Thymus mongolicus
Thymus mongolicus
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Thymus mongolicus
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN4123
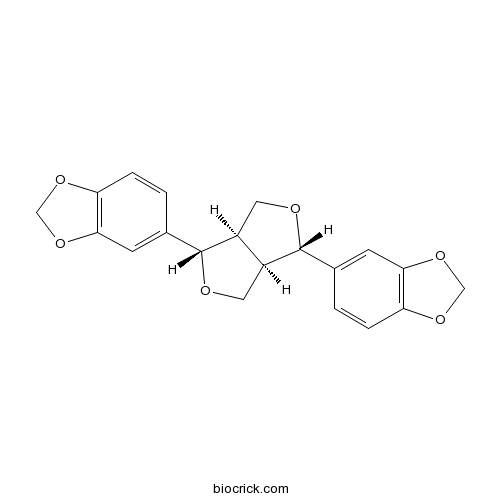
Sesamin607-80-7
Instructions
[Concentrations of different carbon and nitrogen fractions in rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soils of typical plant species in mountainous area of southern Ningxia, Northwest China].[Pubmed: 23898655]
Taking the rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soils of five typical plants Agropyron cristatum, Artemisia frigida, Pseudoraphis bungeana, Thymus mongolicus, and Artemisia sacrorum in a mountainous area of southern Ningxia as test objects, this paper studied their C and N forms contents. The C and N forms contents in the rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soils differed with plant species. In the rhizosphere soil of A. sacrorum, the C content was the highest, with the total soil organic C (TOC), light fraction organic C (LFOC), and heavy fraction organic C contents being 22.94, 1.95, and 20. 88 g kg-1, respectively. In the rhizosphere soil of P. bungeana, the N content was the highest, with the total N (TN), mineralizable N (MN), and available N contents being 2.05 g kg-1 , 23.73 mg kg-1, and 11.99 mg kg-1 , respectively. In the rhizosphere soil of A. frigida, the LFOC/TOC and MN/TN ratios were the highest, which benefited the C and N transformed into more active forms. Light fraction organic C and mineralizable N could be used as the sensitive indicators of plant habitat change. For the five plant species, the contents of different C and N forms in the rhizosphere soil were generally higher than those in the non-rhizosphere soil.
[Allelopathic effects of Artemisia sacrorum population in typical steppe based on niche theory].[Pubmed: 22720610]
By using modified Levins niche width index and Pianka niche overlap index, this paper analyzed the ecological competition between constructive and dominant species in a typical steppe. The stem- and leaf extracts from the constructive species (Artemisia sacrorum) were utilized to study their allelopathic potential on the seed germination and plant growth of the dominant species (Stipa bungeana, Thymus mongolicus, S. grandis, and Leymus secalinus), and the ecological position of A. sacrorum in the steppe succession. In the steppe, S. bungeana had the widest niche width (0.99), followed by T. mongolicus (0.94), A. sacrorum (0.82), S. grandis (0.76), and L. secalinus (0.73). The niche overlap value between A. sacrorum and S. bungeana, S. bungeana and T. mongolicus, T. mongolicus and S. grandis, and A. sacrorum and T. mongolicus was 0.90, 0.95, 0.94, and 0.86, respectively. The allelopathic effects of A. sacrorum extracts varied with their concentration. For the seed germination, root growth, and shoot growth of the dominant species, A. sacrorum extracts showed a trend of promoting at low concentrations and inhibiting at high concentrations. The extracts of A. sacrorum had a stronger promotion effect on the root growth of S. bungeana than on that of T. mongolicus, but a stronger inhibition effect on the shoot growth of T. mongolicus than on that of S. bungeana. Methanol extracts had stronger allelopathic effects than aqueous extracts. The high niche overlap between A. sacrorum and S. bungeana, and T. mongolicus and S. grandis indicated that the steppe community would continue succession to S. bungeana, while A. sacrorum population was only an important transitional stage during the succession. The allelopathic effect of A. sacrorum played a driving role in the succession process.
[Micro-community characteristics of vegetations in blowouts and depositional areas of Hulunbuir grassland, Inner Mongolia].[Pubmed: 19123352]
By using traditional sampling methods, the micro-communities of vegetations in fixed, semi-bare, and bare blowouts of Hulunbuir grassland were investigated, and the investigation data were statistical analyzed. The results showed that the vegetation coverage decreased in the order of fixed blowout, semi-bare blowout, and bare blowout, and was lower than that of the primary vegetation Form. Stipa grandis. Potentilla acaulis and Kengia squarrosa were the dominant species in fixed blowout, with the coverage being 5%; while P. acaulis and Carex sp. were the dominant species in semi-bare blowout, with the coverage being 2%. The dominant species in depositional areas of semi-bare blowout were P. acaulis, K. squarrosa, Agropyron cristatum, and Thymus mongolicus, and the coverage was 4%. The dominant species on the southwest slope of bare blowout was Agriophyllum pungens. The middle depositional area of bare blowout was also occupied by A. pungens (coverage 4.7%), and the edge of it was dominated by A. cristatum (coverage 2.7%), Carex sp. (coverage 2.6%), and T. mongolicus (coverage 1.7%) from the edge of the depositional area to primary grassland. The mean species importance value in fixed, semi-bare, and bare blowouts was 12.64%, 13.38%, and 20.08%, while that in the depositional area of semi-bare blowout and in the middle and edge of bare blowout was 12.55%, 40.18%, and 11.15%, respectively.


