Rhodomyrtus tomentosa
Rhodomyrtus tomentosa
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Rhodomyrtus tomentosa
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN5692
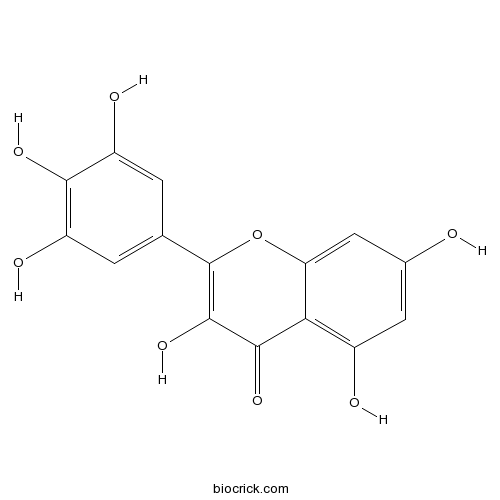
Myricetin529-44-2
Instructions
Cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory active phloroglucinol derivatives from Rhodomyrtus tomentosa.[Pubmed: 29906657]
Seven undescribed phloroglucinol derivatives, tomentodiones N-T, and eleven known ones were isolated from Rhodomyrtus tomentosa. Tomentodione N is the first example of a β-triketone unit coupled with an isoamyl alcohol through a furan fused-ring, and tomentodiones N, S, T were three racemates. The undescribed structures were elucidated by means of spectroscopic, X-ray diffraction, electronic circular dichroism calculation, and chemical methods. In addition, the isolated compounds were determined for the cytotoxic activities on HeLa cells and anti-inflammatory activities in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells.
Immune-related gene expression and physiological responses in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) after intraperitoneal administration of Rhodomyrtus tomentosa leaf extract: A potent phytoimmunostimulant.[Pubmed: 29571768]
The immunostimulatory effects of Rhodomyrtus tomentosa leaf extract were evaluated in rainbow trout through changes in expression profile of genes involved in innate immune and antioxidant response, hematology and stress indicators. The concentrations of R. tomentosa at 10 and 100 μg per fish were administrated by intraperitoneal injection, alone or in combination with LPS. After 6 h of administration, the gene expression was measured in head kidney, spleen, and intestine. Results indicated that R. tomentosa exerted immunostimulatory effects by inducing the expression of il10, saa, hepcidin, and sod in head kidney and the expression of il10, tgfβ, and inos in intestine. In combination with LPS, the plant suppressed the expression of pro-inflammtory cytokine il1β, il8 and other consisting of saa and gpx1 in head kidney and il1β in spleen, pointing out its anti-inflammatory activities. Furthermore, the plant did not exert any impact on hematological parameters, but it was able to reduce cortisol levels when co-administered with LPS, indicating that R. tomentosa could attenuate stress response in rainbow trout. Our observations suggest that R. tomentosa induced the expression of genes involved in cytokine and innate immune response and modulated the physiological stress response as indicated by the suppressed cortisol in rainbow trout.
The novel antibiotic rhodomyrtone traps membrane proteins in vesicles with increased fluidity.[Pubmed: 29451901]
The acylphloroglucinol rhodomyrtone is a promising new antibiotic isolated from the rose myrtle Rhodomyrtus tomentosa, a plant used in Asian traditional medicine. While many studies have demonstrated its antibacterial potential in a variety of clinical applications, very little is known about the mechanism of action of rhodomyrtone. Preceding studies have been focused on intracellular targets, but no specific intracellular protein could be confirmed as main target. Using live cell, high-resolution, and electron microscopy we demonstrate that rhodomyrtone causes large membrane invaginations with a dramatic increase in fluidity, which attract a broad range of membrane proteins. Invaginations then form intracellular vesicles, thereby trapping these proteins. Aberrant protein localization impairs several cellular functions, including the respiratory chain and the ATP synthase complex. Being uncharged and devoid of a particular amphipathic structure, rhodomyrtone did not seem to be a typical membrane-inserting molecule. In fact, molecular dynamics simulations showed that instead of inserting into the bilayer, rhodomyrtone transiently binds to phospholipid head groups and causes distortion of lipid packing, providing explanations for membrane fluidization and induction of membrane curvature. Both its transient binding mode and its ability to form protein-trapping membrane vesicles are unique, making it an attractive new antibiotic candidate with a novel mechanism of action.
Rhodomyrtone (Rom) is a membrane-active compound.[Pubmed: 29317198]
Particularly in Asia medicinal plants with antimicrobial activity are used for therapeutic purpose. One such plant-derived antibiotic is rhodomyrtone (Rom) isolated from Rhodomyrtus tomentosa leaves. Rom shows high antibacterial activity against a wide range of Gram-positive bacteria, however, its mode of action is still unclear. Reporter gene assays and proteomic profiling experiments in Bacillus subtilis indicate that Rom does not address classical antibiotic targets like translation, transcription or DNA replication, but acts at the cytoplasmic membrane. In Staphylococcus aureus, Rom decreases the membrane potential within seconds and at low doses, causes release of ATP and even the excretion of cytoplasmic proteins (ECP), but does not induce pore-formation as for example nisin. Lipid staining revealed that Rom induces local membrane damage. Rom's antimicrobial activity can be antagonized in the presence of a very narrow spectrum of saturated fatty acids (C15:0, C16:0, or C18:0) that most likely contribute to counteract the membrane damage. Gram-negative bacteria are resistant to Rom, presumably due to reduced penetration through the outer membrane and its neutralization by LPS. Rom is cytotoxic for many eukaryotic cells and studies with human erythrocytes showed that Rom induces eryptosis accompanied by erythrocyte shrinkage, cell membrane blebbing, and membrane scrambling with phosphatidylserine translocation to the erythrocyte surface. Rom's distinctive interaction with the cytoplasmic membrane reminds on the amphipathic, alpha-helical peptides, the phenol-soluble modulins (PSMs), and renders Rom an important tool for the investigation of membrane physiology.
Effects of Rhodomyrtus tomentosa extract on virulence factors of Candida albicans and human neutrophil function.[Pubmed: 29247856]
Candida albicans has become a major problem of oral candidiasis due to increase in antibiotic resistance. Rhodomyrtus tomentosa, a medicinal plant possessing several phytochemical constituents, has been considered as a potential source of antimicrobial and immunomodulatory agents. The aim of this study was to investigate anti-virulence and immunostimulatory activity of R. tomentosa ethanolic leaf extract against C. albicans.
Immunomodulatory effects of Rhodomyrtus tomentosa leaf extract and its derivative compound, rhodomyrtone, on head kidney macrophages of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss).[Pubmed: 29238889]
None
Integrated proteomic and metabolomic analysis reveals that rhodomyrtone reduces the capsule in Streptococcus pneumoniae.[Pubmed: 28578394]
The emergence of antibiotic-resistant pathogenic bacteria is a healthcare problem worldwide. We evaluated the antimicrobial activity of rhodomyrtone, an acylphloroglucinol present in Rhodomyrtus tomentosa leaves, against the human Gram-positive pathogen Streptococcus pneumoniae. The compound exhibited pronounced anti-pneumococcal activity against a broad collection of clinical isolates. We studied the effects at the molecular level by integrated proteomic and metabolomic analysis. The results revealed alterations in enzymes and metabolites involved in several metabolic pathways including amino acid biosynthesis, nucleic acid biosynthesis, glucid, and lipid metabolism. Notably, the levels of two enzymes (glycosyltransferase and UTP-glucose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase) and three metabolites (UDP-glucose, UDP-glucuronic acid and UDP-N-acetyl-D-galactosamine) participating in the synthesis of the pneumococcal capsule clearly diminished in the bacterial cells exposed to rhodomyrtone. Rhodomyrtone-treated pneumococci significantly possessed less amount of capsule, as measured by a colorimetric assay and visualized by electron microscopy. These findings reveal the utility of combining proteomic and metabolomic analyses to provide insight into phenotypic features of S. pneumoniae treated with this potential novel antibiotic. This can lead to an alternative antibiotic for the treatment of S. pneumoniae infections, because of the growing concern regarding antimicrobial resistance.
Rhodomyrtus tomentosa Leaf Extract Inhibits Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Adhesion, Invasion, and Intracellular Survival in Human HaCaT Keratinocytes.[Pubmed: 28475464]
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) has an ability to invade nonprofessional phagocytic cells, resulting in persistent infections and most likely host cell death. Series of our studies have claimed pronounced antibacterial efficacy of Rhodomyrtus tomentosa leaf extract. This study was to further investigate potency of the extract in intracellular killing of human HaCaT keratinocytes. Pretreatment of MRSA with the extract resulted in a remarkable reduction in the bacterial adhesion to HaCaT keratinocytes, compared with untreated control (p < 0.001). In addition, at least 60% inhibition of the bacterial invasion into HaCaT cells was observed. Intracellular killing assay demonstrated that the extract exhibited strong antibacterial activity against intracellular MRSA at nontoxic concentrations (128 mg/L), which may have resulted from the increase in bactericidal activity under phagolysosomal pH. Transmission electron microscopy displayed the effects of the extract on alterations in the bacterial cell morphology with cell lysis. Fluorescence microscopy revealed that the extract decreased MRSA-induced apoptosis in HaCaT cells. In addition, cytotoxicity of HaCaT cells caused by MRSA supernatant was reduced at least 50% by the extract. The potential activities of R. tomentosa extract may be useful in an alternative treatment of MRSA infections in slight acidic compartments, particularly skin infections.
Watsonianone A from Rhodomyrtus tomentosa Fruit Attenuates Respiratory-Syncytial-Virus-Induced Inflammation In Vitro.[Pubmed: 28436225]
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is one of the most common respiratory pathogens. Immoderate inflammation plays a great role in causing RSV-induced diseases. In the present study, watsonianone A, isolated from the fruit of Rhodomyrtus tomentosa (Ait.) Hassk, was found to show a good inhibitory effect on RSV-induced NO production, with a half-maximal inhibitory concentration of 37.2 ± 1.6 μM. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and fluorescence quantitative polymerase chain reaction analyses indicated that watsonianone A markedly reduced both mRNA and protein levels of tumor necrosis factor α, interleukin 6, and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 in RSV-infected RAW264.7 cells. Mechanistically, watsonianone A inhibited nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) activation by suppressing IκBα phosphorylation. Further analysis revealed that watsonianone A activated the thioredoxin system and decreased intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels, which are closely associated with NF-κB activation in RSV-infected cells. These results reveal that watsonianone A can attenuate RSV-induced inflammation via the suppression of ROS-sensitive inflammatory signaling.


