Camptotheca acuminata
Camptotheca acuminata
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Camptotheca acuminata
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
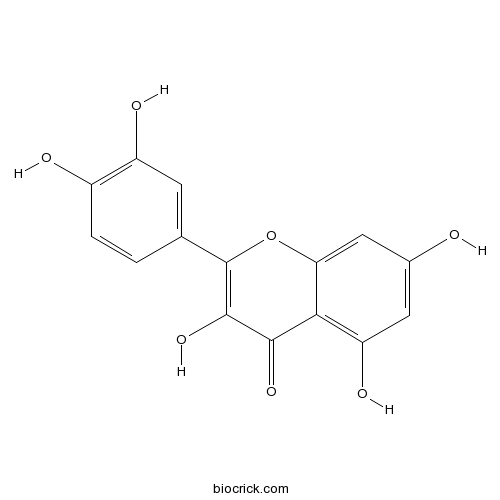
BCN6049
Quercetin117-39-5
Instructions
-
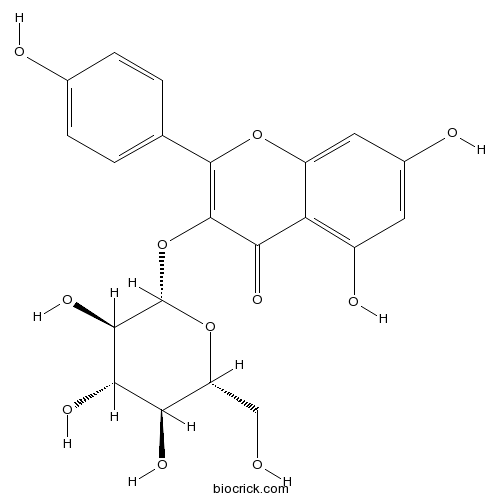
BCN5549
Astragalin480-10-4
Instructions
-
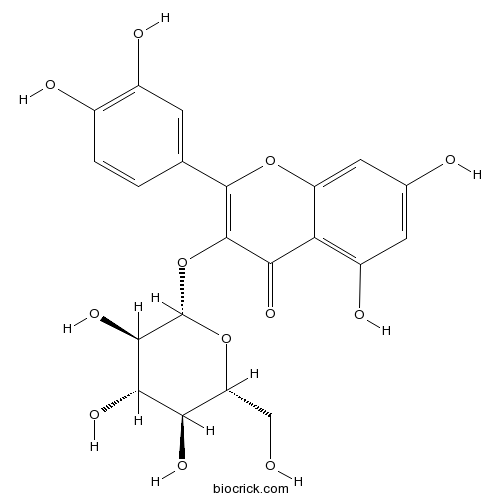
BCN5569
Isoquercitrin482-35-9
Instructions
-
BCN5570
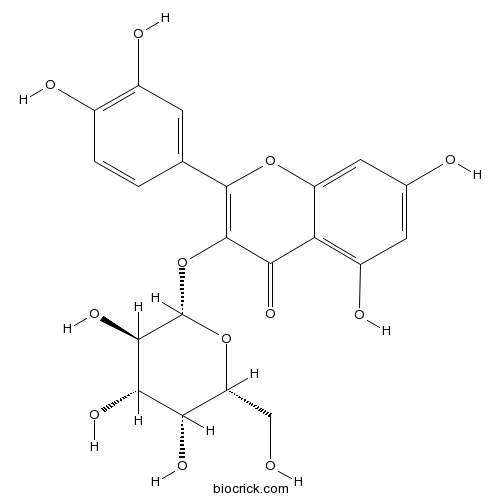
Hyperoside482-36-0
Instructions
-
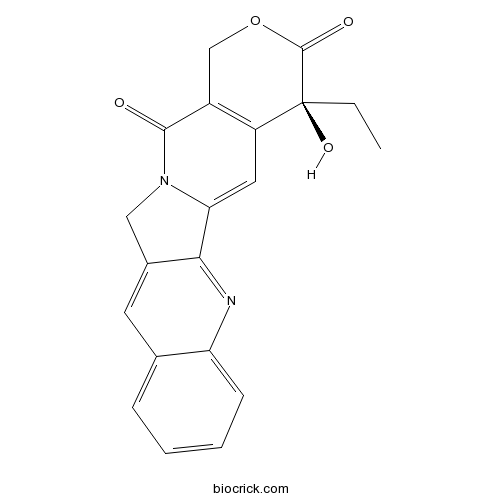
BCN4318
Camptothecin7689-03-4
Instructions
Triterpenes from the fruit of Camptotheca acuminata suppress human hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation through apoptosis induction.[Pubmed: 29923429]
None
Bicarbonate stimulates non-structural carbohydrate pools of Camptotheca acuminata.[Pubmed: 29900556]
None
Camptotheca acuminata 10-hydroxycamptothecin O-methyltransferase: an alkaloid biosynthetic enzyme co-opted from flavonoid metabolism.[Pubmed: 29681057]
The medicinal plant Camptotheca acuminata accumulates camptothecin, 10-hydroxycamptothecin, and 10-methoxycamptothecin as its major bioactive monoterpene indole alkaloids. Here, we describe identification and functional characterization of 10-hydroxycamptothecin O-methyltransferase (Ca10OMT), a member of the Diverse subclade of class II OMTs. Ca10OMT is highly active toward both its alkaloid substrate and a wide range of flavonoids in vitro and in this way contrasts with other alkaloid OMTs in the subclade that only utilize alkaloid substrates. Ca10OMT shows a strong preference for the A-ring 7-OH of flavonoids, which is structurally equivalent to the 10-OH of 10-hydroxycamptothecin. The substrates of other alkaloid OMTs in the subclade bear little similarity to flavonoids, but the 3-D positioning of the 7-OH, A- and C-rings of flavonoids is nearly identical to the 10-OH, A- and B-rings of 10-hydroxycamptothecin. This structural similarity likely explains the retention of flavonoid OMT activity by Ca10OMT and also why kaempferol and quercetin aglycones are potent inhibitors of its 10-hydroxycamptothecin activity. The catalytic promiscuity and strong inhibition of Ca10OMT by flavonoid aglycones in vitro prompted us to investigate the potential physiological roles of the enzyme in vivo. Based on its regioselectivity, kinetic parameters and absence of 7-OMT flavonoids in vivo, we conclude that the major and likely only substrate of Ca10OMTin vivo is 10-hydroxycamptothecin. This is likely accomplished by Ca10OMT being kept spatially separated at the tissue levels from potentially inhibitory flavonoid aglycones, and flavonoid aglycones being rapidly glycosylated to non-inhibitory flavonoid glycosides.
A review on camptothecin analogs with promising cytotoxic profile.[Pubmed: 29589546]
Camptothecin (CPT), obtained from Camptotheca acuminata (Nyssaceae), is a quinoline type of alkaloid. Apart from various traditional uses, it is mainly used as a potential cytotoxic agent acting against a variety of cancer cell lines. Though researches have been continuing for last six decades, still it is a demanding task to design potent and cytotoxic CPTs. Different CPT analogs are synthesized to enhance the cytotoxic potential as well as to increase the pharmacokinetic properties of these analogs. Some of these analogs were proven to be clinically effective in different cancer cell lines. In this article, different CPT analogs have been highlighted extensively to get a detail insight about the structure-property relationships as well as different quantitative structure-activity relationships (QSARs) modeling of these analogs are also discussed. This study may be beneficial for designing newer CPT analogs in future.
One-step targeted accumulation and detection of camptothecin analogues from fruits of Camptotheca acuminata Decne using bilayer solid-phase extraction coupled with ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.[Pubmed: 28992990]
Camptothecins, a kind of monoterpene-quinoline alkaloids from Camptotheca acuminata Decne, have long attracted much attention worldwide as an anti-cancer drug. However, there is still a lack of effective methods for the accumulation and discovery of camptothecin analogues from botanic resources for camptothecin-based drug research. This work develops a one-step method for the targeted accumulation, quick detection, and identification of camptothecin analogues from C. acuminata fruit using bilayer solid-phase extraction coupled with ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (bilayer-SPE-UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS). The bilayer-SPE cartridge, with polyamide (PA) as the upper layer and octadecyl silane (ODS) as the lower layer, was designed for the removal of flavonoid and ellagic acid impurities and the enrichment of camptothecins for further MS analysis. Subsequently, the mass spectrometry fragmentations, especially multistage retro-Diels-Alder cleavage, were summarized based on the MS/MS data of 10 reference camptothecins. The UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS conditions were optimized, and the MS/MS data of the potential camptothecin analogues in the bilayer-SPE enriched fractions were analyzed. A total of 30 camptothecin analogues, including 15 new compounds, were identified from the fruit according the fragmentation pathways of the reference standards. The proposed structure of peak 20 was confirmed using its NMR data through rapid enrichment and purification. Overall, the bilayer-SPE enrichment and reliable mass spectrometry fragmentation in our work could provide an effective and simple method for the exploration of the biosynthesis pathway and metabolomics of camptothecin analogues.
De novo genome assembly of Camptotheca acuminata, a natural source of the anti-cancer compound camptothecin.[Pubmed: 28922823]
Camptotheca acuminata is 1 of a limited number of species that produce camptothecin, a pentacyclic quinoline alkaloid with anti-cancer activity due to its ability to inhibit DNA topoisomerase. While transcriptome studies have been performed previously with various camptothecin-producing species, no genome sequence for a camptothecin-producing species is available to date. We generated a high-quality de novo genome assembly for C. acuminata representing 403 174 860 bp on 1394 scaffolds with an N50 scaffold size of 1752 kbp. Quality assessments of the assembly revealed robust representation of the genome sequence including genic regions. Using a novel genome annotation method, we annotated 31 825 genes encoding 40 332 gene models. Based on sequence identity and orthology with validated genes from Catharanthus roseus as well as Pfam searches, we identified candidate orthologs for genes potentially involved in camptothecin biosynthesis. Extensive gene duplication including tandem duplication was widespread in the C. acuminata genome, with 2571 genes belonging to 997 tandem duplicated gene clusters. To our knowledge, this is the first genome sequence for a camptothecin-producing species, and access to the C. acuminata genome will permit not only discovery of genes encoding the camptothecin biosynthetic pathway but also reagents that can be used for heterologous expression of camptothecin and camptothecin analogs with novel pharmaceutical applications.


