trans-Fertaric acidCAS# 74282-22-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 74282-22-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 641605 | Appearance | Yellow powder |
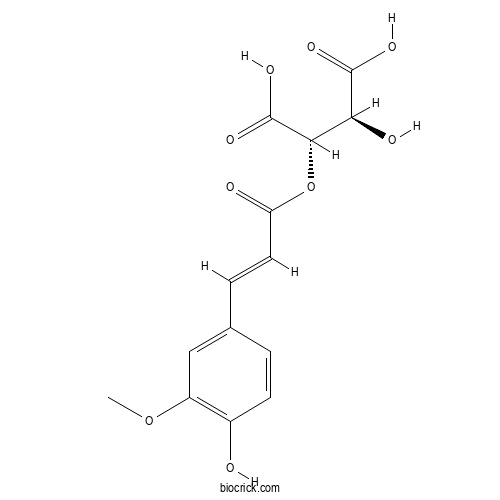
| Formula | C14H14O9 | M.Wt | 326.3 |
| Type of Compound | Phenylpropanoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | trans-Feruloyl tartaric acid | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in water | ||
| Chemical Name | (2S,3S)-2-hydroxy-3-[(E)-3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-enoyl]oxybutanedioic acid | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C=CC(=C1)C=CC(=O)OC(C(C(=O)O)O)C(=O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | XIWXUSFCUBAMFH-SCBUBVSKSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C14H14O9/c1-22-9-6-7(2-4-8(9)15)3-5-10(16)23-12(14(20)21)11(17)13(18)19/h2-6,11-12,15,17H,1H3,(H,18,19)(H,20,21)/b5-3+/t11-,12-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Reference standards. | |||||

trans-Fertaric acid Dilution Calculator

trans-Fertaric acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.0647 mL | 15.3233 mL | 30.6466 mL | 61.2933 mL | 76.6166 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6129 mL | 3.0647 mL | 6.1293 mL | 12.2587 mL | 15.3233 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3065 mL | 1.5323 mL | 3.0647 mL | 6.1293 mL | 7.6617 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0613 mL | 0.3065 mL | 0.6129 mL | 1.2259 mL | 1.5323 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0306 mL | 0.1532 mL | 0.3065 mL | 0.6129 mL | 0.7662 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Tricetin
Catalog No.:BCN9818
CAS No.:520-31-0
- Withanoside V
Catalog No.:BCN9817
CAS No.:256520-90-8
- 3-Aminocoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN9816
CAS No.:1635-31-0
- 7-Ethoxy-4-methylcoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN9815
CAS No.:87-05-8
- Vicinin 2
Catalog No.:BCN9814
CAS No.:90456-53-4
- 1,2,3-Tri-n-Octanoylglycerol
Catalog No.:BCN9813
CAS No.:538-23-8
- Norcamphor
Catalog No.:BCN9812
CAS No.:497-38-1
- 3-Hydroxycoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN9811
CAS No.:939-19-5
- Quercetin 3-rutinoside 7-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN9810
CAS No.:30311-61-6
- Isoedultin
Catalog No.:BCN9809
CAS No.:43043-08-9
- DL-Phenylalanine
Catalog No.:BCN9808
CAS No.:150-30-1
- Polygalacin D2
Catalog No.:BCN9807
CAS No.:66663-92-1
- beta-Citronellol
Catalog No.:BCN9820
CAS No.:106-22-9
- Cimicifugic acid F
Catalog No.:BCN9821
CAS No.:220618-91-7
- Eclalbasaponin II
Catalog No.:BCN9822
CAS No.:78285-90-3
- Morindin
Catalog No.:BCN9823
CAS No.:60450-21-7
- Acetic acid hexyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN9824
CAS No.:142-92-7
- Grayanotoxin I
Catalog No.:BCN9825
CAS No.:4720-09-6
- Vaccarin E
Catalog No.:BCN9826
CAS No.:2252345-81-4
- 6-Hydroxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN9827
CAS No.:6665-83-4
- Picrotoxinin
Catalog No.:BCN9828
CAS No.:17617-45-7
- 4,4'-Dimethoxychalcone
Catalog No.:BCN9829
CAS No.:2373-89-9
- Urushiol (15:1)
Catalog No.:BCN9830
CAS No.:35237-02-6
- 28-Homobrassinolide
Catalog No.:BCN9831
CAS No.:82373-95-3
Targeted UPLC-QqQ-MS/MS profiling of phenolic compounds for differentiation of monovarietal wines and corroboration of particular varietal typicity concepts.[Pubmed:31357018]
Food Chem. 2019 Dec 1;300:125251.
Targeted ultra-performance liquid chromatography with triple quadrupole mass spectrometric (UPLC-QqQ-MS/MS) profiling of phenolic compounds was utilised for varietal differentiation of 173 wines made from four red and six white grape varieties. Among 58 identified phenols many were found relevant as exclusive or partial discriminators between wines. Successful differentiation models were built by linear discriminant analysis with the percentage of correct classification higher than 95% in all cases, with peonidin 3-(6''-acetyl)-glucoside and taxifolin as the most potent differentiators between red, and cis-piceid between white monovarietal wines. Diverse typical colour attributes among the monovarietal wines were tentatively ascribed to the variations in the composition of monomeric anthocyanins. Plavac mali red wine exhibited the most specific composition, and its most typical samples were distinguished by the abundance in trans-Fertaric acid, isorhapontin, phlorizin, quercetin 3-rhamnoside, and myricitrin. Despite positive correlations with particular astringent flavonols, the typical astringency of Plavac mali wine remained unresolved.
Identification of (poly)phenolic compounds in concord grape juice and their metabolites in human plasma and urine after juice consumption.[Pubmed:21812481]
J Agric Food Chem. 2011 Sep 14;59(17):9512-22.
Analysis of Concord grape juice by HPLC with ESI-MS(n), PDA, and fluorescence detection resulted in the identification and quantification of 60 flavonoids and related phenolic compounds, which were present at an overall concentration of 1508 +/- 31 mumol/L. A total of 25 anthocyanins were detected, which were mono- and di-O-glucosides, O-acetylglucosides, O-p-coumaroyl-O-diglucosides, and O-p-coumaroylglucosides of delphinidin, cyanidin, petunidin, peonidin, and malvidin. The anthocyanins represented 46% of the total phenolic content of the juice (680 mumol/L). Tartaric esters of hydroxycinnamic acids, namely, trans-caftaric and trans-coutaric acids, and to a lesser extent trans-Fertaric acid accounted for 29% of the phenolic content, with a total concentration of 444 mumol/L, of which 85% comprised trans-caftaric acid. Free hydroxycinnamic acids were also quantified but contributed to <1% of the total phenolic content (8.4 mumol/L). The other groups of polyphenolic compounds present in the juice, accounting for 24% of the total, comprised monomeric and oligomeric units of (epi)catechin and (epi)gallocatechin (248 mumol/L), flavonols (76 mumol/L), gallic acid (51 mumol/L), and trans-resveratrol (1.5 mumol/L). The bioavailability of the (poly)phenolic compounds in 350 mL of juice was investigated following acute intake by healthy volunteers. Plasma and urine were collected over 0-24 h and analyzed for parent compounds and metabolites. In total, 41 compounds, principally metabolites, were identified.
The fate of trans-caftaric acid administered into the rat stomach.[Pubmed:17300159]
J Agric Food Chem. 2007 Feb 21;55(4):1604-11.
trans-Caftaric acid is the most abundant nonflavonoid phenolic compound in grapes and wines. It occurs in chicory and is one of the bioactive components of Echinacea purpurea. In order to fill the gap of knowledge about its bioavailability in mammals, we investigated its absorption, tissue distribution, and metabolism in rats. Assuming that the stomach is a relevant site of absorption of dietary polyphenols, a solution of trans-caftaric acid was maintained in the ligated stomach of anaesthetized rats for 20 min. Intact trans-caftaric acid was detected in rat plasma at both 10 and 20 min (293 +/- 45 and 334 +/- 49 ng/mL, respectively), along with its O-methylated derivative trans-Fertaric acid, whose concentration rose over time (from 92 +/- 12 to 185 +/- 24 ng/mL). At 20 min, both trans-caftaric acid and trans-Fertaric acid were detected in the kidney (443 +/- 78 and 2506 +/- 514 ng/g, respectively) but not in the liver. Only trans-Fertaric acid was found in the urine (33.3 +/- 12.8 microg/mL). In some rats, trans-caftaric acid was detected in the brain (180 +/- 20 ng/g).


