AtrazineCAS# 1912-24-9 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1912-24-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 2256 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C8H14ClN5 | M.Wt | 215.7 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
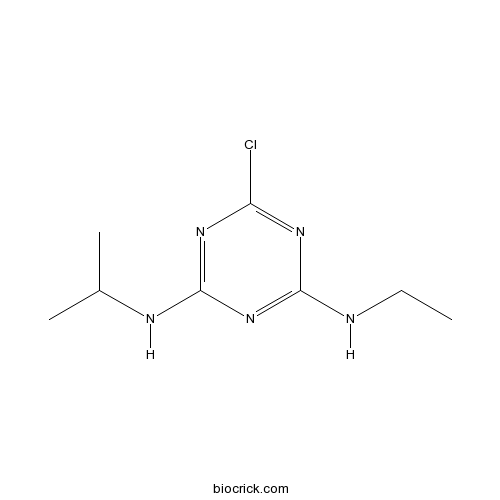
| Chemical Name | 6-chloro-4-N-ethyl-2-N-propan-2-yl-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine | ||
| SMILES | CCNC1=NC(=NC(=N1)Cl)NC(C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | MXWJVTOOROXGIU-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C8H14ClN5/c1-4-10-7-12-6(9)13-8(14-7)11-5(2)3/h5H,4H2,1-3H3,(H2,10,11,12,13,14) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Atrazine Dilution Calculator

Atrazine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.6361 mL | 23.1803 mL | 46.3607 mL | 92.7214 mL | 115.9017 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.9272 mL | 4.6361 mL | 9.2721 mL | 18.5443 mL | 23.1803 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4636 mL | 2.318 mL | 4.6361 mL | 9.2721 mL | 11.5902 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0927 mL | 0.4636 mL | 0.9272 mL | 1.8544 mL | 2.318 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0464 mL | 0.2318 mL | 0.4636 mL | 0.9272 mL | 1.159 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Telithromycin
Catalog No.:BCC5273
CAS No.:191114-48-4
- Oplopanone
Catalog No.:BCN1179
CAS No.:1911-78-0
- Kuguacin R
Catalog No.:BCN3057
CAS No.:191097-54-8
- K-7174
Catalog No.:BCC6435
CAS No.:191089-60-8
- L-168,049
Catalog No.:BCC7325
CAS No.:191034-25-0
- Salvigenin
Catalog No.:BCN1178
CAS No.:19103-54-9
- Benzyl 4-Oxo-1-piperidinecarboxylate
Catalog No.:BCC8870
CAS No.:19099-93-5
- Calystegine C2
Catalog No.:BCN1878
CAS No.:190957-44-9
- Triptocallic acid A
Catalog No.:BCN1176
CAS No.:190906-61-7
- Isocupressic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1177
CAS No.:1909-91-7
- Gracillin
Catalog No.:BCN5360
CAS No.:19083-00-2
- Bepotastine Besilate
Catalog No.:BCC4538
CAS No.:190786-44-8
- Solasonine
Catalog No.:BCN2302
CAS No.:19121-58-5
- Pramipexole 2HCl Monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4466
CAS No.:191217-81-9
- YM 976
Catalog No.:BCC7190
CAS No.:191219-80-4
- C 75
Catalog No.:BCC2386
CAS No.:191282-48-1
- Boc-Asp(OtBu)-OH.DCHA
Catalog No.:BCC3369
CAS No.:1913-12-8
- 1-Deoxynojirimycin
Catalog No.:BCN1032
CAS No.:19130-96-2
- 6-Deoxy-3-O-methyl-beta-allopyranosyl(1-4)-beta-cymaronic acid delta-lactone
Catalog No.:BCN1514
CAS No.:19131-13-6
- Ursolic aldehyde
Catalog No.:BCN7712
CAS No.:19132-81-1
- Fmoc-Tyr(HPO3Bzl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3565
CAS No.:191348-16-0
- 3-Benzoylpropionic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1928
CAS No.:2051-95-8
- AGN 195183
Catalog No.:BCC5419
CAS No.:191469-29-1
- LY 379268
Catalog No.:BCC7368
CAS No.:191471-52-0
Atrazine exposure shifts activity but has minimal effects on courtship in an agrobiont spider.[Pubmed:30969405]
Ecotoxicology. 2019 Apr 9. pii: 10.1007/s10646-019-02041-1.
The behavior of many animals relies upon the input of chemical signals throughout the environment. Those animals that live in close proximity to humans may then be at risk, as the input of anthropogenic chemicals can have significant sublethal effects by masking or altering these naturally occurring signals. While the herbicide Atrazine has been found to have the potential to alter such chemical information, research is lacking on how it may impact agrobiont arthropods which are the first and most direct line of exposure. Here we investigated the sublethal effects Atrazine may be playing on an agrobiont wolf spider that makes up a major component of agricultural spider communities in the Eastern United States. We exposed spiders to ecologically relevant doses of Atrazine and monitored general activity patterns as well as mating behaviors. We found that while sex determined a large portion of activity variation in these predators, both males and females spent more time mobile but at lower speeds in the presence of Atrazine. We did not find any evidence for info-disruption based on male courtship rate and mating success, but with increasing dosage of Atrazine came shortened bouts of courtship leading to copulation. These results suggest that Atrazine changed activity patterns of a wolf spider, which may result in altered foraging, survival, and reproduction.
Solubility Enhancement of Atrazine by Complexation with Cyclosophoraose Isolated from Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar trifolii TA-1.[Pubmed:30960458]
Polymers (Basel). 2019 Mar 12;11(3). pii: polym11030474.
Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar trifolii TA-1, a kind of soil bacteria, produces cyclosophoraoses (Cys). Cyclosophoraoses contain various ring sizes with degrees of polymerization ranging from 17 to 23. Atrazine is a hardly-soluble herbicide that contaminates soil and drinking water, and remains in soil for a long time. To remove this insoluble contaminant from aqueous solutions, we have enhanced the solubility of Atrazine by complexation with Cys. The complex formation of Cys and Atrazine was confirmed using (1)H nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy, differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), rotating frame nuclear overhauser spectroscopy (ROESY), and molecular modeling studies. The aqueous solubility of Atrazine was enhanced 3.69-fold according to the added concentrations (20 mM) of Cys, compared to the 1.78-fold enhancements by beta-cyclodextrin (beta-CD). Cyclosophoraoses as an excellent solubility enhancer with long glucose chains that can effectively capture insoluble materials showed a potential application of microbial polysaccharides in the removal of hazardous hardly-soluble materials from aqueous solutions in the fields of biological and environmental industry.
A mechanistic view of interactions of a nanoherbicide with target organism.[Pubmed:30933503]
J Agric Food Chem. 2019 Apr 1.
Atrazine is one of the most used herbicides and has been associated with persistent surface and groundwater contamination, and novel formulations derived from nanotechnology can be a potential solution. We used poly-epsilon caprolactone nano-encapsulation of Atrazine (NC+ATZ) to develop a highly effective herbicidal formulation. Detailed structural study of interaction between the formulation and Brassica juncea plants was carried out with evaluation of the foliar uptake of nanoAtrazine and structural alterations induced in the leaves. Following post-emergent treatment, NC+ATZ adhered to the leaf and penetrated mesophyll tissue mainly through the hydathode regions. NC+ATZ was transported directly through the vascular tissue of the leaves and into the cells where it degraded the chloroplasts resulting in herbicidal activity. Nanocarrier systems, such as the one used in this study, have a great potential for agricultural applications in terms of maintenance of herbicidal activity at low concentrations and a substantial increase in the herbicidal efficacy.
Application of denitrifying bioreactors for the removal of atrazine in agricultural drainage water.[Pubmed:30884289]
J Environ Manage. 2019 Jun 1;239:48-56.
Atrazine and nitrate NO3-N are two agricultural pollutants that occur widely in surface and groundwater. One of the pathways by which these pollutants reach surface water is through subsurface drainage tile lines. Edge-of-field anaerobic denitrifying bioreactors apply organic substrates such as woodchips to stimulate the removal of NO3-N from the subsurface tile waters through denitrification. Here we investigated the co-removal of NO3-N and Atrazine by these bioreactors. Laboratory experiments were conducted using 12-L woodchips-containing flow-through bioreactors, with and without the addition of biochar, to treat two concentrations of Atrazine (20 and 50mugL(-1)) and NO3-N (1.5 and 11.5mgL(-1)), operated at four hydraulic retention time, HRT, (4h, 8h, 24h, 72h). Additionally, we examined the effect of aerating the bioreactors on Atrazine removal. Furthermore, we tested Atrazine removal by a field woodchip denitrifying bioreactor. The removal of both NO3-N and Atrazine increased with increasing HRT in the laboratory bioreactors. At 4h, the woodchip bioreactors removed 65% of NO3-N and 25% of Atrazine but, at 72h, the bioreactors eliminated all the NO3-N and 53% of Atrazine. Biochar-amended bioreactors removed up to 90% of Atrazine at 72-h retention time. We concluded that Atrazine removal was primarily via adsorption because neither aeration nor NO3-N levels had an effect. At 4-h retention time, the field bioreactors achieved 2.5 times greater Atrazine removal than the laboratory bioreactors. Our findings thus highlighted hydraulic retention time and biochar amendments as two important factors that may control the efficiency of Atrazine removal by denitrifying bioreactors. In sum, laboratory and field data demonstrated that denitrifying bioreactors have the potential to decrease pesticide transport from agricultural lands to surface waters.
Comprehensive investigation of pesticides in Brazilian surface water by high resolution mass spectrometry screening and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry quantitative analysis.[Pubmed:30878932]
Sci Total Environ. 2019 Jun 15;669:248-257.
In this work, a comprehensive investigation on the occurrence of pesticides in the Parana 3 hydrographic basin of Parana State, Brazil, was made by application of wide-scope screening based on ultra-high performance liquid chromatography (LC) and gas chromatography (GC) both coupled to quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (QTOF MS). The use of two complementary techniques, such as GC-QTOF MS and LC-QTOF MS, allowed screening a large number of compounds with different polarity and volatility. This screening approach was applied to 17 samples, enabling the detection of fifty-two pesticides and six metabolites. In a second step, an specific research was made on the herbicide Atrazine, one of the most frequent compounds in samples, and its major transformation products (TPs), which were quantitatively analyzed by dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction (DLLME) followed by GC-MS measurement. Twenty-one agricultural streams from the Parana 3 hydrographic basin were sampled twice in 2017, each time along six successive weeks. Additional samples were also collected after rain events exceeding 10mm. In total, 407 samples were quantitatively analyzed by DLLME/GC-MS. Atrazine concentrations did not exceed the maximum permitted concentration of 2mugL(-1) according to Brazilian legislation, and only one surface water sample, collected after precipitation events, was slightly above this value (2.89mugL(-1)). The maximum concentrations for the TPs desethylAtrazine and deisopropylAtrazine were 0.80 and 1.22mugL(-1), respectively. Based on the quantification results, a map was produced showing the occurrence of Atrazine and its TPs in the area under study. This is the first time that the presence of agrochemicals is evaluated in the Parana 3 hydrographic basin.


