AH 7614FFA4/GPR120 antagonist CAS# 6326-06-3 |
- Amyloid β-Protein (1-15)
Catalog No.:BCC1003
CAS No.:183745-81-5
- Beta-Amyloid (1-11)
Catalog No.:BCC1002
CAS No.:190436-05-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 6326-06-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 233085 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C20H17NO3S | M.Wt | 351.42 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
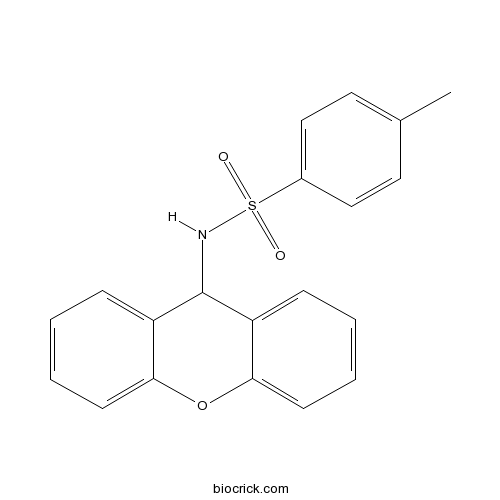
| Chemical Name | 4-methyl-N-(9H-xanthen-9-yl)benzenesulfonamide | ||
| SMILES | CC1=CC=C(C=C1)S(=O)(=O)NC2C3=CC=CC=C3OC4=CC=CC=C24 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | OZCQEUZTOAAWDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H17NO3S/c1-14-10-12-15(13-11-14)25(22,23)21-20-16-6-2-4-8-18(16)24-19-9-5-3-7-17(19)20/h2-13,20-21H,1H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Selective free fatty acid receptor 4 (FFA4/GPR120) antagonist (pIC50 values are 7.1 and <4.6 for human FFA4 and FFA1 receptors respectively). Inhibits linoleic acid and GSK 137647A-induced intracellular calcium accumulation in U2OS osteosarcoma cells expressing the FFA4 receptor. |

AH 7614 Dilution Calculator

AH 7614 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8456 mL | 14.228 mL | 28.456 mL | 56.912 mL | 71.1399 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5691 mL | 2.8456 mL | 5.6912 mL | 11.3824 mL | 14.228 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2846 mL | 1.4228 mL | 2.8456 mL | 5.6912 mL | 7.114 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0569 mL | 0.2846 mL | 0.5691 mL | 1.1382 mL | 1.4228 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0285 mL | 0.1423 mL | 0.2846 mL | 0.5691 mL | 0.7114 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Target: FFA4/GPR120
IC50: N/A
AH7614 is a selective and potent free fatty acid receptor 4 (FFA4/GPR120) antagonist with pIC50 values of 7.1, 8.1 and 8.1 at the human, mouse and rat receptor, respectively [1]. The free fatty acid receptor 4 (FFA4/GPR120), a member of the G protein-coupled receptor family, is a potential 7TM receptor involved in long-chain fatty acid-stimulated glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) secretion. FFA4 is highly expressed in the intestinal endocrine cell line STC-1 and the intestine. GLP-1 regulates multiple physiological functions including eating behavior [2].
In vitro: AH7614 (0.063, 0.25, and 1μM) blocked linoleic acid and GSK137647A-induced intracellular calcium increase in U2OS osteosarcoma cells expressing the FFA4 receptor [1]. In addition, the increase of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion by GSK137647A (50 μM) was abolished in the presence of the selective FFA4 antagonist AH7614 (100 μM) in the MIN6 mouse insulinoma cell line. Moreover, AH7614 (100 μM) blocked GSK137647A (100μM)-mediated a modest increase of GLP-1 secretion in the NCIH716 cells [1].
In vivo: N/A
References:
1. Sparks SM, Chen G, Collins JL, Danger D, Dock ST, Jayawickreme C, et al. Identification of diarylsulfonamides as agonists of the free fatty acid receptor 4 (FFA4/GPR120). Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014;24(14):3100-3.
2. Martin C, Passilly-Degrace P, Chevrot M, Ancel D, Sparks SM, Drucker DJ, et al. Lipid-mediated release of GLP-1 by mouse taste buds from circumvallate papillae: putative involvement of GPR120 and impact on taste sensitivity. J Lipid Res. 2012;53(11):2256-65.
- Benzoylmesaconine
Catalog No.:BCN5398
CAS No.:63238-67-5
- Benzoylhypacoitine
Catalog No.:BCN2821
CAS No.:63238-66-4
- Ginsenoside Rh1
Catalog No.:BCN1069
CAS No.:63223-86-9
- Cannabispirenone A
Catalog No.:BCN7603
CAS No.:63213-00-3
- Pifithrin-α (PFTα)
Catalog No.:BCC2241
CAS No.:63208-82-2
- Wogonin
Catalog No.:BCN4171
CAS No.:632-85-9
- Rose Bengal
Catalog No.:BCC8024
CAS No.:632-69-9
- H-D-Thr-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3108
CAS No.:632-20-2
- 4-Acetoxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5364
CAS No.:6318-20-3
- Methyl 2,5-dihydroxycinnamate
Catalog No.:BCC6702
CAS No.:63177-57-1
- 4-(Phenylthio)benzyl alcohol
Catalog No.:BCC8653
CAS No.:6317-56-2
- Benzo[b]thiophene-2-carboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8848
CAS No.:6314-28-9
- Bis(carboxymethyl) trithiocarbonate
Catalog No.:BCC8886
CAS No.:6326-83-6
- Rebaudioside D
Catalog No.:BCN2403
CAS No.:63279-13-0
- Calcifediol monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCC1443
CAS No.:63283-36-3
- Grantianine
Catalog No.:BCN2084
CAS No.:633-10-3
- Echiumine
Catalog No.:BCN1972
CAS No.:633-16-9
- Berberine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN6319
CAS No.:633-65-8
- Berberine hydrogen sulphate
Catalog No.:BCN2574
CAS No.:633-66-9
- Azaphen dihydrochloride monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCC1391
CAS No.:63302-99-8
- Jacoumaric acid
Catalog No.:BCN3245
CAS No.:63303-42-4
- Secoisolariciresinol monoglucoside
Catalog No.:BCN6990
CAS No.:63320-67-2
- VU 10010
Catalog No.:BCC7577
CAS No.:633283-39-3
- Bromethalin
Catalog No.:BCC5472
CAS No.:63333-35-7
Cyp1b1-mediated suppression of lymphoid progenitors in bone marrow by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons coordinately impacts spleen and thymus: a selective role for the Ah Receptor.[Pubmed:28116098]
Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2016 Jul 29;4(4):e00245.
Bone marrow (BM) hematopoietic stem cells differentiate to common lymphoid progenitors (CLP) that emigrate to the thymus to form T cells or differentiate into immature B cells that then migrate to the spleen for maturation. Rapid in vivo suppression of BM progenitor cells by a single oral or intraperitoneal dose of 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene (DMBA) subsequently decreased mature lymphoid populations in BM, spleen, and thymus. These suppressions depended on BM CYP1B1, but not on aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) activity. Suppression of pre-B colony formation at 6 h, correlated with subsequent decreases in mature BM, spleen, and thymus populations (48-168 h). Thymus T-cell ratios were unaffected, suggesting low local toxicity. DMBA treatment suppressed progenitor cells 24-h post treatment in wild type (WT), AhRb mice, but not in Cyp1b1-ko mice. The stem cell populations were sustained. Benzo(a)pyrene (BP) mediated a similar progenitor suppression up to 6 h, but reversal rapidly ensued. This recovery was absent in mice with a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH)-resistant, AhRd genotype. This AhR-dependent progenitor recovery with BP induction accounts for the absence of suppression of B220+ BM and spleen populations at 48-168 h. However, DMBA and BP produced similar profiles for thymus cell suppression, independent of AhR genotype. Thus, lymphoid progenitors may exit the BM to the thymus prior to the BP reversal. This progenitor recovery is associated with elevated chemokines and cytokines that depend on AhR-mediated induction of CYP1A1. This response increased constitutively in Cyp1b1-ko BM, demonstrating that CYP1B1 metabolizes local stimulants that impact a basal progenitor protection process.
Post space preparation timing of root canals sealed with AH Plus sealer.[Pubmed:28194361]
Restor Dent Endod. 2017 Feb;42(1):27-33.
OBJECTIVES: To determine the optimal timing for post space preparation of root canals sealed with epoxy resin-based AH Plus sealer in terms of its polymerization and influence on apical leakage. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The epoxy polymerization of AH Plus (Dentsply DeTrey) as a function of time after mixing (8, 24, and 72 hours, and 1 week) was evaluated using Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy and microhardness measurements. The change in the glass transition temperature (Tg ) of the material with time was also investigated using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). Fifty extracted human single-rooted premolars were filled with gutta-percha and AH Plus, and randomly separated into five groups (n = 10) based on post space preparation timing (immediately after root canal obturation and 8, 24, and 72 hours, and 1 week after root canal obturation). The extent of apical leakage (mm) of the five groups was compared using a dye leakage test. Each dataset was statistically analyzed by one-way analysis of variance and Tukey's post hoc test (alpha = 0.05). RESULTS: Continuous epoxy polymerization of the material with time was observed. Although the Tg values of the material gradually increased with time, the specimens presented no clear Tg value at 1 week after mixing. When the post space was prepared 1 week after root canal obturation, the leakage was significantly higher than in the other groups (p < 0.05), among which there was no significant difference in leakage. CONCLUSIONS: Poor apical seal was detected when post space preparation was delayed until 1 week after root canal obturation.
Retreatability of two endodontic sealers, EndoSequence BC Sealer and AH Plus: a micro-computed tomographic comparison.[Pubmed:28194360]
Restor Dent Endod. 2017 Feb;42(1):19-26.
OBJECTIVES: Recently, bioceramic sealers like EndoSequence BC Sealer (BC Sealer) have been introduced and are being used in endodontic practice. However, this sealer has limited research related to its retreatability. Hence, the aim of this study was to evaluate the retreatability of two sealers, BC Sealer as compared with AH Plus using micro-computed tomographic (micro-CT) analysis. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Fifty-six extracted human maxillary incisors were instrumented and randomly divided into 4 groups of 14 teeth: 1A, gutta-percha, AH Plus retreated with chloroform; 1B, gutta-percha, AH Plus retreated without chloroform; 2A, gutta-percha, EndoSequence BC Sealer retreated with chloroform; 2B, gutta-percha, EndoSequence BC Sealer retreated without chloroform. Micro-CT scans were taken before and after obturation and retreatment and analyzed for the volume of residual material. The specimens were longitudinally sectioned and digitized images were taken with the dental operating microscope. Data was analyzed using an ANOVA and a post-hoc Tukey test. Fisher exact tests were performed to analyze the ability to regain patency. RESULTS: There was significantly less residual root canal filling material in the AH Plus groups retreated with chloroform as compared to the others. The BC Sealer samples retreated with chloroform had better results than those retreated without chloroform. Furthermore, patency could be re-established in only 14% of teeth in the BC Sealer without chloroform group. CONCLUSION: The results of this study demonstrate that the BC Sealer group had significantly more residual filling material than the AH Plus group regardless of whether or not both sealers were retreated with chloroform.
Cytotoxicity of GuttaFlow Bioseal, GuttaFlow2, MTA Fillapex, and AH Plus on Human Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells.[Pubmed:28343929]
J Endod. 2017 May;43(5):816-822.
INTRODUCTION: The aim of the present study was to evaluate the in vitro cytotoxicity of endodontic sealers (GuttaFlow Bioseal, GuttaFlow2, and MTA Fillapex) on human periodontal ligament stem cells (hPDLSCs). As a reference, AH Plus was compared with the more recent endodontic sealers regarding cell viability and cell attachment. METHODS: Biological testing was carried out in vitro on hPDLSCs. Cell viability assay was performed by using eluates from each endodontic sealer. To assess cell morphology and attachment to the different sealers, the hPDLSCs were directly seeded onto the material surfaces and analyzed by scanning electron microscopy. Chemical composition of the sealers was determined by energy-dispersive x-ray, and eluates were analyzed by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Statistical differences were assessed by analysis of variance and Tukey test (P < .05). RESULTS: Cell viability was evident after 24 hours in the presence of GuttaFlow Bioseal and GuttaFlow 2 but not in the case of AH Plus or MTA Fillapex. At 168 hours, GuttaFlow Bioseal and GuttaFlow 2 exhibited high and moderate cell viability, respectively, whereas AH Plus and MTA Fillapex revealed low rates of cell cell viability (P < .001). Finally, scanning electron microscopy studies revealed a high degree of proliferation, cell spreading, and attachment, especially when using GuttaFlow Bioseal disks. CONCLUSIONS: GuttaFlow Bioseal and GuttaFlow2 showed lower cytotoxicity than MTA Fillapex and AH plus. Further in vitro and in vivo investigations are required to confirm the suitability of GuttaFlow Bioseal for clinical application.
Identification of diarylsulfonamides as agonists of the free fatty acid receptor 4 (FFA4/GPR120).[Pubmed:24881566]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014 Jul 15;24(14):3100-3.
The exploration of a diarylsulfonamide series of free fatty acid receptor 4 (FFA4/GPR120) agonists is described. This work led to the identification of selective FFA4 agonist 8 (GSK137647A) and selective FFA4 antagonist 39. The in vitro profile of compounds 8 and 39 is presented herein.


