Sedum lineare
Sedum lineare
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Sedum lineare
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN5549
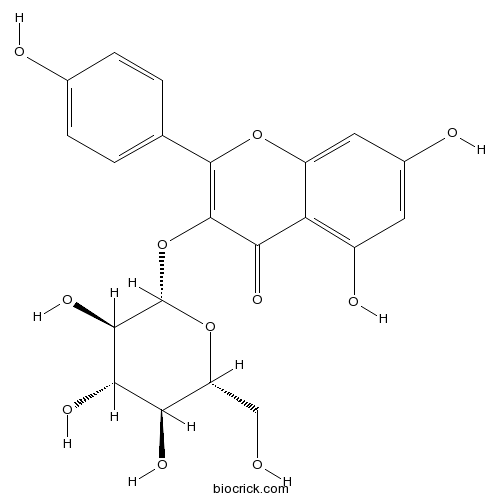
Astragalin480-10-4
Instructions
Biochar increases plant growth and alters microbial communities via regulating the moisture and temperature of green roof substrates.[Pubmed: 29669299]
Green roofs have increasingly been designed and applied to relieve environmental problems, such as water loss, air pollution as well as heat island effect. Substrate and vegetation are important components of green roofs providing ecosystem services and benefiting the urban development. Biochar made from sewage sludge could be potentially used as the substrate amendment for green roofs, however, the effects of biochar on substrate quality and plant performance in green roofs are still unclear. We evaluated the effects of adding sludge biochar (0, 5, 10, 15 and 20%, v/v) to natural soil planted with three types of plant species (ryegrass, Sedum lineare and cucumber) on soil properties, plant growth and microbial communities in both green roof and ground ecosystems. Our results showed that sludge biochar addition significantly increased substrate moisture, adjusted substrate temperature, altered microbial community structure and increased plant growth. The application rate of 10-15% sludge biochar on the green roof exerted the most significant effects on both microbial and plant biomass by 63.9-89.6% and 54.0-54.2% respectively. Path analysis showed that biochar addition had a strong effect on microbial biomass via changing the soil air-filled porosity, soil moisture and temperature, and promoted plant growth through the positive effects on microbial biomass. These results suggest that the applications of biochar at an appropriate rate can significantly alter plant growth and microbial community structure, and increase the ecological benefits of green roofs via exerting effects on the moisture, temperature and nutrients of roof substrates.
δ-Amyrone inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory cytokines and protects against endotoxic shock in mice.[Pubmed: 26271896]
δ-Amyrone (13(18)-Oleanen-3-one), which is an active constituent extracted and separated from Sedum lineare Thunb., has been found to possess a potent anti-inflammatory effect in different inflammation model animals. But its effects on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced endotoxic shock have not been previous explored. The aim of this study is to evaluate the effect of δ-Amyrone on LPS-induced inflammatory cytokines and the protective effect on endotoxic shock mice. Experimental animals received δ-amyrone (4 and 8 mg/kg, i.p.) and dexamethasone (DEX) (5 mg/kg, i.p.) at 24 and 1 h before LPS injection. δ-Amyrone treatment significantly decreased mortality rate, tissues myeloperoxodase (MPO) activity, p65 NF-κB protein expression when compared with the LPS groups. The levels of tumor nectosis factor-alphagene (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) both in serum and lung, liver, kidney tissues, as well as the accumulation of nitric oxide (NO) in serum were decreased by δ-amyrone in response to p65 nuclear factors-kappa B (NF-κB). These results suggest that the protective activity of δ-amyrone on LPS-induced endotoxic shock is attributed to reducing NO production and mediating the pro-inflammatory cytokines, inhibited NF-κB expression.
Antimony in the Soil-Plant System in an Sb Mining/Smelting Area of Southwest China.[Pubmed: 26067424]
The distribution, bioavailability, and accumulation of antimony (Sb) at the interface of rhizospheric soils and indigenous plants from a large Sb mining/smelting area in Southwest China were explored. Results showed that the local soil was severely polluted by Sb, and the aluminum magnesium silicate minerals and the carbonate fraction may mainly contribute to bound Sb. The sequential extraction results of soil samples revealed that the portion of bioavailable Sb was low, but the bioavailable Sb concentration was up to 67.2 mg/kg, due to high total Sb concentrations in the soil. The Sb content in local plants showed a wide range, from 21 to 21148 mg/kg. The species of Chenopodium album Linn., Sedum emarginatum Migo, and Sedum lineare Thunb showed high accumulation of Sb at levels of above 1000 mg/kg. The Sb contents in the tissues for most plants decreased with the order of root > leaf > stem. The bioaccumulation coefficients and/or the biological transfer factors for most plants were less than 1. All of the studied plant species were not identified as Sb-hyperaccumulators, but the species of Chenopodium album Linn., Sedum emarginatum Migo, and Sedum lineare Thunb could be applied as alternative plants for phytoremediating Sb-polluted soils.
[HPLC characteristic fingerprints of sedi linearis herba and sedi herba].[Pubmed: 25345129]
To study HPLC characteristic fingerprint of Sedum lineare from different harvest periods, and to compare with its related species Sedum sarmentosum.
δ-Amyrone, a specific inhibitor of cyclooxygenase-2, exhibits anti-inflammatory effects in vitro and in vivo of mice.[Pubmed: 24813716]
The whole plant of Sedum lineare Thunb has been used as traditional folk medicines for the treatment of sore throat, persistent hepatitis, jaundice and dysentery. δ-Amyrone (13(18)-Oleanen-3-one), a pentacyclic triterpene compound from S. lineare Thunb, was found to possess a potent anti-inflammatory effect in different inflammation model animals. Pretreatment with δ-Amyrone (i.p.) inhibited the ear edema in xylene-induced mouse ear edema. δ-Amyrone also decreased the level of nitric oxide (NO), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and leukocyte numbers in acetic acid-induced peritonitis in vivo. To clarify the possible mechanism of δ-Amyrone, we investigated the effect of δ-Amyrone in lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induced peritoneal macrophages. The data indicated that δ-Amyrone notably inhibited IL-6, TNF-α and NO production. In addition, the result showed that δ-Amyrone may control the cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) regulation and not the cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1) at protein levels. These results suggest that δ-Amyrone is a bioactive agent which possesses anti-inflammatory effects, which may be relevant to the regulation of COX-2.
[Study on ultrasonic extraction and macroporous resin purification techniques of total flavones from Sedum lineare].[Pubmed: 23901658]
To optimize the ultrasonic extraction condition and purification process of total flavonoids in Sedum lineare by macroporous resin.
Simultaneous determination by HPLC of quercetin and kaempferol in three Sedum medicinal plants harvested in different seasons.[Pubmed: 23572321]
A high-performance liquid chromatography method was established for the fast quantification of quercetin and kaempferol in three Sedum crude medicines: Sedi Herba (Sedum sarmentosum Bunge.), Sedi Linearis Herba (Sedum lineare Thunb.) and Sedi Emarginati Herba (Sedum emarginatum Migo.). The column used was a YMC-pack ODS-A (250 × 4.6 mm, 5 µm), the mobile phase was a solution of methanol-0.4% phosphoric acid (47:53) with a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min at 35°C and the detection wavelength was 360 nm. The calibration curves for quercetin and kaempferol were linear over the range of 0.01-0.62 µg for quercetin and 0.02-0.78 µg for kaempferol, and the average recoveries were 99.72% [relative standard deviation (RSD): 1.63% and 99.50% (RSD: 1.16%), respectively]. In conclusion, the method established in this paper is accurate and repeatable. It can be used for the determination of quercetin and kaempferol, controlling the quality of the three crude drugs. Furthermore, the experimental data showed that the best harvest season for the three Sedum medicinal species should be the full-bloom period between the end of April and the beginning of May.
Extra-gynoecial pollen-tube growth in apocarpous angiosperms is phylogenetically widespread and probably adaptive.[Pubmed: 21955061]
• Fusion of floral carpels (syncarpy) in angiosperms is thought to have allowed for significant improvements in offspring quantity and quality in syncarpous species over gymnosperms and apocarpous (free-carpelled) angiosperms. Given the disadvantages of apocarpy, it remains an evolutionary puzzle why many angiosperm lineages with free carpels (apocarpy) have been so successful and why some lineages show reversals to apocarpy. • To investigate whether some advantages of syncarpy may accrue in other ways to apocarpous species, we reviewed previous studies of pollen-tube growth in apocarpous species and also documented pollen-tube growth in nine additional apocarpous species in six families. • Anatomical studies of a scattering of apocarpous paleodicots, monocots, and eudicots show that, after transiting the style, 'extra' pollen tubes exit fully fertilized carpels and grow to other carpels with unfertilized ovules. In many species this occurs via openings in the simple carpels, as we report here for Sagittaria potamogetifolia, Sagittaria pygmaea, Sedum lineare, and Schisandra sphenanthera. • The finding that extra-gynoecial pollen-tube growth is widespread in apocarpous species eliminates the possibility of a major fitness cost of apocarpy relative to syncarpy and may help to explain the persistence of, and multiple reversals to, apocarpy in the evolutionary history of angiosperms.


