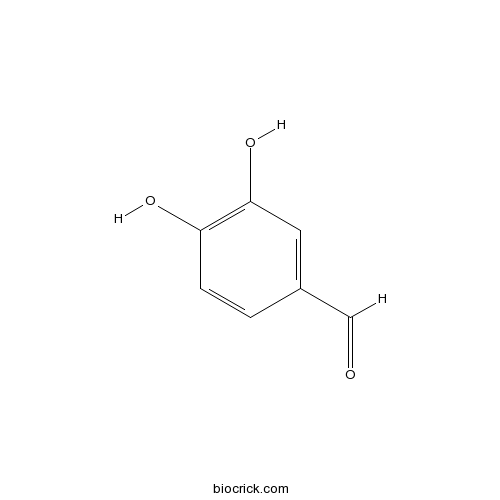
3,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde, isolated from the outer skin of green ,has been shown to inhibit the growth of Gloeosporium musarum, a fungus which causes ripe fruit rot in the banana.[1]
3,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde can inhibit oxidative DNA damage and apoptosis via its antioxidant activity.[2]
3,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde inhibits the phosphotransferase activity of CKII with IC(50) of about 783 microM, it may function by inhibiting oncogenic disease, at least in part, through the inhibition of CKII activity.3]
3,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde inhibits the H2O2-induced apoptosis of granulosa cells, promotes estradiol secretion in granulosa cells and enhanced the mRNA expression levels of steroidogenic factor 1, a promoter of key steroidogenic enzymes. [4]
3,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde has tyronase inhibitory effect.[5]
English website: 3,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde
Japanese website: 3,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde
Chinese website: 3,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde
[1] Mulvena D, Webb E C, Zerner B. Phytochemistry, 1969, 8(2):393-5.
[2] Jeong J, Hong S H. Phytomed Intl J Phytother Phytopharm, 2009, 16(1):85-94.
[3] Lee B H, Yoon S H, Kim Y S, et al. Nat Prod Res, 2008, 22(22):1441-50.
[4] Kono R, Nomura S, Okuno Y, et al. Acta Histochem Cytoc, 2014, 47(3):103-12.
[5] Shin Dong-Soo, Paik, Do-Hyeon, Yoon Do-Young, et al. The Korea Jounnal of Herbology, 2006, 21(2):1-7.
[6] Xia C Y, Chen L M, Hu W X. Synthetic chemistry, 2004, 12 (5): 484-6.