects on pancreatic cancer cells. The best studied catechin and the major polyphenol present in green tea is epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG).
|

(-)-Catechin gallate(CG) Dilution Calculator

(-)-Catechin gallate(CG) Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2606 mL | 11.3028 mL | 22.6055 mL | 45.211 mL | 56.5138 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4521 mL | 2.2606 mL | 4.5211 mL | 9.0422 mL | 11.3028 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2261 mL | 1.1303 mL | 2.2606 mL | 4.5211 mL | 5.6514 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0452 mL | 0.2261 mL | 0.4521 mL | 0.9042 mL | 1.1303 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0226 mL | 0.113 mL | 0.2261 mL | 0.4521 mL | 0.5651 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
(-)-Catechin gallate is a minor constituent in green tea catechins. (-)-Catechin gallate inhibits the activity of COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes.
In Vitro:(-)-Catechin gallate (CG) directly interacts with DNA oligomers and inhibits the activity of COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes, the gene expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in macrophage-differentiated HL-60 myeloid leukemia cells, the adipocyte uptake of glucose by the transporter, GLUT4, and the activities of various proteasomes, i.e., the multicatalytic proteases responsible for the degradation of most cellular proteins. The relative cytotoxicities of a 3-day exposure to (-)-Catechin gallate are determined for cancerous CAL27 and HSG cells, immortalized epithelioid S-G cells, and normal HGF-1 gingival fibroblasts. The concentration at which toxicity (P≤0.01) initially occur is 25 μM (-)-Catechin gallate for S-G cells, 50 μM (-)-Catechin gallate for CAL27 cells, 62.5 μM (-)-Catechin gallate for HSG cells and 75 μM (-)-Catechin gallate for HGF-1 fibroblasts. The calculated neutral red (NR50) values for a 3-day exposure to (-)-Catechin gallate are 58 μM for S-G cells, 62 μM for CAL27 cells, 90 μM for HSG cells and 132 μM for HGF-1 fibroblasts[1].
References:
[1]. Babich H, et al. In vitro cytotoxicity of (-)-catechin gallate, a minor polyphenol in green tea. Toxicol Lett. 2007 Jul 10;171(3):171-80.
- Paulownin
Catalog No.:BCN6160
CAS No.:13040-46-5
- (RS)-MCPG disodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7756
CAS No.:1303994-09-3
- CHPG Sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7755
CAS No.:1303993-73-8
- DL-AP5 Sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7753
CAS No.:1303993-72-7
- 2-Oxokolavenol
Catalog No.:BCN4716
CAS No.:130395-82-3
- Pungiolide A
Catalog No.:BCN8128
CAS No.:130395-54-9
- Decinnamoyltaxagifine
Catalog No.:BCN7329
CAS No.:130394-69-3
- Batimastat (BB-94)
Catalog No.:BCC1223
CAS No.:130370-60-4
- AC 45594
Catalog No.:BCC7544
CAS No.:13037-86-0
- MI-773 (SAR405838)
Catalog No.:BCC5648
CAS No.:1303607-60-4
- MI-773
Catalog No.:BCC5155
CAS No.:1303607-07-9
- Cathayanon I
Catalog No.:BCN3678
CAS No.:1303438-52-9
- A-71623
Catalog No.:BCC7354
CAS No.:130408-77-4
- Peucedanocoumarin I
Catalog No.:BCN3434
CAS No.:130464-55-0
- Peucedanocoumarin II
Catalog No.:BCN3435
CAS No.:130464-56-1
- Peucedanocoumarin III
Catalog No.:BCN3471
CAS No.:130464-57-2
- Batimastat sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC2075
CAS No.:130464-84-5
- A 68930 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7104
CAS No.:130465-39-3
- ent-11alpha-Hydroxyabieta-8(14),13(15)-dien-16,12alpha-olide
Catalog No.:BCN7330
CAS No.:130466-20-5
- L-655,708
Catalog No.:BCC7023
CAS No.:130477-52-0
- TC-F 2
Catalog No.:BCC6147
CAS No.:1304778-15-1
- SKF 96365 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6953
CAS No.:130495-35-1
- Cannabisin A
Catalog No.:BCC8138
CAS No.:130508-46-2
- Liriope muscari baily Saponins
Catalog No.:BCN2817
CAS No.:130551-41-6
Synthesis and preliminary anticancer activity studies of C4 and C8-modified derivatives of catechin gallate (CG) and epicatechin gallate (ECG).[Pubmed:17168588]
J Org Chem. 2006 Dec 22;71(26):9701-12.
We have developed an improved and reliable method for stereoselective functionalization at C4 of naturally occurring (+)-catechin. Our method utilizes DDQ oxidation followed by trapping of the quinonemethide intermediate with allyl alcohol. The quinonemethide intermediate can be regenerated from the allyl ether by exposure to boron trifluoride diethyl etherate. This reactive intermediate can be trapped with a wide range of external nucleophiles. NBS bromination, lithium halogen exchange, and alkylation gave access to C8-allyl derivatives of (+)-catechin, and this allyl group was used in a series of cross-metathesis experiments to prepare novel dimeric catechin-derived products. Gallate ester derivatives of the novel C4- and C8-substituted catechins were prepared, and these materials were screened for potential anticancer activity in a range of human cancer cell lines. From these preliminary cytotoxicity assays (MTT) we found that C8-propyl-catechin gallate was more active (IC50 = 31 microM) than catechin gallate (CG, IC50 = 53 microM) or epicatechin gallate (ECG, IC50 = 76 microM) against the colorectal adenocarcinoma cell line HCT116. Differential sensitivity in pancreas (Pan1), bladder (RT112), stomach (MGLVA1), liver (HepG2), and fibroblasts (46Br.1G1) cell lines was also observed.
In vitro cytotoxicity of (-)-catechin gallate, a minor polyphenol in green tea.[Pubmed:17606338]
Toxicol Lett. 2007 Jul 10;171(3):171-80.
The cytotoxicity of (-)-catechin gallate (CG), a minor polyphenolic constituent in green tea, towards cells derived from tissues of the human oral cavity was studied. The sequence of sensitivity to CG was: immortalized epithelioid gingival S-G cells>tongue squamous carcinoma CAL27 cells>salivary gland squamous carcinoma HSG cells>>normal gingival HGF-1 fibroblasts. Further studies focused on S-G cells, the cells most sensitive to CG. The response of the S-G cells to CG was dependent on the length of exposure, with midpoint cytotoxicity values of 127, 67 and 58muM CG for 1-, 2- and 3-day exposures, respectively. The sequence of sensitivity of the S-G cells to various green tea catechins was characterized as follows: CG, epicatechin gallate (ECG)>epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG)>epigallocatechin (EGC)>>epicatechin (EC), catechin (C). The cytotoxicity of CG, apparently, was not due to oxidative stress as it was a poor generator of H(2)O(2) in tissue culture medium, had no effect on the intracellular glutathione level, its cytotoxicity was unaffected by catalase, and it did not induce lipid peroxidation. However, CG did enhance Fe(2+)-induced, lipid peroxidation. CG-induced apoptosis was detected by nuclear staining, both with acridine orange and by the more specific TUNEL procedure. The lack of caspase-3 activity in cells exposed to CG and the detection of a DNA smear, rather than of discrete internucleosomal DNA fragmentation, upon agarose gel electrophoresis, suggest, possibly, that the mode of cell death was by a caspase-independent apoptotic pathway. The overall cytotoxicity of CG was similar to its epimer, ECG and both exhibited antiproliferative effects equivalent to, or stronger than, EGCG, the most abundant catechin in green tea.
Epicatechin gallate and catechin gallate are superior to epigallocatechin gallate in growth suppression and anti-inflammatory activities in pancreatic tumor cells.[Pubmed:21241417]
Cancer Sci. 2011 Apr;102(4):728-34.
Green tea catechins are considered as possible cancer preventive agents for several cancer types but little is known regarding their effects on pancreatic cancer cells. The best studied catechin and the major polyphenol present in green tea is epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG). In the present study, we investigated the in vitro anti-tumoral properties of EGCG on human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cells PancTu-I, Panc1, Panc89 and BxPC3 in comparison with the effects of two minor components of green tea catechins, catechin gallate (CG) and epicatechin gallate (ECG). We found that all three catechins inhibited proliferation of PDAC cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Interestingly, CG and ECG exerted much stronger anti-proliferative effects than EGCG. Western blot analyses performed with PancTu-I cells revealed catechin-mediated modulation of cell cycle regulatory proteins (cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases [CDK], CDK inhibitors). Again, these effects were clearly more pronounced in CG or ECG than in EGCG-treated cells. Importantly, catechins, in particular ECG, inhibited TNFalpha-induced activation of NF-kappaB and consequently secretion of pro-inflammatory and invasion promoting proteins like IL-8 and uPA. Overall, our data show that green tea catechins ECG and CG exhibit potent and much stronger anti-proliferative and anti-inflammatory activities on PDAC cells than the most studied catechin EGCG.


