Paris verticillata
Paris verticillata
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Paris verticillata
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
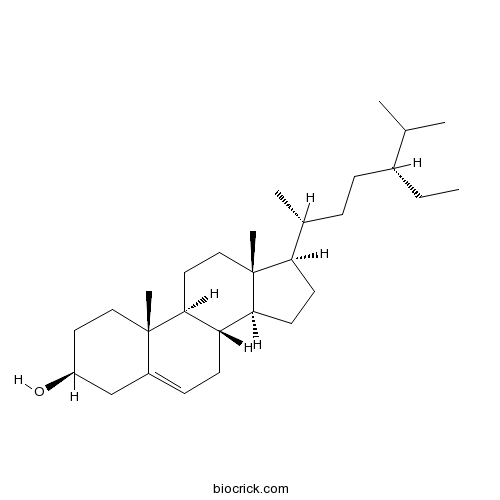
BCN1015
Beta-Sitosterol83-46-5
Instructions
Analysis of the floral MADS-box genes from monocotyledonous Trilliaceae species indicates the involvement of SEPALLATA3-like genes in sepal-petal differentiation.[Pubmed: 26706077]
The evolution of greenish sepals from petaloid outer tepals has occurred repeatedly in various lineages of non-grass monocots. Studies in distinct monocot species showed that the evolution of sepals could be explained by the ABC model; for example, the defect of B-class function in the outermost whorl was linked to the evolution of sepals. Here, floral MADS-box genes from three sepal-bearing monocotyledonous Trilliaceae species, Trillium camschatcense, Paris verticillata, and Kinugasa japonica were examined. Unexpectedly, expression of not only A- but also B-class genes was detected in the sepals of all three species. Although the E-class gene is generally expressed across all floral whorls, no expression was detected in sepals in the three species examined here. Overexpression of the E-class SEPALLATA3-like gene from T. camschatcense (TcamSEP) in Arabidopsis thaliana produced phenotypes identical to those reported for orthologs in other monocots. Additionally, yeast hybrid experiments indicated that TcamSEP could form a higher-order complex with an endogenous heterodimer of B-class APETALA3/DEFICIENS-like (TcamDEF) and PISTILLATA/GLOBOSA-like (TcamGLO) proteins. These results suggest a conserved role for Trilliaceae SEPALLATA3-like genes in functionalization of the B-class genes, and that a lack of SEPALLATA3-like gene expression in the outermost whorl may be related to the formation of greenish sepals.
Steroidal saponins with induced platelet aggregation activity from the aerial parts of Paris verticillata.[Pubmed: 25453339]
In order to utilize and protect the resources of Rhizoma Paridis rationally, we carried out a phytochemical investigation on the non-medicinal (aerial) parts of Paris verticillata that led to the isolation of fifteen steroidal saponins. Among them, three are new spirostanol saponins, named parisverticosides A–C (1–3), as well as one new cholestane glycoside, named parisverticoside D (4). Their structures were elucidated by extensive spectroscopic analysis and acid hydrolysis. The aglycone of compound 1 is a new spirostane and identified as (23S,24S,25S)-spirost-5-en-1b,3b,23, 24-tetraol. The selected isolates were evaluated for induced platelet aggregation activity and compound 5 showed 62% maximal platelet aggregation rate at the concentration of 300 lg/mL.
A trnI_CAU triplication event in the complete chloroplast genome of Paris verticillata M.Bieb. (Melanthiaceae, Liliales).[Pubmed: 24951560]
The chloroplast is an essential plant organelle responsible for photosynthesis. Gene duplication, relocation, and loss in the chloroplast genome (cpDNA) are useful for exploring the evolution and phylogeny of plant species. In this study, the complete chloroplast genome of Paris verticillata was sequenced using the 454 sequencing system and Sanger sequencing method to trace the evolutionary pattern in the tribe Parideae of the family Melanthiaceae (Liliales). The circular double-stranded cpDNA of P. verticillata (157,379 bp) consists of two inverted repeat regions each of 28,373 bp, a large single copy of 82,726 bp, and a small single copy of 17,907 bp. Gene content and order are generally similar to the previously reported cpDNA sequences within the order Liliales. However, we found that trnI_CAU was triplicated in P. verticillata. In addition, cemA is suspected to be a pseudogene due to the presence of internal stop codons created by poly(A) insertion and single small CA repeats. Such changes were not found in previously examined cpDNAs of the Melanthiaceae or other families of the Liliales, suggesting that such features are unique to the tribe Parideae of Melanthiaceae. The characteristics of P. verticillata cpDNA will provide useful information for uncovering the evolution within Paris and for further research of plastid genome evolution and phylogenetic studies in Liliales.
[Chemical constituents from herbs of Paris verticillata].[Pubmed: 19894514]
To study the chemical constituents in herbs of Paris verticillata.
A new phenolic amide from the roots of Paris verticillata.[Pubmed: 18259128]
A new phenolic amide 8, together with the nine known phenolic compounds 1-7, 9 and 10 were isolated from the MeOH extract of the roots of Paris verticillata. The structure of the new compound 8 was determined to be 1-N-feruloylaminobutyl-4-rho-hydroxybenzamide by spectroscopic methods. The isolated compounds were tested for cytotoxicity against four human tumor cell lines using the SRB assay.


