Cichorium intybus
Cichorium intybus
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Cichorium intybus
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
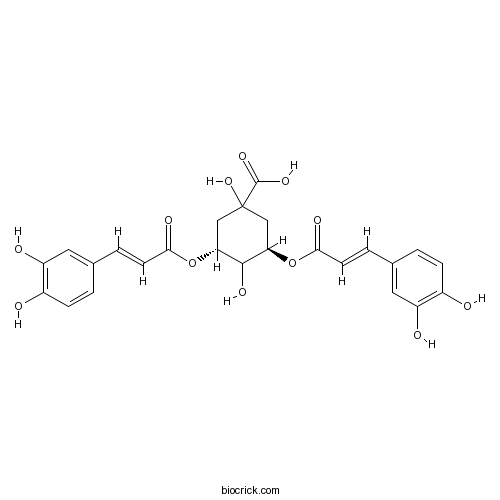
BCN5908
Isochlorogenic acid A2450-53-5
Instructions
-
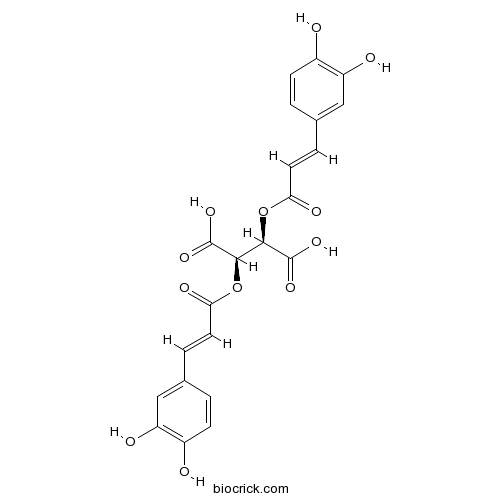
BCN9033
Cichoric acid6537-80-0
Instructions
Effects of Cichorium intybus on serum oxidative stress, liver and kidney volume, and cyclin B1 and Bcl-2 levels in the brains of rats with ethanol induced damage.[Pubmed: 29974843]
We investigated the effects of an aqueous root extract of Cichorium intybus on Bcl-2 and cyclin B1 levels in the brain, kidney and liver volumes and changes of serum total antioxidant status (TAS) and total oxidant status (TOS) levels in ethanol induced damage in rats. The rats were divided into five groups: non-treated controls (C), maltodextrin in tap water treated (MD), 6.4% ethanol in tap water treated (ET), Cichorium intybus + maltodextrin in tap water treated (CI+MD), and Cichorium intybus + 6.4% ethanol in tap water treated (CI+ET). Rats in the CI+MD and CI+ET groups were treated with 200 mg/kg water extract of Cichorium intybus. Chronic ethanol aMDinistration significantly increased cyclin B1 and decreased Bcl-2 levels in the brain and significantly decreased TAS values, increased TOS values of serum and significantly decreased kidney volume in the ET group. There was no significant difference in the liver volume or liver cell count. Our data revealed that ethanol aMDinistration induces an overexpression of cyclin B1 and decreases levels of Bcl-2 in rat brains and induced oxidative stress in the blood. C. intybus treatment possessed a partial amelioration effect on cyclin B1 levels and TAS values.
Chicory (Cichorium intybus L.) polysaccharides attenuate high-fat diet induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via AMPK activation.[Pubmed: 29964102]
Chicory polysaccharides (CP) from Cichorium intybus L. roots were extracted and fractionated to isolate two novel polysaccharide fractions, CP-1 and CP-2. CP-1 is a heteropolysaccharide that is mainly composed of sorbin, glucose, fructose, and glucitol at a molar ratio of 1.00:5.58:13.97:10.32. The molecular weight of CP-1 was 8511.4 Da. The hepatoprotective effect of CP-1 was investigated in a rat model of high-fat diet induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) rats. Results indicated that the oral administration of CP-1 significantly decreased body weight and liver index in NAFLD rats. CP-1 also significantly increased serum levels of SOD and HDLC, and decreased the levels of ALT, AST, TG, TC, LDL-C, GLU, ALP, LDH, and MDA in NAFLD rats. Meanwhile, CP-1 effectively decreased MDA, TC, and TG, and increased SOD and T-AOC in the livers of NAFLD rats. Furthermore, CP-1 also increased the hepatic expression of p-AMPKα, ATGL, CPT-1, and p-ACC, and reduced the hepatic expression of ACC, FAS, and SCD-1. Moreover, histopathological examination of the livers showed that CP-1 significantly ameliorated the symptoms of NAFLD rats. Therefore, CP-1 significantly attenuated the high-fat diet-induced NAFLD in rats via AMPK activation.


