3-O-cis-p-Coumaroyltormentic acidCAS# 121072-40-0 |
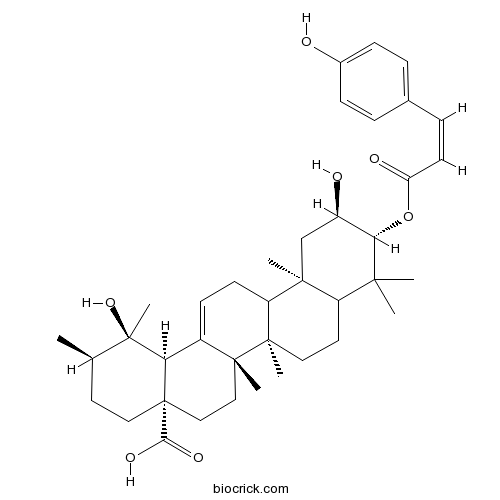
- 3-O-trans-p-Coumaroyltormentic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4724
CAS No.:121064-78-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 121072-40-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 102004779 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C39H54O7 | M.Wt | 634.9 |
| Type of Compound | Triterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (1R,2R,4aS,6aS,6bR,10R,11R,12aR,14bS)-1,11-dihydroxy-10-[(Z)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoyl]oxy-1,2,6a,6b,9,9,12a-heptamethyl-2,3,4,5,6,6a,7,8,8a,10,11,12,13,14b-tetradecahydropicene-4a-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC1CCC2(CCC3(C(=CCC4C3(CCC5C4(CC(C(C5(C)C)OC(=O)C=CC6=CC=C(C=C6)O)O)C)C)C2C1(C)O)C)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | BZORLJPADUHVJE-MSLXMTJKSA-N | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 3beta-O-cis-p-Coumaroyltormentic acid, and 3beta-O-trans-p-coumaroyltormentic acid are weakly selective for vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (VRE) compared with eukaryotic cells, with an MIC of 59.4microg/mL and a 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 72.0microg/mL for monkey kidney epithelial (MA104) cells. A mixture of 3-O-cis-p-coumaroyltormentic acid and 3-O-trans-p-coumaroyltormentic acid shows an inhibitory effect comparable to (-)-epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) of green tea on the activation of Epstein-Barr virus early antigen (EBV-EA) induced by 12-O-tetradeca-noylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA). |
| In vitro | Antibacterial compounds from Planchonia careya leaf extracts.[Pubmed: 18289814 ]J. Ethnopharmacol.,2008 Mar 28;116(3):554- 60.
Production of bioactive triterpenes by Eriobotrya japonica calli.[Pubmed: 11830140]Phytochemistry,2002 Feb;59(3):315-23.Callus tissue cultures induced from an axenic leaf of Eriobotrya japonica (Rosaceae) produced triterpenes in large amounts (ca. 50 mg/g dry wt).
|

3-O-cis-p-Coumaroyltormentic acid Dilution Calculator

3-O-cis-p-Coumaroyltormentic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.5751 mL | 7.8753 mL | 15.7505 mL | 31.501 mL | 39.3763 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.315 mL | 1.5751 mL | 3.1501 mL | 6.3002 mL | 7.8753 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1575 mL | 0.7875 mL | 1.5751 mL | 3.1501 mL | 3.9376 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0315 mL | 0.1575 mL | 0.315 mL | 0.63 mL | 0.7875 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0158 mL | 0.0788 mL | 0.1575 mL | 0.315 mL | 0.3938 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 3-O-trans-p-Coumaroyltormentic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4724
CAS No.:121064-78-6
- Melanotan II
Catalog No.:BCC7414
CAS No.:121062-08-6
- Abiesadine I
Catalog No.:BCN6104
CAS No.:1210347-50-4
- PF-04971729
Catalog No.:BCC1852
CAS No.:1210344-57-2
- IEM 1460
Catalog No.:BCC7135
CAS No.:121034-89-7
- Nelarabine
Catalog No.:BCC1072
CAS No.:121032-29-9
- Secretin (rat)
Catalog No.:BCC5848
CAS No.:121028-49-7
- JZL 195
Catalog No.:BCC7966
CAS No.:1210004-12-8
- N-Acetyl-5-Hydroxytryptamine
Catalog No.:BCC9080
CAS No.:1210-83-9
- ST 1936 oxalate
Catalog No.:BCC7919
CAS No.:1210-81-7
- 3'-Nitroacetophenone
Catalog No.:BCN2256
CAS No.:121-89-1
- Propyl gallate
Catalog No.:BCN8431
CAS No.:121-79-9
- L-670,596
Catalog No.:BCC5857
CAS No.:121083-05-4
- EG00229
Catalog No.:BCC5376
CAS No.:1210945-69-9
- Cefprozil hydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4951
CAS No.:121123-17-9
- LEE011
Catalog No.:BCC3926
CAS No.:1211441-98-3
- LEE011 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4101
CAS No.:1211443-80-9
- Rauvoyunine C
Catalog No.:BCN4833
CAS No.:1211543-01-9
- TC-N 1752
Catalog No.:BCC6179
CAS No.:1211866-85-1
- [Ala1,3,11,15]-Endothelin
Catalog No.:BCC5731
CAS No.:121204-87-3
- Secodihydro-hydramicromelin B
Catalog No.:BCN4783
CAS No.:1212148-58-7
- Calphostin C
Catalog No.:BCC7131
CAS No.:121263-19-2
- ICI 204,448 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6806
CAS No.:121264-04-8
- Alendronate
Catalog No.:BCC4885
CAS No.:121268-17-5
Production of bioactive triterpenes by Eriobotrya japonica calli.[Pubmed:11830140]
Phytochemistry. 2002 Feb;59(3):315-23.
Callus tissue cultures induced from an axenic leaf of Eriobotrya japonica (Rosaceae) produced triterpenes in large amounts (ca. 50 mg/g dry wt). Nine triterpenes were characterized as ursolic acid, oleanolic acid, 2alpha-hydoxyursolic acid, maslinic acid, tormentic acid, 2alpha, 19alpha-dihydroxy-3-oxo-urs-12-en-28-oic acid, hyptadienic acid and a mixture of 3-O-cis-p-Coumaroyltormentic acid and 3-O-trans-p-coumaroyltormentic acid. The triterpene composition in the callus tissues was noticeably different from that in intact leaves. The contents of tormentic acid with antidiabetic action, and 2alpha, 19alpha-dihydroxy-3-oxo-urs-12-en-28-oic acid with anti-HIV activity, were much larger than those in the intact leaves. All of the triterpenes isolated from the callus tissues showed an inhibitory effect comparable to (-)-epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) of green tea on the activation of Epstein-Barr virus early antigen (EBV-EA) induced by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA). 2alpha, 19alpha-Dihydroxy-3-oxo-urs-12-en-28-oic acid was the most potent inhibitor among them and caused a significant delay of two-stage carcinogenesis on mouse skin.
Antibacterial compounds from Planchonia careya leaf extracts.[Pubmed:18289814]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2008 Mar 28;116(3):554-60.
AIM OF THE STUDY: The leaves of Planchonia careya (F. Muell.) R. Knuth (Lecythidaceae) have been traditionally implemented in the treatment of wounds by the indigenous people of northern Australia, although the compounds responsible for the medicinal properties have not been identified. In this study, antibacterial compounds from the leaf extracts were isolated and characterized, and the biological activity of each compound was assessed. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Compounds were isolated from the leaf extracts using HPLC-piloted activity-guided fractionation. The minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) were assessed with plate-hole diffusion assays, and the cytotoxicity was determined with MTT assays using monkey kidney epithelial (MA104) cells. RESULTS: Six known compounds were isolated from the leaf extracts and were identified as 1, (+)-gallocatechin; 2, gallocatechin-(4alpha-->8)-gallocatechin; 3, 9(S)-hydroxy-10E,12Z-octadecadienoic acid (alpha-dimorphecolic acid); 4, 2alpha,3beta,24-trihydroxyolean-12-en-28-oic acid (hyptatic acid-A); 5, 3beta-O-cis-p-coumaroyltormentic acid; and 6, 3beta-O-trans-p-coumaroyltormentic acid. Compounds 5 and 6 were weakly selective for vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (VRE) compared with eukaryotic cells, with an MIC of 59.4microg/mL and a 50% inhibitory concentration (IC(50)) of 72.0microg/mL for MA104 cells. CONCLUSIONS: The isolation of six antibacterial compounds from the leaves of Planchonia careya validates the use of this species as a topical wound-healing remedy.


