AgomelatineMT1/MT2 / 5-HT2C agonist CAS# 138112-76-2 |
- AM580
Catalog No.:BCC5373
CAS No.:102121-60-8
- AGN 194310
Catalog No.:BCC5416
CAS No.:229961-45-9
- Palovarotene
Catalog No.:BCC4185
CAS No.:410528-02-8
- AGN 205728
Catalog No.:BCC5418
CAS No.:859498-05-8
- AGN 196996
Catalog No.:BCC5417
CAS No.:958295-17-5
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

Chemical structure

3D structure
| Cas No. | 138112-76-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 82148 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C15H17NO2 | M.Wt | 243.3 |
| Type of Compound | Miscellaneous | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (411.02 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
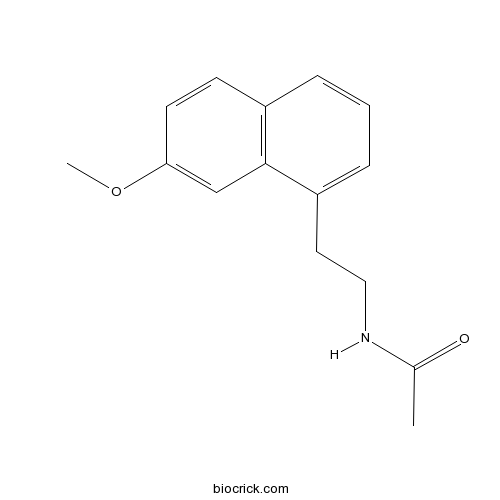
| Chemical Name | N-[2-(7-methoxynaphthalen-1-yl)ethyl]acetamide | ||
| SMILES | CC(=O)NCCC1=CC=CC2=C1C=C(C=C2)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | YJYPHIXNFHFHND-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Agomelatine is a competitive antagonist of human and porcine serotonin (5-HT2C) receptors (pKi = 6.2 and 6.4, respectively) as well as human 5-HT2B receptors (pKi = 6.6). Agomelatine is a melatonin (MT) analogue with agonistic properties and has been proven to be effective for various types of depressive symptoms, agomelatine also has anticonvulsant activity. Agomelatine treatment could represent a novel useful approach to the clinical care of subjects with Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS). Agomelatine administration protects liver cells from paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity via antioxidant activity and reduced proinflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-6. |
| Targets | TNF-α | IL Receptor | P450 (e.g. CYP17) | 5-HT Receptor |
| In vivo | Agomelatine: an antidepressant with new potent hepatoprotective effects on paracetamol-induced liver damage in rats.[Pubmed: 23584358]Hum Exp Toxicol. 2013 Aug;32(8):846-57.Paracetamol was shown to induce hepatotoxicity or more severe fatal acute hepatic damage. Agomelatine, commonly known as melatonin receptor agonist, is a new antidepressant, which resynchronizes circadian rhythms with subjective and objective improvements in sleep quality and architecture, as melatonin does. Agomelatine but not melatonin improves fatigue perception: a longitudinal proof-of-concept study.[Pubmed: 24636462]Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014 Jun;24(6):939-44.Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS) represents a disabling condition characterized by persistent mental and physical fatigue, bodily discomfort and cognitive difficulties. To date the neural bases of CFS are poorly understood; however, mono-aminergic abnormalities, sleep-wake cycle changes and prefrontal dysfunctions are all thought to play a role in the development and maintenance of this condition. Pharmacokinetic evaluation of agomelatine for the treatment of generalised anxiety disorder.[Pubmed: 24717138]Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2014 Jun;10(6):885-92.Preliminary data indicate Agomelatine as a promising molecule for both acute and long-term treatment of generalised anxiety disorder (GAD).
Effect of CYP1A2 polymorphism on the pharmacokinetics of agomelatine in Chinese healthy male volunteers.[Pubmed: 24372004]J Clin Pharm Ther. 2014 Apr;39(2):204-9.Agomelatine is a melatonin (MT) analogue with agonistic properties and has been proven to be effective for various types of depressive symptoms. Following oral administration, Agomelatine is primarily metabolized by the hepatic cytochrome P450 isoenzyme CYP1A2. The purpose of this study was to assess the influence of CYP1A2 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs, rs762551, rs2069514, rs2472304, rs2470890) on Agomelatine pharmacokinetics in the Chinese population. |
| Animal Research | Anticonvulsant effects of agomelatine in mice.[Pubmed: 22658946]Epilepsy Behav. 2012 Jul;24(3):324-8.Agomelatine is a potent MT1 and MT2 melatonin receptor agonist and a 5-HT2C serotonin receptor antagonist. |

Agomelatine Dilution Calculator

Agomelatine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.1102 mL | 20.5508 mL | 41.1015 mL | 82.203 mL | 102.7538 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.822 mL | 4.1102 mL | 8.2203 mL | 16.4406 mL | 20.5508 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.411 mL | 2.0551 mL | 4.1102 mL | 8.2203 mL | 10.2754 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0822 mL | 0.411 mL | 0.822 mL | 1.6441 mL | 2.0551 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0411 mL | 0.2055 mL | 0.411 mL | 0.822 mL | 1.0275 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Agomelatine is an agonist of melatonin receptors and an antagonist of the serotonin 5-HT2C receptor with Ki values of 0.062nM and 0.268nM and IC50 value of 0.27μM, respectively for MT1, MT2 and 5-HT2C [1].
Agomelatine is a unique antidepressant and is developed for treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD). Agomelatine is selective against 5-HT2C. It shows low affinities to cloned human 5-HT2A and 5-HT1A. For melatonin receptors, agomelatine shows similar affinities to cloned human MT1 and MT2 with Ki values of 0.09nM and 0.263nM, respectively. In the in vivo studies, agomelatine causes increase of dopamine and noradrenaline levels via blocking the inhibitory input of 5-HT2C. Moreover, the administration of agomelatine counteractes the stress-induced decrease in sucrose consumption in a rat model of depression. Besides that, agomelatine exerts alleviated anxiety efficacy in a rodent model of anxiety [1].
References:
[1] Zupancic M, Guilleminault C. Agomelatine. CNS drugs, 2006, 20(12): 981-992.
- (R,R)-THC
Catalog No.:BCC7224
CAS No.:138090-06-9
- Acetylanonamine
Catalog No.:BCN2140
CAS No.:138079-62-6
- G007-LK
Catalog No.:BCC6383
CAS No.:1380672-07-0
- LDK378 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1694
CAS No.:1380575-43-8
- 2-(4-Hydroxy-2-oxoindolin-3-yl)acetonitrile
Catalog No.:BCN1575
CAS No.:1380540-77-1
- YM 750
Catalog No.:BCC7542
CAS No.:138046-43-2
- EHop-016
Catalog No.:BCC5022
CAS No.:1380432-32-5
- KML 29
Catalog No.:BCC6312
CAS No.:1380424-42-9
- Valeriandoid B
Catalog No.:BCN6754
CAS No.:1380399-57-4
- EPZ004777 HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4550
CAS No.:1380316-03-9
- EPZ5676
Catalog No.:BCC2215
CAS No.:1380288-87-8
- KB SRC 4
Catalog No.:BCC6253
CAS No.:1380088-03-8
- 7-Methoxy-1-naphthylacetonitrile
Catalog No.:BCN2242
CAS No.:138113-08-3
- H-β-HoPhe-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3240
CAS No.:138165-77-2
- (RS)-(Tetrazol-5-yl)glycine
Catalog No.:BCC6599
CAS No.:138199-51-6
- ML 289
Catalog No.:BCC6343
CAS No.:1382481-79-9
- Stearyl glycyrrhetinate
Catalog No.:BCN8486
CAS No.:13832-70-7
- Hedycoronen A
Catalog No.:BCN7653
CAS No.:1383441-73-3
- CYM 9484
Catalog No.:BCC6238
CAS No.:1383478-94-1
- BD 1008 dihydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCC6674
CAS No.:138356-09-9
- BD 1047 dihydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCC6863
CAS No.:138356-21-5
- Alvimopan monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCC1349
CAS No.:1383577-62-5
- Boc-Arg(Tos)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3067
CAS No.:13836-37-8
- Afzelechin-(4alpha->8)-epiafzelechin
Catalog No.:BCN7709
CAS No.:1383627-30-2
Pharmacokinetic evaluation of agomelatine for the treatment of generalised anxiety disorder.[Pubmed:24717138]
Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2014 Jun;10(6):885-92.
INTRODUCTION: Preliminary data indicate Agomelatine as a promising molecule for both acute and long-term treatment of generalised anxiety disorder (GAD). AREAS COVERED: The present review illustrates the pharmacokinetic properties of Agomelatine and their implications for the management of GAD patients. A search of the main database sources (Medline, Isi Web of Knowledge and Medscape) was performed in order to obtain a complete and balanced evaluation of Agomelatine pharmacokinetics for the treatment of GAD. The word 'Agomelatine' was associated with 'pharmacokinetics', 'GAD', 'anxiety' and 'tolerability'. No restriction criteria were established in relation to methodology or year of publication. Only English-language articles were included. EXPERT OPINION: Short half-life and 1-day administration make Agomelatine an interesting molecule for GAD treatment. However, potential interactions with a number of compounds necessitate caution when prescribing and using Agomelatine in patients with psychiatric (e.g., alcohol abuse) or medical comorbidities. Further data are necessary to define a precise risk/benefit ratio in special populations such as elderly patients suffering from GAD.
Agomelatine: an antidepressant with new potent hepatoprotective effects on paracetamol-induced liver damage in rats.[Pubmed:23584358]
Hum Exp Toxicol. 2013 Aug;32(8):846-57.
Paracetamol was shown to induce hepatotoxicity or more severe fatal acute hepatic damage. Agomelatine, commonly known as melatonin receptor agonist, is a new antidepressant, which resynchronizes circadian rhythms with subjective and objective improvements in sleep quality and architecture, as melatonin does. In the present study, it was aimed to evaluate the hepatoprotective activity of Agomelatine on paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity and to understand the relationship between the hepatoprotective mechanism of Agomelatine and antioxidant system and proinflammatory cytokines. A total of 42 rats were divided into 7 groups as each composed of 6 rats: (1) intact, (2) 40 mg/kg Agomelatine, (3) 140 mg/kg N-acetylcysteine (NAC), (4) 2 g/kg paracetamol, (5) 2 g/kg paracetamol + 140 mg/kg NAC, (6) 2 g/kg paracetamol + 20 mg/kg Agomelatine, and (7) 2 g/kg paracetamol + 40 mg/kg Agomelatine groups. Paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity was applied and liver and blood samples were analyzed histopathologically and biochemically. There were statistically significant increases in the activities of aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) and 8-iso-prostane, and decreases in the activity of superoxide dismutase and level of glutathione in the group treated with paracetamol. Administration of Agomelatine and NAC separately reversed these changes significantly. In conclusion, Agomelatine administration protects liver cells from paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity via antioxidant activity and reduced proinflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-alpha and IL-6.
Agomelatine but not melatonin improves fatigue perception: a longitudinal proof-of-concept study.[Pubmed:24636462]
Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014 Jun;24(6):939-44.
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS) represents a disabling condition characterized by persistent mental and physical fatigue, bodily discomfort and cognitive difficulties. To date the neural bases of CFS are poorly understood; however, mono-aminergic abnormalities, sleep-wake cycle changes and prefrontal dysfunctions are all thought to play a role in the development and maintenance of this condition. Here we explored in a group of 62 CFS subjects the impact on fatigue levels of Agomelatine, an antidepressant with agonist activity at melatonin receptors (MT1 and MT2) and antagonist activity at serotoninergic 2C receptors (5HT2C). To tease out the relative effects of MT-agonism and 5HT2C antagonism on fatigue, we compared Agomelatine 50mg u.i.d. with sustained release melatonin 10mg u.i.d. in the first 12-week-long phase of the study, and then switched all melatonin-treated subjects to Agomelatine in the second 12-week-long phase of the study. Agomelatine treatment, but not melatonin, was associated with a significant reduction of perceived fatigue and an increase in perceived quality of life. Moreover the switch from melatonin to Agomelatine was associated with a reduction of fatigue levels. Agomelatine was well tolerated by all enrolled subjects. Our data, albeit preliminary, suggest that Agomelatine treatment could represent a novel useful approach to the clinical care of subjects with CFS.
Anticonvulsant effects of agomelatine in mice.[Pubmed:22658946]
Epilepsy Behav. 2012 Jul;24(3):324-8.
Agomelatine is a potent MT1 and MT2 melatonin receptor agonist and a 5-HT2C serotonin receptor antagonist. We analyzed whether Agomelatine has anticonvulsant properties. The anticonvulsant activity of Agomelatine (25, 50 or 75 mg/kg, i.p.) was evaluated in mouse models of pentylenetetrazole (PTZ-85 mg/kg, i.p.), pilocarpine (400mg/kg, i.p.), picrotoxin (7 mg/kg, i.p.), strychnine (75 mg/kg, i.p.) or electroshock-induced convulsions. In the PTZ-induced seizure model, Agomelatine (at 25 or 50mg/kg) showed a significant increase in latency to convulsion, and Agomelatine (at 50 or 75 mg/kg) also increased significantly time until death. In the pilocarpine-induced seizure model, only Agomelatine in high doses (75 mg/kg) showed a significant increase in latency to convulsions and in time until death. In the strychnine-, electroshock- and picrotoxin-induced seizure models, Agomelatine caused no significant alterations in latency to convulsions and in time until death when compared to controls. Our results suggest that Agomelatine has anticonvulsant activity shown in PTZ- or pilocarpine-induced seizure models.
Effect of CYP1A2 polymorphism on the pharmacokinetics of agomelatine in Chinese healthy male volunteers.[Pubmed:24372004]
J Clin Pharm Ther. 2014 Apr;39(2):204-9.
WHAT IS KNOWN AND OBJECTIVE: Agomelatine is a melatonin (MT) analogue with agonistic properties and has been proven to be effective for various types of depressive symptoms. Following oral administration, Agomelatine is primarily metabolized by the hepatic cytochrome P450 isoenzyme CYP1A2. The purpose of this study was to assess the influence of CYP1A2 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs, rs762551, rs2069514, rs2472304, rs2470890) on Agomelatine pharmacokinetics in the Chinese population. METHODS: Seventy-two healthy Chinese male volunteers enrolled in the study received an oral dose of 25 mg of Agomelatine after providing written informed consent. CYP1A2 SNPs were genotyped by polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP). Agomelatine plasma concentrations were determined by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry, and the pharmacokinetics analyses were evaluated by nonparametric methods. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION: After a single oral dose of 25 mg Agomelatine, no significant differences existed in Agomelatine pharmacokinetics between the rs2069514 GG homozygotes (n = 35) and the rs2069514 AG allele (n = 35) in all subjects. The mean Agomelatine AUC0-7 , AUC0-infinity and Cmax for the rs762551 CC homozygotes (n = 9), rs2470890 CC homozygotes (n = 54) and rs2472304 GG homozygotes (n = 51) were much higher than the rs762551 AA allele (n = 31), rs2470890 CT allele (n = 17) and rs2472304 AG allele (n = 20) respectively (P < 0.05). WHAT IS NEW AND CONCLUSION: The rs762551 A, rs2470890 T and rs2472304 A genotype presented a significantly lower level of Agomelatine exposure (AUC, Cmax ) compared with the rs762551 C, rs2470890 C and rs2472304 G genotype in Chinese healthy subjects. It suggested that the rs762551, rs2470890 and rs2472304 genetic polymorphism might be associated with the marked interindividual variability of Agomelatine, and the pharmacokinetic profile of Agomelatine may be different in different races.


