Momordica cochinchinensis
Momordica cochinchinensis
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Momordica cochinchinensis
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN1296
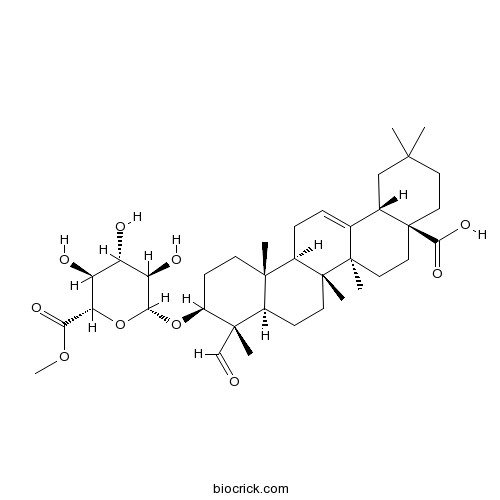
Methyl gypsogenin 3-O-beta-D-glucuronopyranoside96553-02-5
Instructions
[Studies on liposoluble constituents from Momordicae Semen].[Pubmed: 29676125]
The liposoluble constituents in Momordicae Semen were investigated in the present study. By silica gel, Sephadex LH-20 column chromatography, and semi-preparative HPLC, 22 compounds were isolated and purified from dichloromethane and ethyl acetate fraction. Based on NMR and MS spectra analyses, these compounds were identified as lupeol (1), 5-(1'-hydroxypentyl)-5H-furan-2-one (2), palmitic acid (3), viscumamide (4), clavatustide C (5), laxanol (6), threo-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-{4-[2-formyl-(E)-vinyl]-2-methoxyphenoxyl}-propane-1, 3-diol (7), α-spinasterol-3-O-β-D-glucoside (8), chushizisin F (9), ehletianol C (10), tanegool (11), (7R, 8R, 8'R)-4'-guaiacylglyceryl-evofolin B (12), ligballinone (13), (7R, 8S, 8'R)- 4, 4', 9-trihydroxy- 7, 9'-epoxy- 8, 8'-lignan (14), chushizisin I (15), chushizisin A (16), chushizisin G (17), p-coumaraldehyde (18), α-spinasterol (19), p-hydroxybenzoic acid (20), chushizisin E (21), and 3-[2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-hydroxyphenyl-2, 3-dihydro-1-benzofuran-5-yl] propane-1-ol (22), respectively. Compounds 1-17 were isolated from Momordica cochinchinensis for the first time. Compound 2 was a new natural product while compounds 4 and 5 were first found in the terrestrial organism.
Carotenoids from gac fruit aril (Momordica cochinchinensis [Lour.] Spreng.) are more bioaccessible than those from carrot root and tomato fruit.[Pubmed: 28847429]
Using a simulated digestion procedure in vitro, liberation and bioaccessibility of β-carotene (29.5±1.7% and 22.6±0.9%, respectively) and lycopene (51.3±2.6% and 33.2±3.1%, respectively) from gac fruit aril were found to be significantly higher than from carrot root (β-carotene, 5.2±0.5% and 0.5±0.2%, respectively) and tomato fruit (lycopene, 15.9±2.8% and 1.8±0.5%, respectively). Gac fruit aril naturally contained significantly more lipids (11% on fresh weight base) than carrot root and tomato fruit (<1%). However, when test meals were supplemented with an O/W emulsion to match the content of gac fruit aril, carotenoid bioaccessibility was still considerably lower than that from genuine gac fruit aril. Carotenoids in gac fruit aril were found to be stored in small, round-shaped chromoplasts. Despite the high lipid content, these carotenoids are unlikely to occur in a lipid-dissolved state according to simple solubility estimations, instead being possibly deposited as submicroscopic crystallites. In contrast, carotenoids of carrot root and tomato fruit were stored in large, needle-like crystallous chromoplasts. Consequently, we hypothesized the natural deposition form to be majorly responsible for the observed differences in bioaccessibility. A favorable surface-to-volume ratio of the deposition form in gac fruit aril might have allowed a more rapid micellization during digestion, and thus, an enhanced bioaccessibility. Irrespective of the ultimate reason, gac fruit aril provided a highly bioaccessible form of both lycopene and provitamin A (β-carotene), thus offering a most valuable dietary source of both carotenoids. Currently, gac is majorly grown in Southeast Asia, where its consumption might help to diminish the 'hidden hunger' namely the insufficient supply with vitamin A. Ultimately, gac fruit might thus contribute to alleviating most severe health implications of vitamin A deficiency, such as anaemia and xerophthalmia, the prevailing cause of preventable childhood blindness, as well as mortality from infectious diseases.
Src/Syk-Targeted Anti-Inflammatory Actions of Triterpenoidal Saponins from Gac (Momordica cochinchinensis) Seeds.[Pubmed: 28367713]
Momordica cochinchinensis Spreng (family Cucurbitaceae), also known as gac, or red melon, is an edible Southeast Asian fruit valued for its nutritional and medicinal properties. Specifically, Momordicae Semen, the seeds of the gac fruit, is used in traditional Chinese medicine to treat boils, rheumatic pain, muscle spasm, hemorrhoids, and hemangiomas. In this study, a chemical investigation into a gac seed ethanol (EtOH) extract resulted in the identification of three triterpenoidal saponins (1-3), which were investigated for their anti-inflammatory effects. Among the saponins, momordica saponin I (compound 3) reduced the production of nitric oxide (NO) in LPS-activated RAW264.7 cells without inducing cytotoxicity. The mRNA levels of inducible NO synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 were decreased by momordica saponin I. Additionally, the translocation of p65 and p50 (subunits of the transcription factor NF-[Formula: see text]B) into the nucleus was remarkably inhibited. Furthermore, the phosphorylation levels of inflammatory signaling proteins (I[Formula: see text]B[Formula: see text], Src, and Syk) known to be upstream regulatory molecules of p65 were decreased under momordica saponin I-treated conditions. The molecular targets of momordica saponin I were confirmed in overexpression experiments and through immunoblot analyses with Src and Syk. This study provides evidence that momordica saponin I could be beneficial in treating inflammatory diseases, and should be considered a bioactive immunomodulatory agent with anti-inflammatory properties.
Dual-targeting anti-angiogenic cyclic peptides as potential drug leads for cancer therapy.[Pubmed: 27734947]
Peptide analogues derived from bioactive hormones such as somatostatin or certain growth factors have great potential as angiogenesis inhibitors for cancer applications. In an attempt to combat emerging drug resistance many FDA-approved anti-angiogenesis therapies are co-administered with cytotoxic drugs as a combination therapy to target multiple signaling pathways of cancers. However, cancer therapies often encounter limiting factors such as high toxicities and side effects. Here, we combined two anti-angiogenic epitopes that act on different pathways of angiogenesis into a single non-toxic cyclic peptide framework, namely MCoTI-II (Momordica cochinchinensis trypsin inhibitor-II), and subsequently assessed the anti-angiogenic activity of the novel compound. We hypothesized that the combination of these two epitopes would elicit a synergistic effect by targeting different angiogenesis pathways and result in improved potency, compared to that of a single epitope. This novel approach has resulted in the development of a potent, non-toxic, stable and cyclic analogue with nanomolar potency inhibition in in vitro endothelial cell migration and in vivo chorioallantoic membrane angiogenesis assays. This is the first report to use the MCoTI-II framework to develop a 2-in-1 anti-angiogenic peptide, which has the potential to be used as a form of combination therapy for targeting a wide range of cancers.
Two New Oleanane-type Triterpenoids from Methanolyzed Saponins of Momordica cochinchinensis.[Pubmed: 27534102]
Two new oleanane-type triterpenoid saponins (1 and 2) were isolated from the methanolyzed total saponins of the seeds of Momordica cochinchinensis (Lour.) Spreng, together with 16 known compounds (3-18). Their structures were elucidated on the basis of detailed spectroscopic, including 1D and 2D NMR, mass spectrometric, methanolysis and LC-MS analysis. All the isolates were tested for their cytotoxic activities against five human cancer cell lines (HL-60, SMMC-7721, PANC-1, A-549, and SW-480) and the glucose uptake activity. The known compound 6 exhibited toxic effects against HL-60 with an IC50 value of 18.1 μM, while 10 showed cytotoxicity against SMMC-7721 and A-549 cell lines, with IC50 values of 34.4 and 32.8 μM, respectively. In addition, the new compound 2 showed glucose uptake activity with a glucose consumption value of 0.29 μM at 10 μM concentration.
Plants Defense-related Cyclic Peptides: Diversity, Structure and Applications.[Pubmed: 27455973]
Plant growth is prone to several unfavorable factors that may compromise or impair development and survival, including abiotic or biotic stressors. Aiming at defending themselves, plants have developed several strategies to survive and adapt to such adversities. Cyclotides are a family of plant-derived proteins that exhibit a diverse range of biological activities including antimicrobial and insecticidal activities that actively participate in plant defense processes. Three main categories of peptides have been described: (i) Cyclotides (ii) Sunflower Trypsin Inhibitor (SFTI) and (iii) peptides MCoTI-I and II, from Momordica cochinchinensis. They comprise proteins of approximately 30 amino acids, containing a head-to-tail cyclized backbone, with three disulfide bonds configured in a cystine knot topology, therefore bearing greater peptide stability. Given their features and multifunctionality, cyclotides stand out as promising sources for the discovery of new antimicrobial agents. The present review describes cyclotide occurrence, abundance and action in plants, also their and evolution. Considerations regarding their use in the context of biomedical and agronomical sciences uses are also presented.


