AspartameCAS# 22839-47-0 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 22839-47-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 134601 | Appearance | Powder |
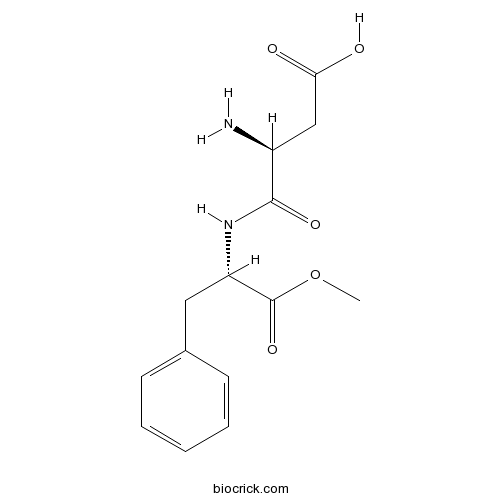
| Formula | C14H18N2O5 | M.Wt | 294.3 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 25 mg/mL (84.95 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : 5 mg/mL (16.99 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
| Chemical Name | (3S)-3-amino-4-[[(2S)-1-methoxy-1-oxo-3-phenylpropan-2-yl]amino]-4-oxobutanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | COC(=O)C(CC1=CC=CC=C1)NC(=O)C(CC(=O)O)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | IAOZJIPTCAWIRG-QWRGUYRKSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C14H18N2O5/c1-21-14(20)11(7-9-5-3-2-4-6-9)16-13(19)10(15)8-12(17)18/h2-6,10-11H,7-8,15H2,1H3,(H,16,19)(H,17,18)/t10-,11-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Aspartame Dilution Calculator

Aspartame Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.3979 mL | 16.9895 mL | 33.9789 mL | 67.9579 mL | 84.9473 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6796 mL | 3.3979 mL | 6.7958 mL | 13.5916 mL | 16.9895 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3398 mL | 1.6989 mL | 3.3979 mL | 6.7958 mL | 8.4947 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.068 mL | 0.3398 mL | 0.6796 mL | 1.3592 mL | 1.6989 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.034 mL | 0.1699 mL | 0.3398 mL | 0.6796 mL | 0.8495 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Aspartame is an artificial, non-saccharide sweetener used as a sugar substitute in some foods and beverages. Target: Others Aspartame is a flavoring agent sweeter than sugar. Aspartame is a methyl ester of a dipeptide used as a synthetic nonnutritive sweetener. Epidemiological studies on aspartame include several case-control studies and one well-conducted prospective epidemiological study with a large cohort, in which the consumption of aspartame was measured. The studies provide no evidence to support an association between aspartame and cancer in any tissue. The weight of existing evidence is that aspartame is safe at current levels of consumption as a nonnutritive sweetener [1]. aspartame is safe, and there are no unresolved questions regarding its safety under conditions of intended use [2]. excessive aspartame ingestion might be involved in the pathogenesis of certain mental disorders (DSM-IV-TR 2000) and also in compromised learning and emotional functioning [3].
References:
[1]. Magnuson, B.A., et al., Aspartame: a safety evaluation based on current use levels, regulations, and toxicological and epidemiological studies. Crit Rev Toxicol, 2007. 37(8): p. 629-727.
[2]. Butchko, H.H., et al., Aspartame: review of safety. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol, 2002. 35(2 Pt 2): p. S1-93.
[3]. Humphries, P., E. Pretorius, and H. Naude, Direct and indirect cellular effects of aspartame on the brain. Eur J Clin Nutr, 2008. 62(4): p. 451-62.
- Boc-D-Val-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3466
CAS No.:22838-58-0
- Miconazole nitrate
Catalog No.:BCC9047
CAS No.:22832-87-7
- Hypoglaunine A
Catalog No.:BCN3086
CAS No.:228259-16-3
- Boc-Met-OH.DCHA
Catalog No.:BCC2602
CAS No.:22823-50-3
- Alisol K 23-acetate
Catalog No.:BCN3363
CAS No.:228095-18-9
- 3-(4-Hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-1,2-propanediol
Catalog No.:BCN1480
CAS No.:22805-15-8
- 1,2,3,7-Tetramethoxyxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN7519
CAS No.:22804-52-0
- 1-Hydroxy-2,3,5-trimethoxyxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN6569
CAS No.:22804-49-5
- Ac-D-Trp-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3116
CAS No.:2280-01-5
- Ecdysterone 2,3:20,22-diacetonide
Catalog No.:BCN5074
CAS No.:22798-98-7
- Ecdysterone 20,22-monoacetonide
Catalog No.:BCN5073
CAS No.:22798-96-5
- EPI-001
Catalog No.:BCC6536
CAS No.:227947-06-0
- Pratensein
Catalog No.:BCN2918
CAS No.:2284-31-3
- 9-Epiblumenol B
Catalog No.:BCN5075
CAS No.:22841-42-5
- VULM 1457
Catalog No.:BCC7533
CAS No.:228544-65-8
- Ki8751
Catalog No.:BCC1116
CAS No.:228559-41-9
- Anisomycin
Catalog No.:BCC7007
CAS No.:22862-76-6
- 6-Acetonyldihydrochelerythrine
Catalog No.:BCN5076
CAS No.:22864-92-2
- Famprofazone
Catalog No.:BCC3779
CAS No.:22881-35-2
- Silymarin
Catalog No.:BCN6299
CAS No.:22888-70-6
- 4-Amino-3,5-dichloropyridine
Catalog No.:BCC8679
CAS No.:22889-78-7
- TAK-779
Catalog No.:BCC4137
CAS No.:229005-80-5
- R 892
Catalog No.:BCC5992
CAS No.:229030-05-1
- Ginkgolic acid C15:1
Catalog No.:BCN2307
CAS No.:22910-60-7
Synergistic Effects of The Enhancements to Mitochondrial ROS, p53 Activation and Apoptosis Generated by Aspartame and Potassium Sorbate in HepG2 Cells.[Pubmed:30696035]
Molecules. 2019 Jan 28;24(3). pii: molecules24030457.
The safety of food additives has been widely concerned. Using single additives in the provisions of scope is safe, but the combination of additives, may induce additive, synergy, antagonism and other joint effects. This study investigated the cytotoxicity of Aspartame (AT) together with potassium sorbate (PS). Thiazolyl Blue Tetrazolium Bromide (MTT) assay indicated that AT and PS had IC50 values of 0.48 g/L and 1.25 g/L at 24 h, respectively. High content analysis (HCA) showed that both AT and PS had a negative effect on mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), reactive oxygen species (ROS) and DNA damage while the joint group behaved more obviously. The biochemical assays revealed typical cell morphological changes and the activation of cytochrome c and caspase-3 verified apoptosis induced by AT together with PS. With dissipation of MMP and increase of cell membrane permeability (CMP), it indicated AT together with PS-induced apoptosis was mediated by mitochondrial pathway. Meanwhile, p53 were involved in DNA damage, and the ratio of Bax/Bcl-2 was increased. Moreover, excessive ROS induced by AT together with PS is a key initiating factor for apoptosis. All these results proved that p53 was involved in apoptosis via mitochondria-mediated pathway and the process was regulated by ROS.
Effect of l-carnitine on aspartame-induced oxidative stress, histopathological changes, and genotoxicity in liver of male rats.[Pubmed:30645201]
J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2019 Jan 15;30(2):219-232.
Background Aspartame (ASP) is used for treatment of obesity and diabetes mellitus. This study was designed to illustrate the biochemical responses and histopathological alterations besides the genotoxicity of ASP alone or with l-carnitine (LC) in the liver of rats. Methods Animals were separated into six groups: control, lower dose of ASP (ASP-LD; 75 mg/kg), higher dose of ASP (ASP-HD; 150 mg/kg), l-carnitine (LC; 10 mg/kg), ASP-LD plus LC, and ASP-HD plus LC. Treatment was carried out orally for 30 consecutive days. Results ASP raised the activity of some enzymes of liver markers and disturbed the lipid profile levels. The hepatic reduced glutathione (GSH) levels, the marker enzymes of antioxidant activities, were obviously diminished, and, possibly, the lipid peroxidation, C-reactive protein, and interleukins levels were increased. ASP significantly increased the DNA deterioration in comparison with the control in a dose-dependent manner. LC prevented ASP-induced liver damage as demonstrated by the enhancement of all the above parameters. Results of histopathological and electron microscopic examination proved the biochemical feedback and the improved LC effect on liver toxicity. Conclusions The co-treatment of LC showed different improvement mechanisms against ASP-induced liver impairment. So, the intake of ASP should be regulated and taken with LC when it is consumed in different foods or drinks to decrease its oxidative stress, histopathology, and genotoxicity of liver.


